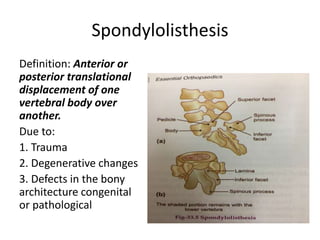
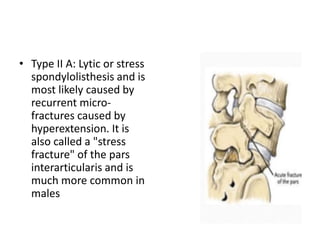
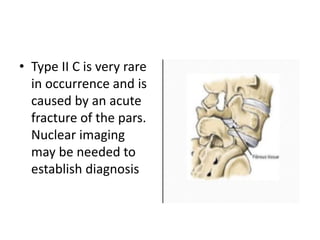
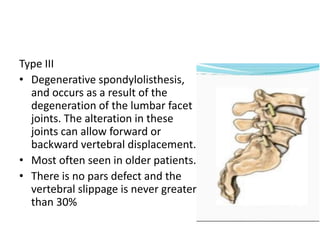
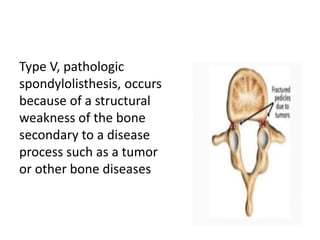
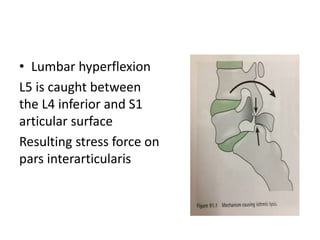
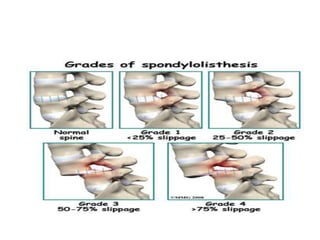
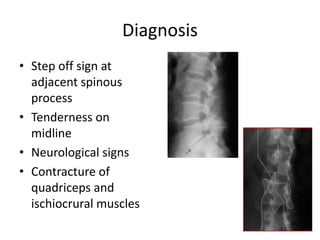
This document discusses spondylolisthesis, defined as anterior or posterior displacement of one vertebral body over another. It can be caused by trauma, degenerative changes, or congenital/pathological defects. The document describes the 5-part Wiltse classification of spondylolisthesis etiology, including dysplastic, isthmic/spondylolytic, degenerative, traumatic, and pathologic types. Isthmic spondylolisthesis is most common and occurs from microfractures or defects in the pars interarticularis. Degenerative spondylolisthesis results from facet joint degeneration. Diagnosis involves tenderness and neurological signs. Treatment options include conservative care, surgical fixation,