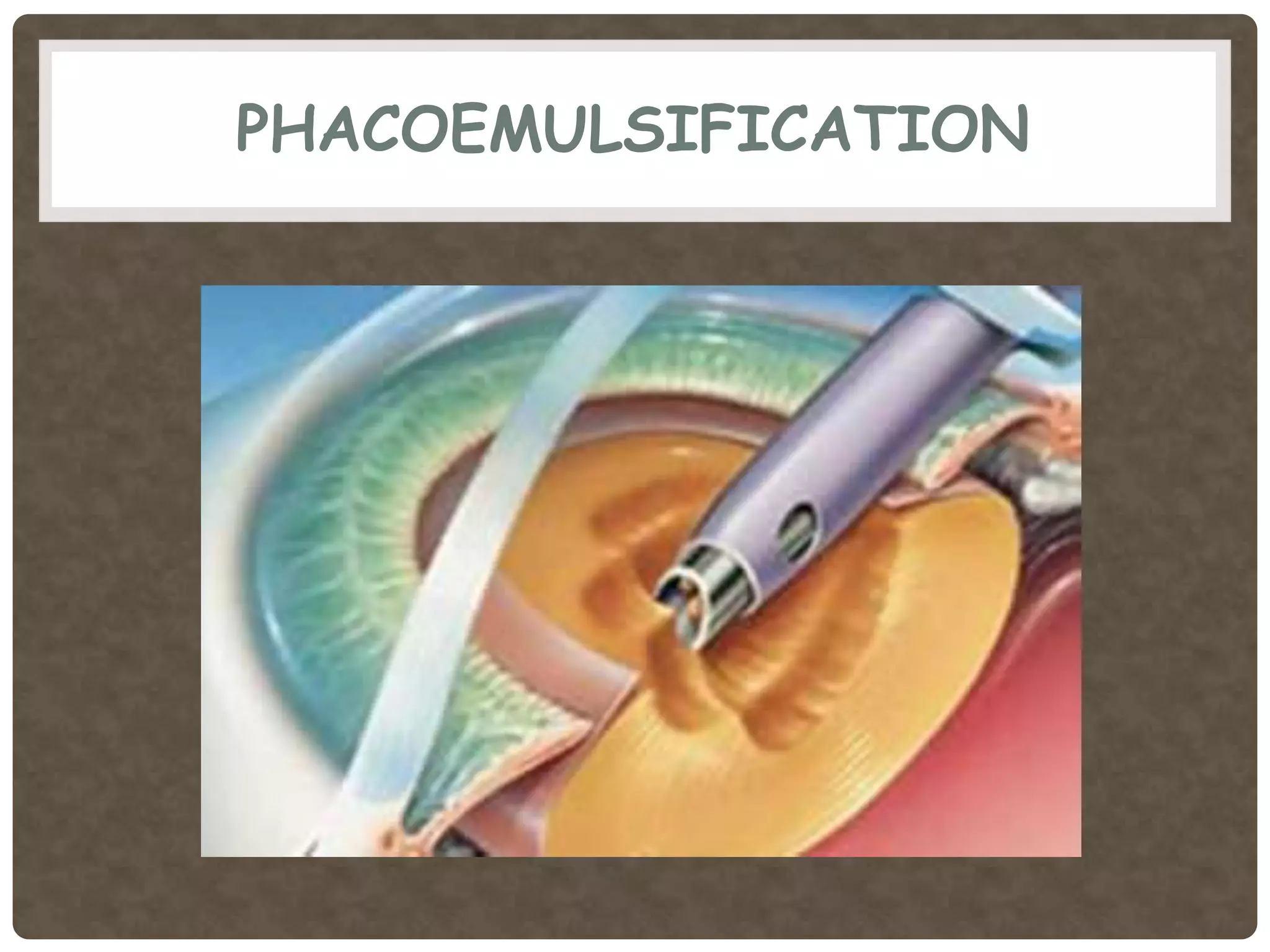
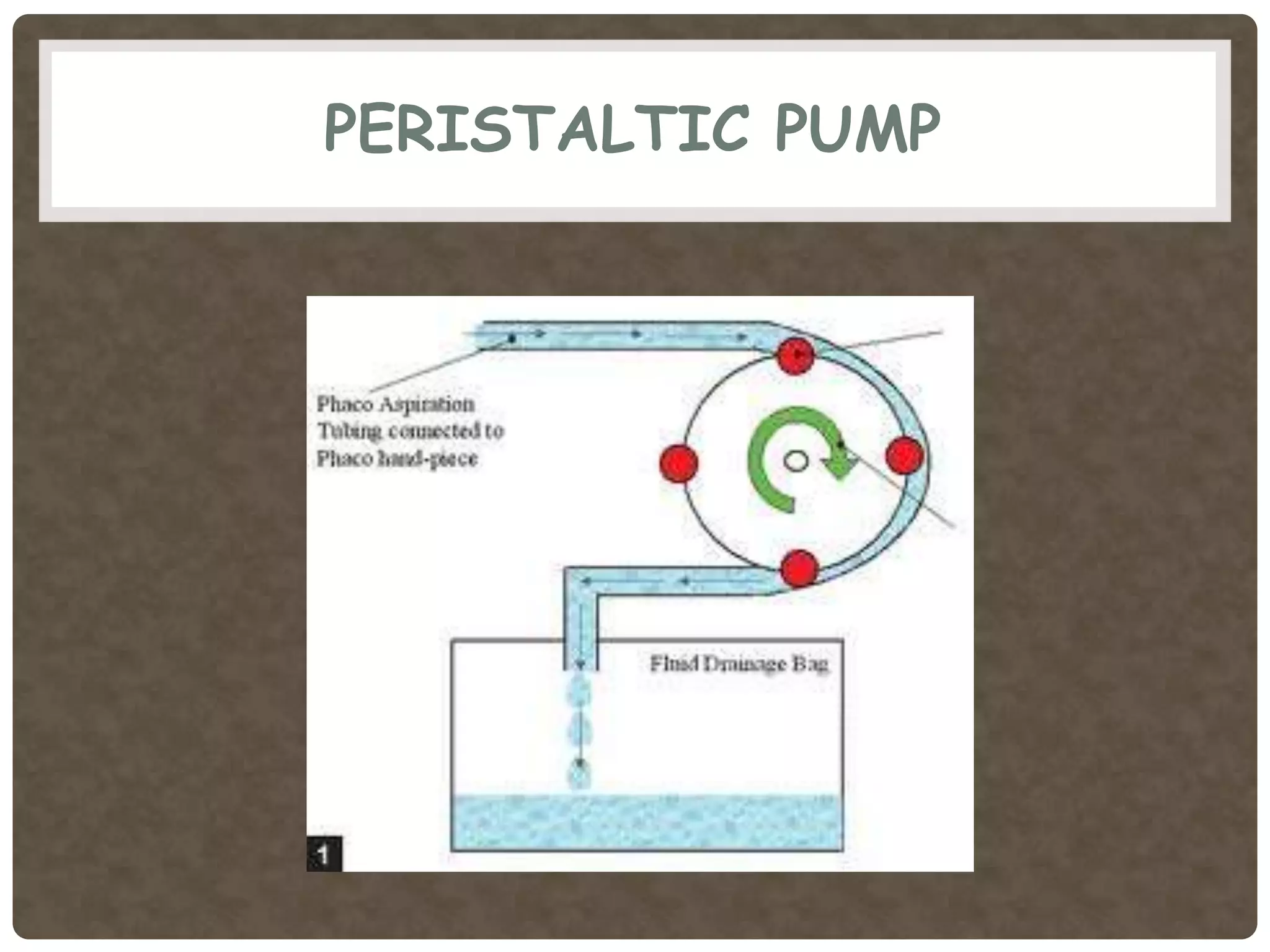
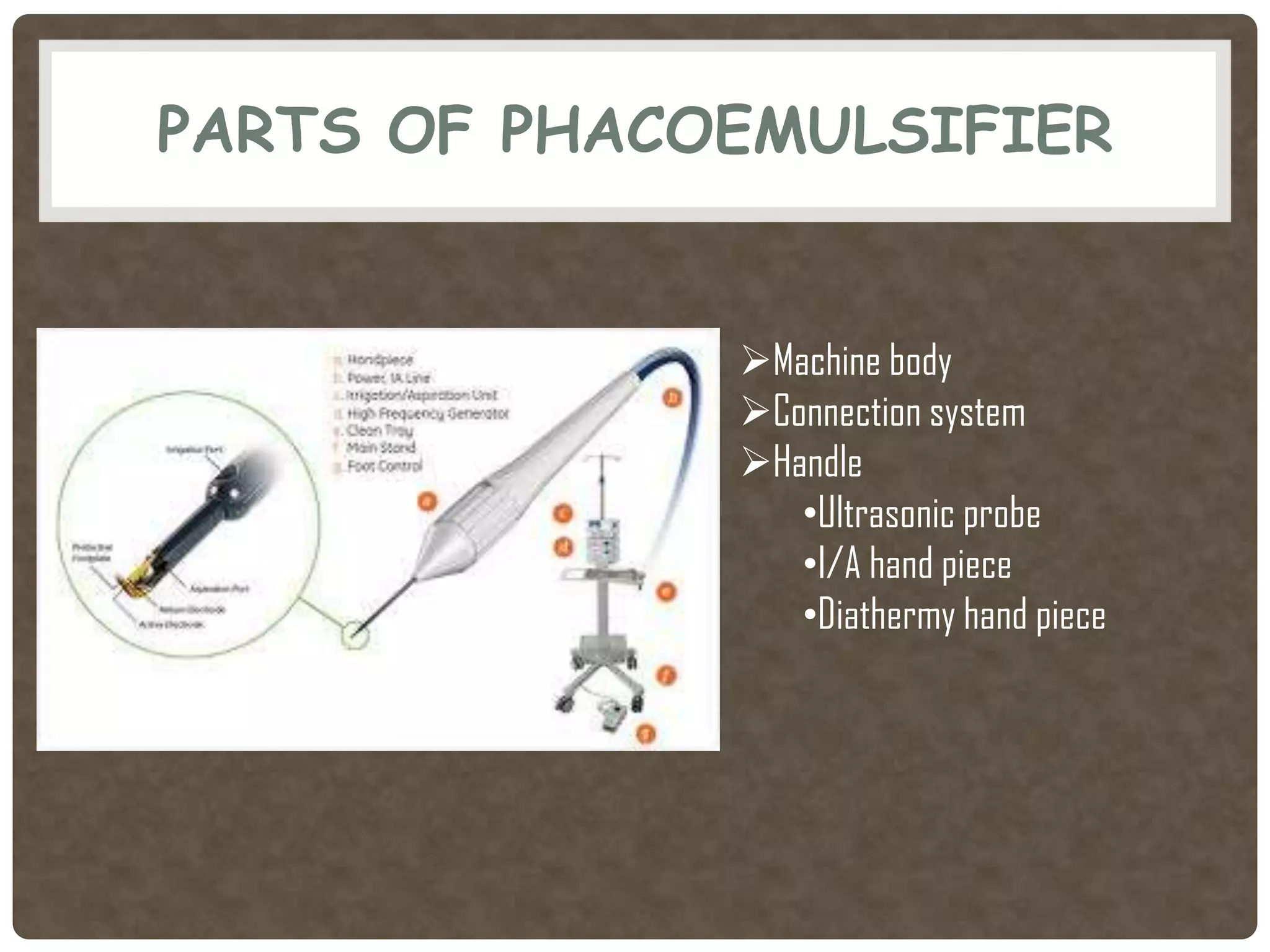
