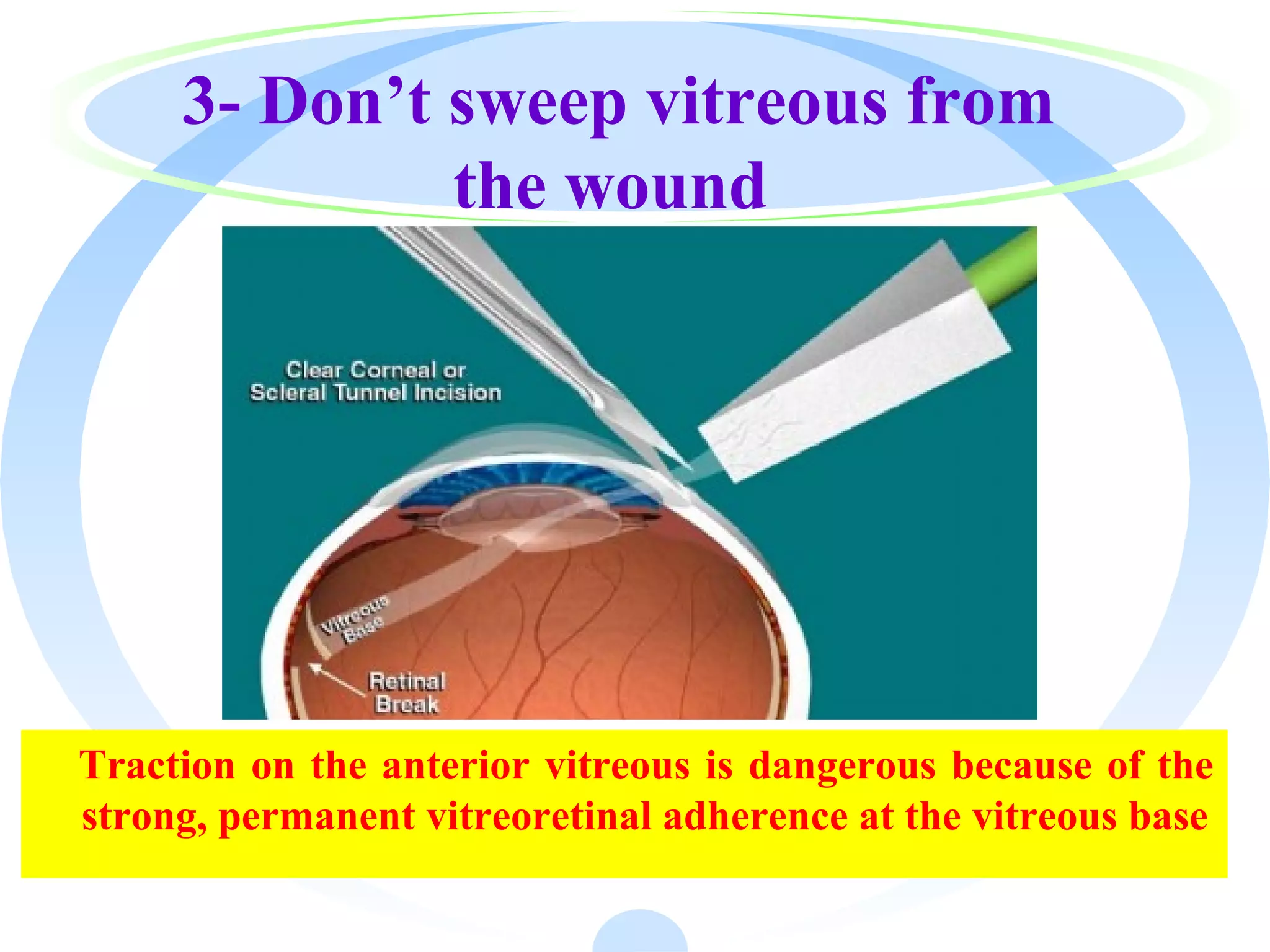
The document outlines the procedures and techniques involved in anterior vitrectomy to prevent vitreous traction and maintain a clean anterior segment during intra/post-operative scenarios. It details the use of a vitreous cutter, irrigation techniques, and machine parameters to efficiently remove vitreous from the eye while minimizing complications. Additionally, it discusses various types of anterior vitrectomy and emphasizes the importance of maintaining a closed chamber and proper visualization throughout the procedure.