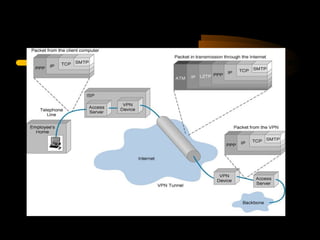
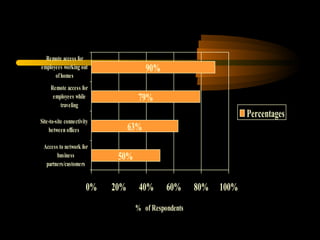
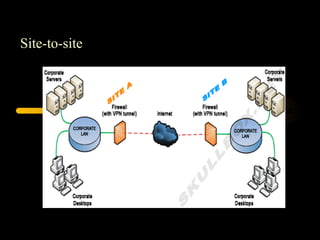
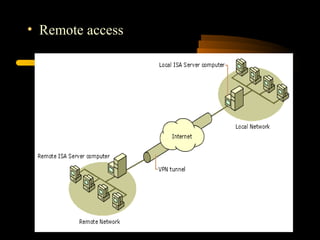
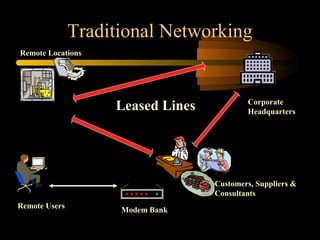
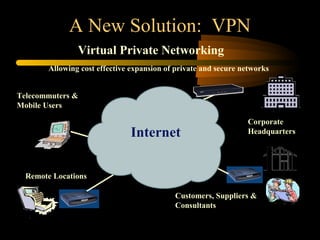
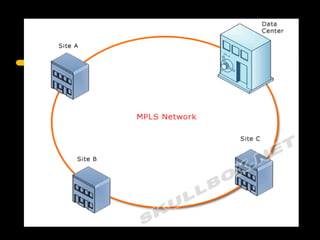
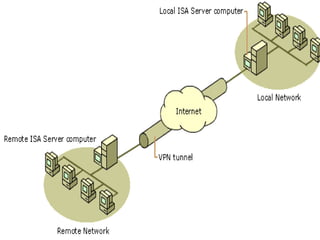
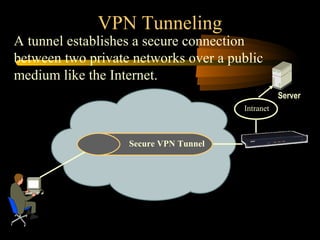
Virtual private networks (VPNs) allow secure connections over public networks like the Internet instead of expensive leased lines. There are three main types of VPNs: trusted VPNs rely on a single provider's network for security; secure VPNs encrypt and authenticate all traffic between agreed parties; and hybrid VPNs combine secure VPN technologies running over trusted VPN technologies. VPNs use technologies like IPSec, SSL/TLS, and PPTP to provide critical functions of authentication, access control, confidentiality, and data integrity. They are commonly used by industries for remote access, site-to-site connectivity between offices, and access to networks for business partners and customers.















![Original Datagram
Encrypted inner datagram
Datagram Header Outer Datagram Data Area
Data encapsulation[from corner]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shradhamaheshwarivpn-121208094704-phpapp01/85/Shradhamaheshwari-vpn-22-320.jpg)