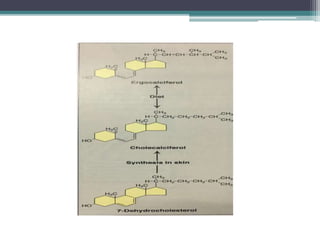
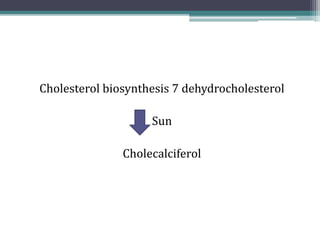
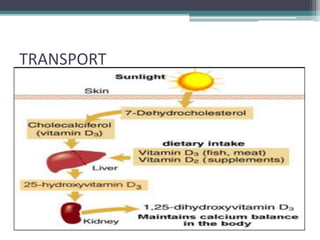
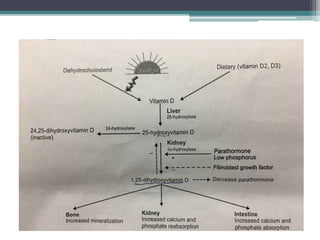
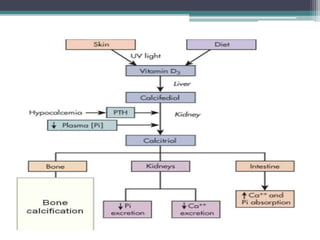
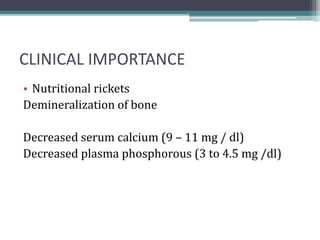
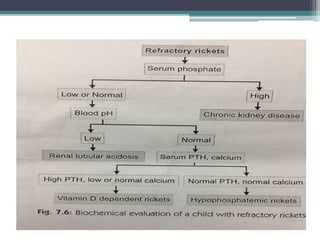
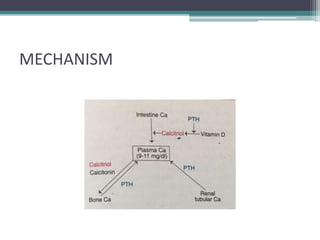
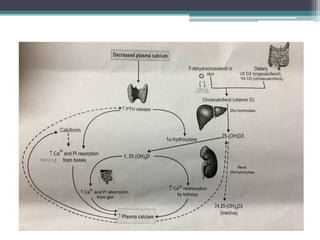
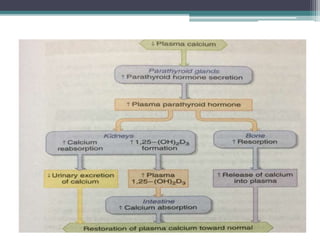
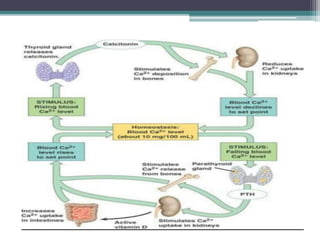
This document discusses vitamin D, calcium, parathyroid hormone, and calcitonin. It covers their roles in calcium regulation and bone health. Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is synthesized in the skin from cholesterol or ingested from plants and animals. It is metabolized in the liver and kidneys to its active form calcitriol, which increases calcium absorption from the intestine and bone resorption. Parathyroid hormone increases serum calcium levels by promoting bone resorption and renal calcium reabsorption. Calcitonin has the opposite effect of parathyroid hormone by inhibiting bone resorption and promoting calcium deposition in bone. Together these elements work to maintain adequate calcium levels in the blood