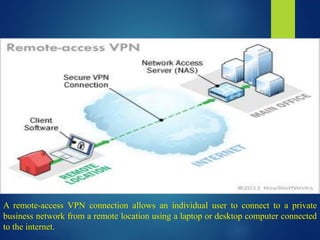
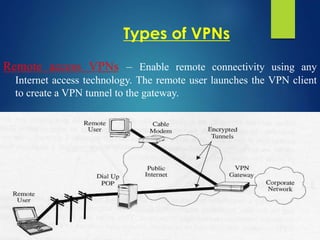
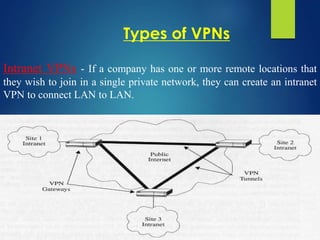
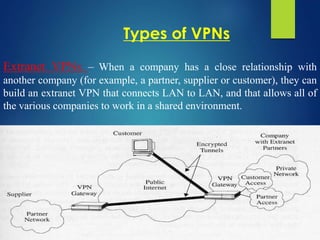
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) allows secure communication between remote devices over the internet, functioning as a private network despite using public channels. Several types of VPNs exist, including remote access, intranet, and extranet, employing different protocols for secure connections, such as PPTP, L2TP, IPsec, and SSL. While VPNs offer advantages like cost reduction and scalability, they also present challenges like the need for security expertise and potential compatibility issues among different vendor products.