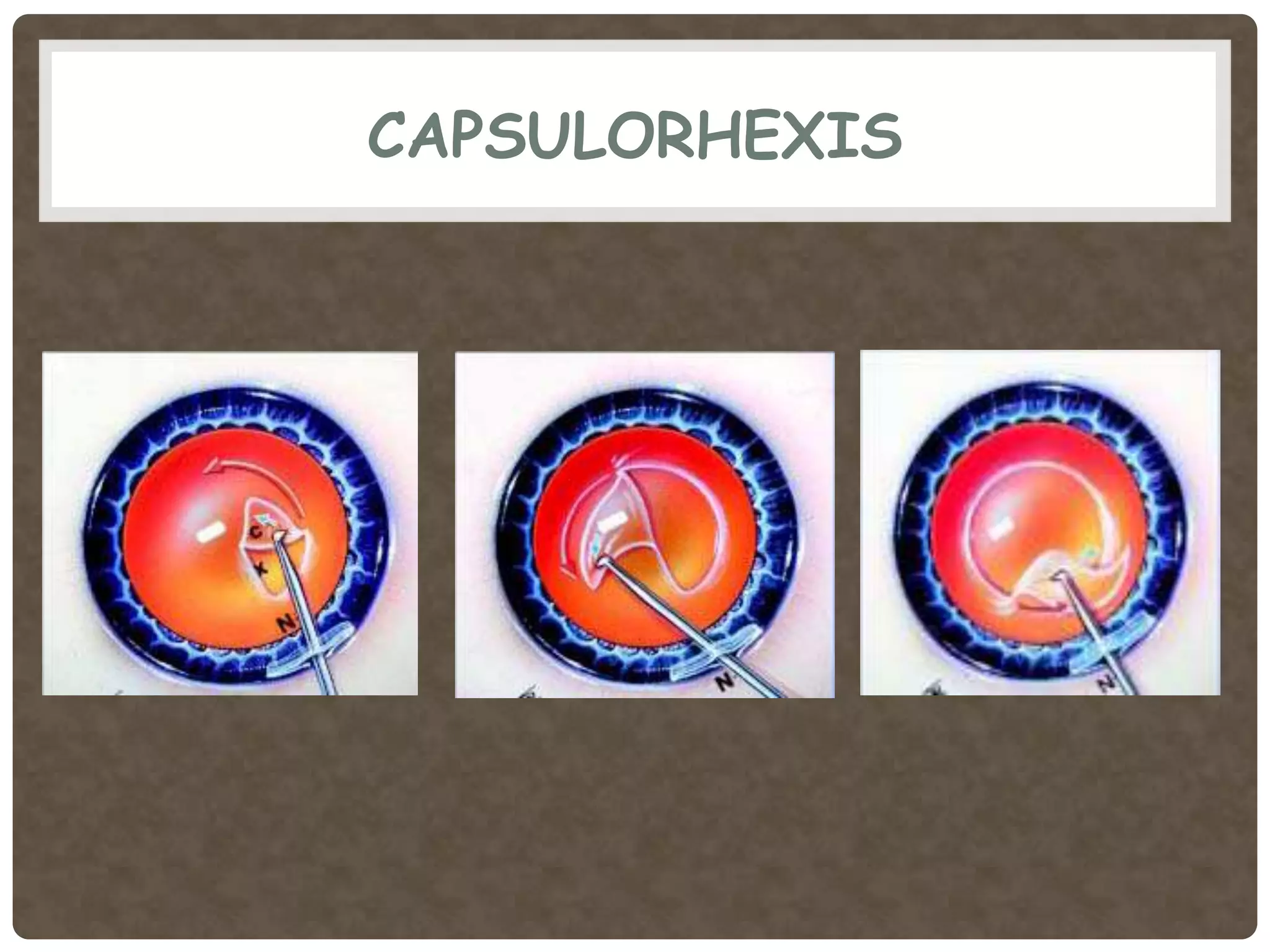
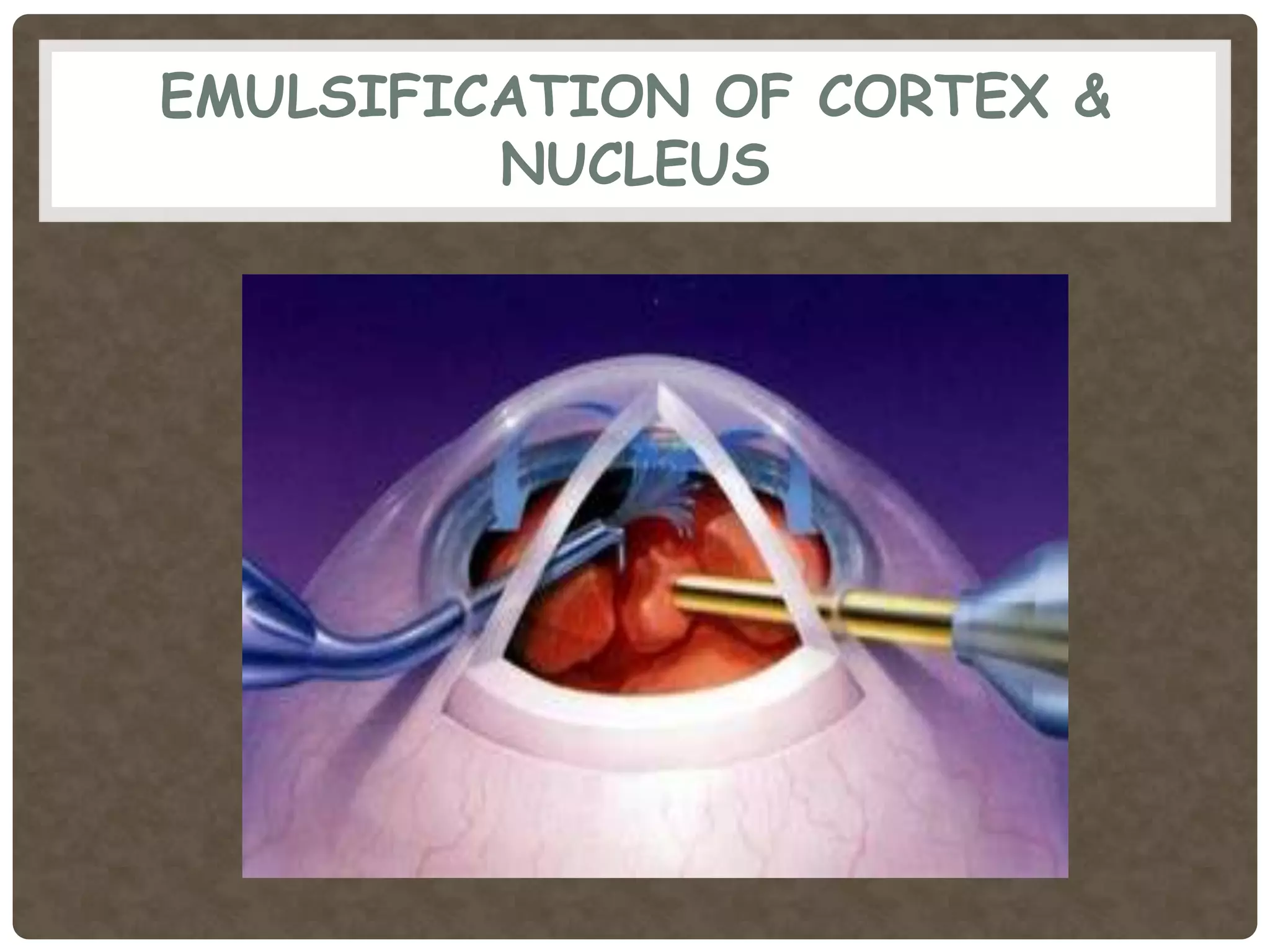
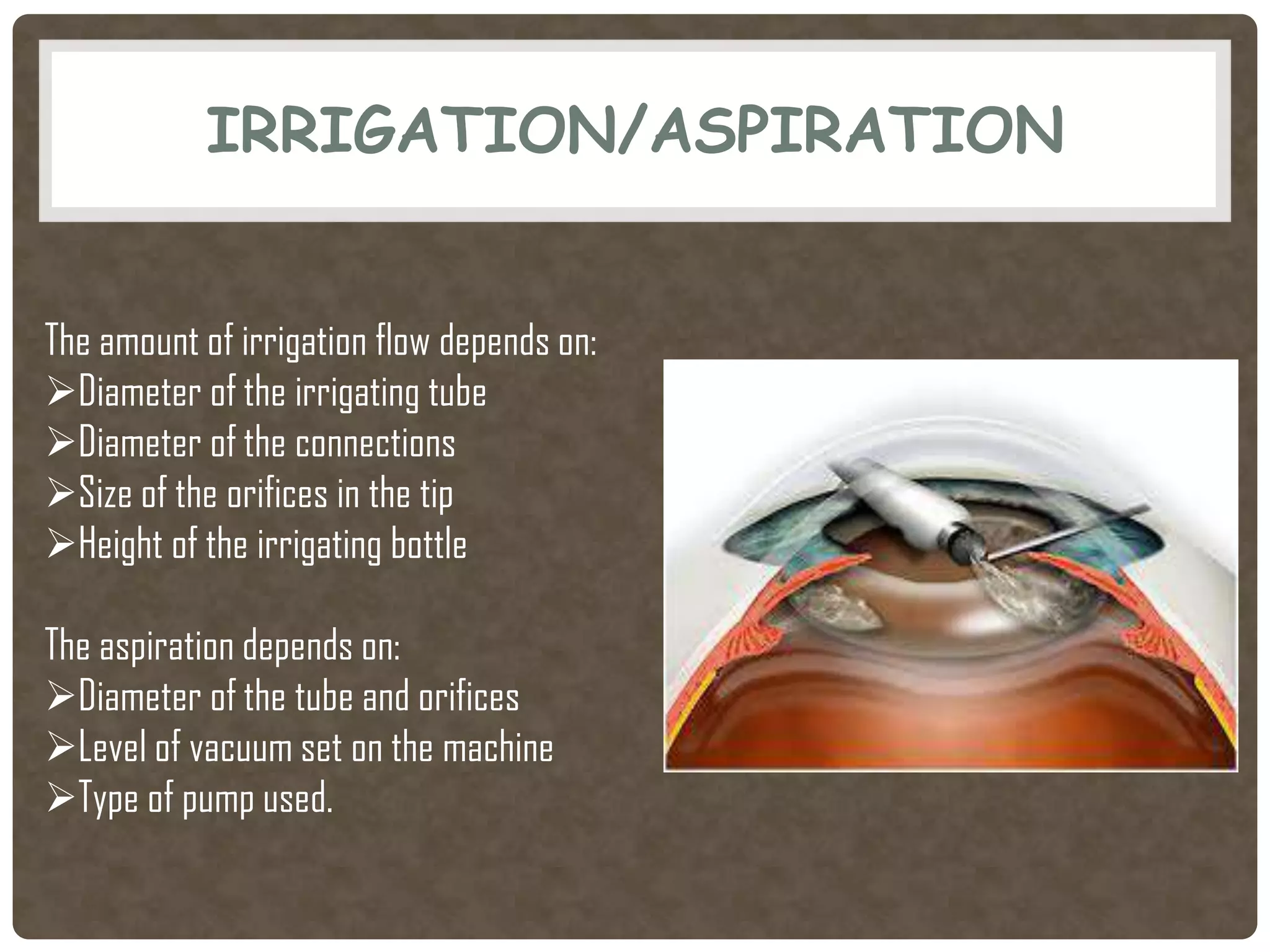
