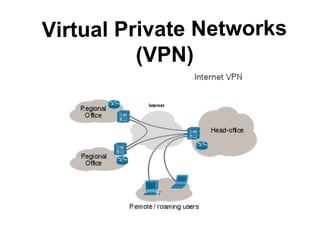
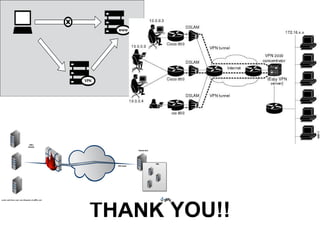
Virtual Private Networks (VPN) allow secure connections over public networks like the Internet. VPNs use encryption to create "virtual private tunnels" between devices. This allows remote users to access resources on a private network as if they were directly connected. There are two main types - remote access VPNs for individual users and site-to-site VPNs to connect multiple office locations. VPNs work by encapsulating data packets within encrypted "tunnels" to securely transmit them between endpoints across public networks while maintaining privacy and security.