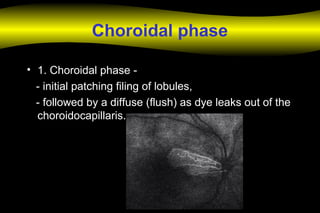
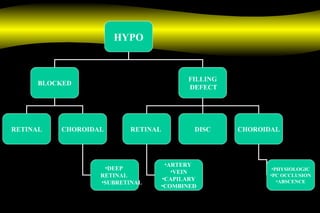
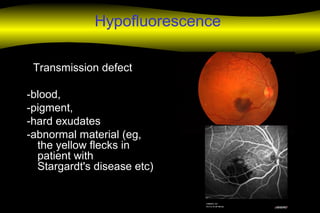
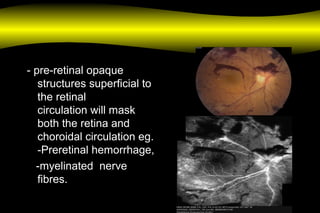
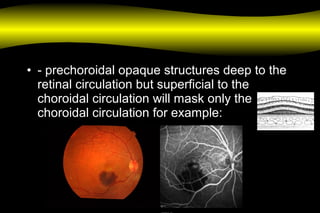
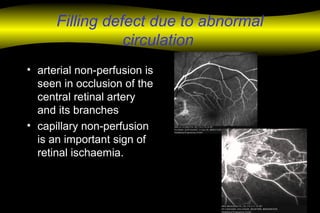
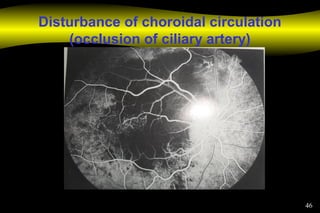
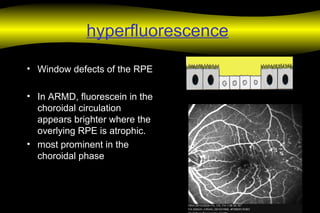
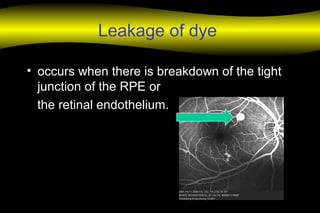
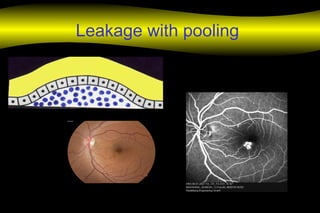
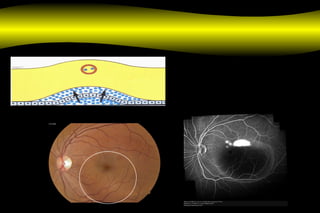
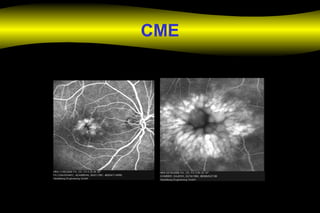
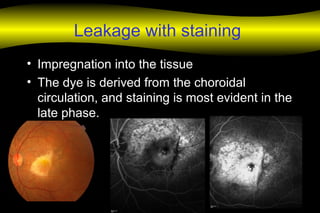
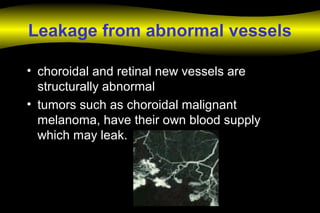
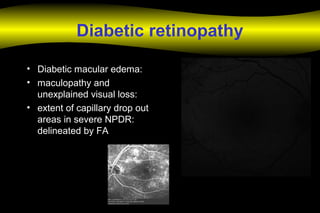
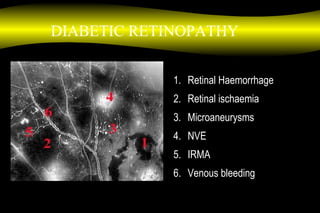
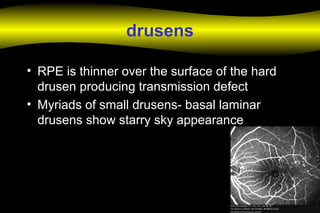
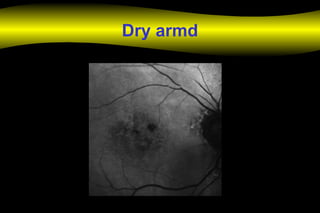
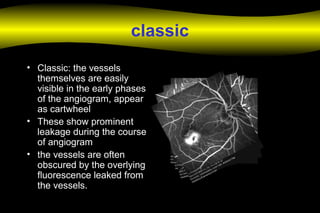
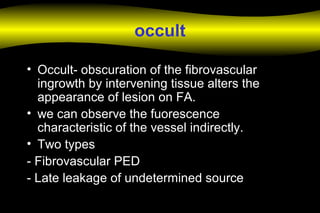
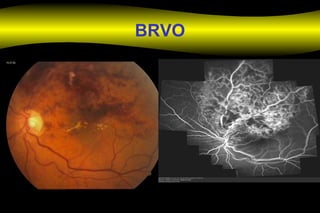
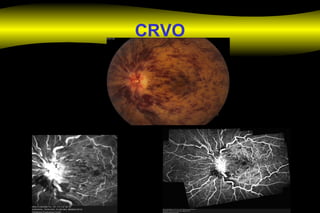
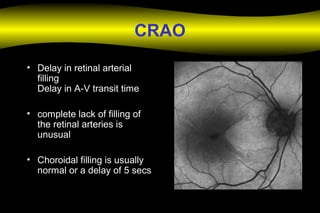
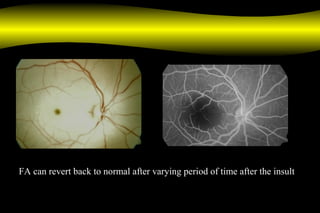
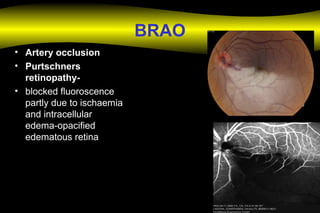
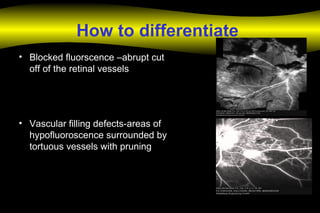
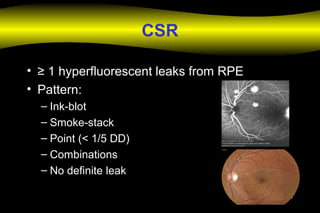
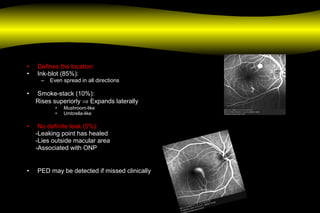
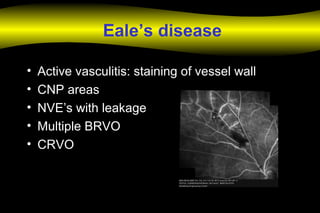
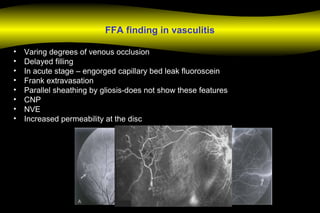
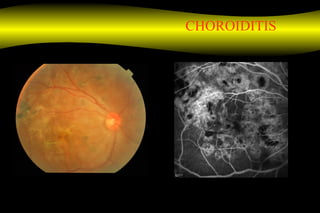
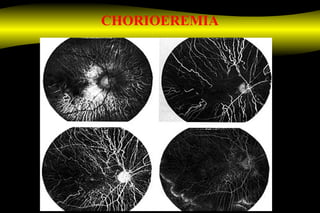
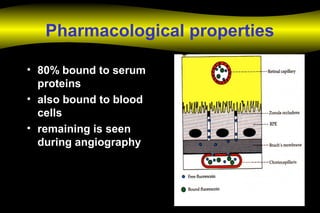
