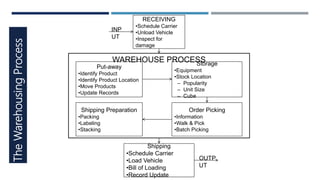
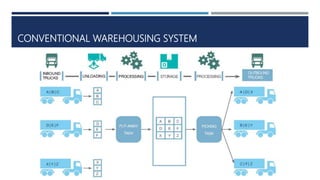
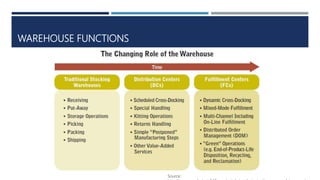
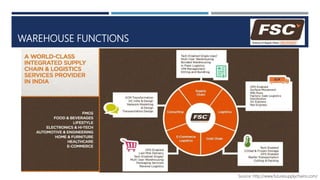
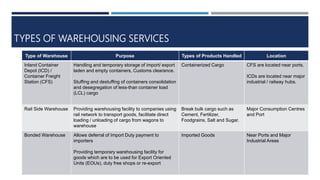
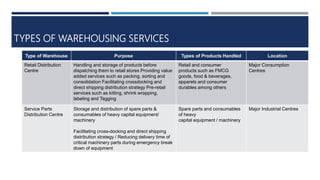
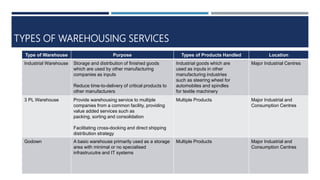
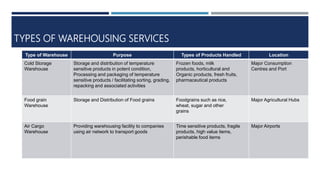
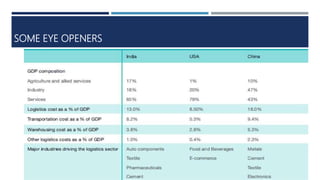
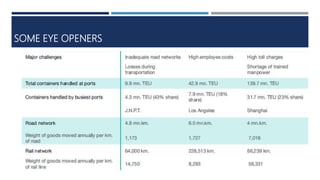
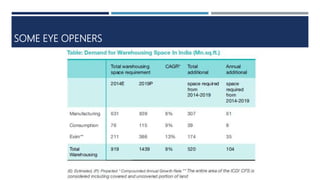
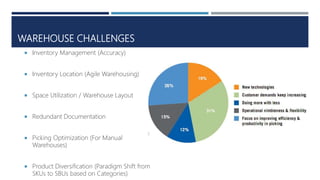
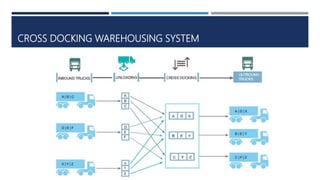
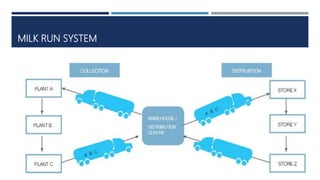
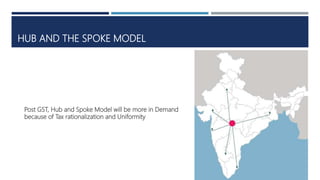
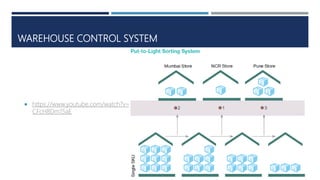
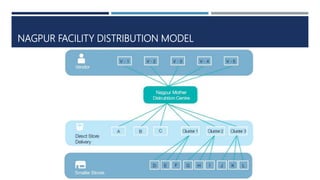
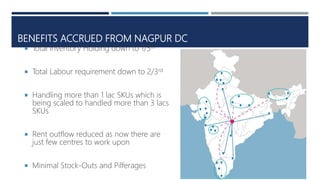
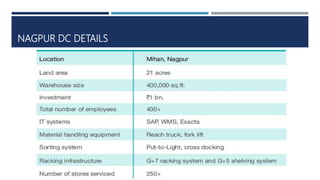
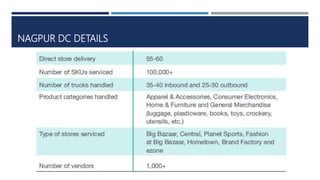
Warehouse management involves several key processes including receiving, put-away, storage, order picking, packing and shipping. The document discusses various warehouse functions like inventory management, space utilization, picking optimization and product diversification. It also covers different types of warehouses based on purpose and products handled. Technology interventions like RFID, WMS, ERP and smart warehouse concepts are changing the way warehouses operate by improving efficiency. The case study highlights how Future Supply Chain transformed its operations by establishing a central mother DC in Nagpur, India which utilizes various technologies and follows a hub and spoke model to efficiently distribute goods.