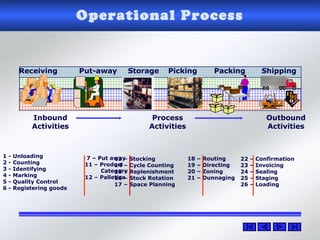
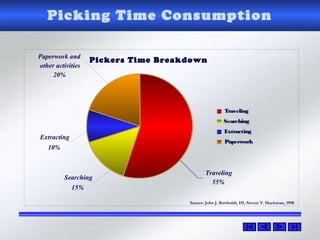
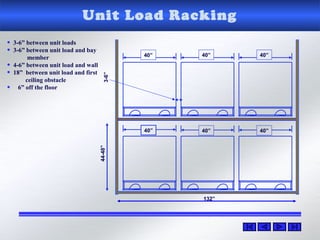
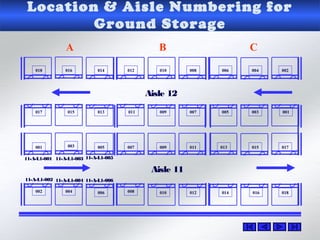
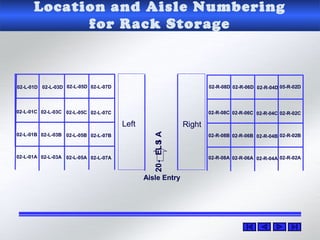
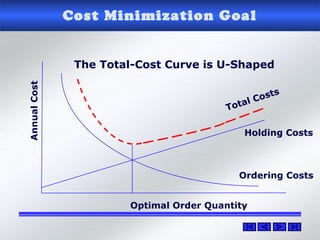
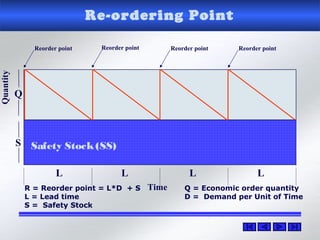
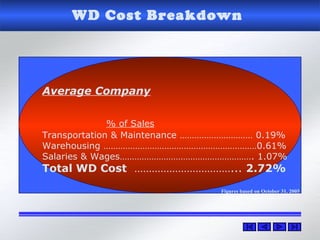
The document provides information about warehouse operations and goals. It discusses maximizing the effective use of space, equipment, labor and information. It outlines warehouse functions like receiving, storing, order picking and shipping. It also describes operational processes, inventory terms and costs, and opportunities to improve warehouse distribution. Controls are discussed around safety, fire prevention, theft and storing hazardous materials. Equipment and tools are also mentioned.