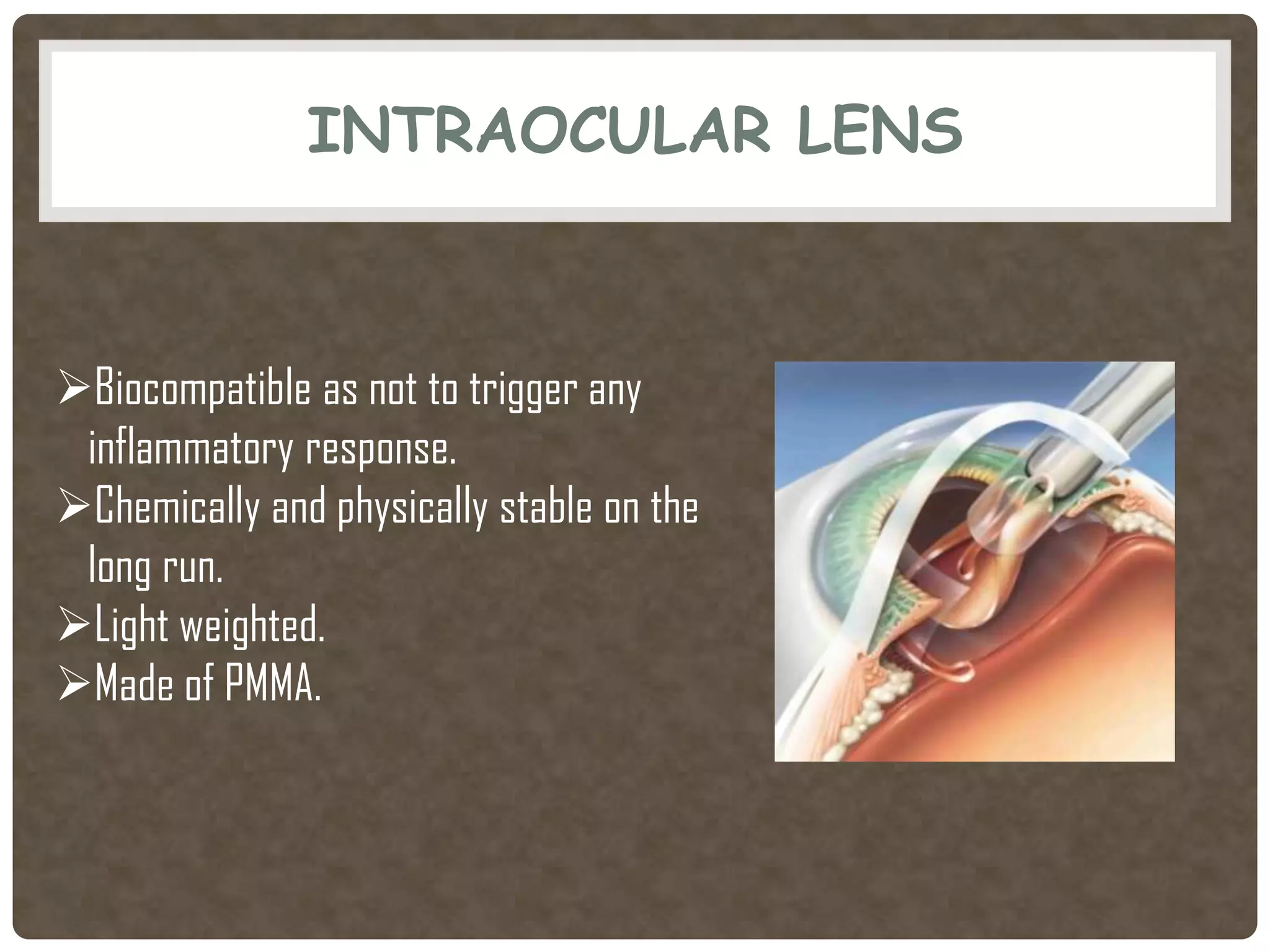
Phacoemulsification is a cataract surgery technique introduced in 1967 involving emulsifying the lens using ultrasonic vibrations. It utilizes a small incision and irrigation/aspiration to gently break up and remove the lens, reducing postoperative complications. Key steps include incision, capsulotomy, hydroprocedures, nucleus emulsification using techniques like divide and conquer, and intraocular lens implantation. Proper fluid dynamics and pump type are important for efficient irrigation and aspiration.