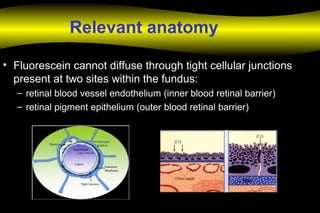
Fluoroscein angiography is a technique used to examine the circulation of the retina and choroid. It involves injecting a fluorescent dye called sodium fluorescein and taking photographs of the eye during different phases as the dye circulates through the vessels. The dye is excited by blue light and emits yellow-green light, allowing visualization of the retinal and choroidal vasculature. Fluorescein angiography provides valuable information used to diagnose and monitor many retinal diseases. Some common uses include detecting leaking blood vessels in wet age-related macular degeneration and evaluating areas of non-perfusion in diabetic retinopathy. While generally safe, rare adverse reactions like allergic reactions may occur.








![PHASES OF ANGIOGRAM
1. PREARTERIAL [ CHOROIDAL FLUSH ] – 10 sec
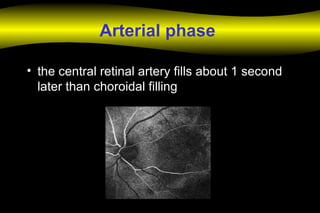
2. ARTERIAL – 12sec
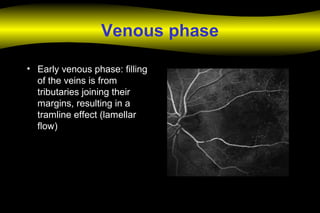
3. ARTERIO-VENOUS
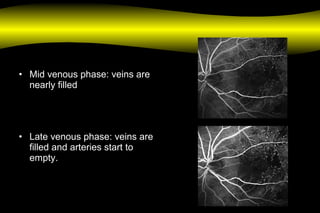
- EARLY TRANSIT – 13 sec
- MID TRANSIT – 16sec
- LATE TRANSIT – 20 sec
3a. Peak phase – 25 sec
4. RECIRCULATION – 30sec
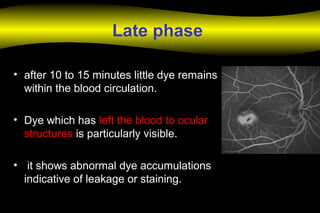
5. LATE FLURESCEIN TRANSIT – after
10 min](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fa-180114131255/85/Fluorescein-Angiography-15-320.jpg)