This document discusses considerations for phacoemulsification cataract surgery in myopic eyes. Key points addressed include:
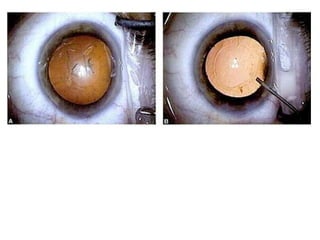
- Myopic eyes have a thinner sclera and weaker zonules, requiring special care during surgery like using clear corneal incisions and suturing if needed.
- The anterior chamber is deeper in myopic eyes, making instrumentation more difficult and increasing risks like iris stretching and reverse pupillary block.
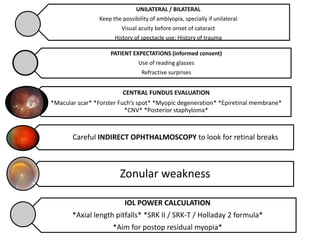
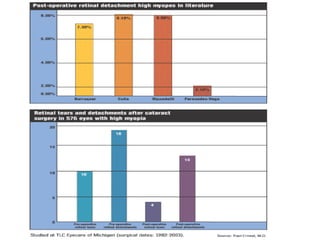
- Careful preoperative evaluation of the fundus is important to assess for macular pathology, retinal breaks, or high myopia that could impact outcomes.
- Intraocular lens power calculation and choice is more complex in myopic eyes to aim for residual myopia and account for axial length