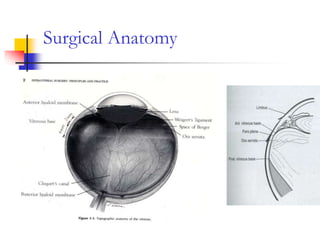
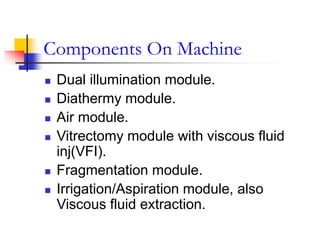
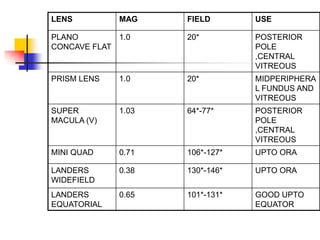
This document provides an overview of vitrectomy principles and techniques. It discusses the history and evolution of vitrectomy surgery. It covers surgical anatomy, the main aims of vitrectomy, components of vitrectomy machines and their functions. It describes techniques for sclerotomies, vitreous cutters, infusion cannulas and viewing systems. It outlines the basic steps of a closed vitrectomy procedure and discusses adjunctive procedures like air-fluid exchange and use of perfluorocarbon liquids, silicone oil and gases. Recent advances discussed include 25-gauge vitrectomy and endoscope-assisted surgery.