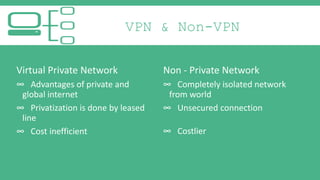
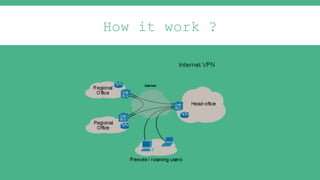
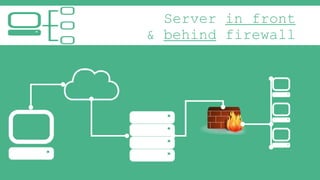
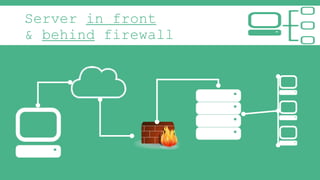
The document provides an introduction to Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), explaining their definition, functionality, and types. It highlights the advantages of VPNs over traditional private networks, emphasizing their cost-effectiveness and security through tunneling protocols like PPTP and L2TP. Additionally, the document discusses the roles of firewalls in VPN setups and outlines the benefits and challenges associated with Mobile VPNs (MVPN).