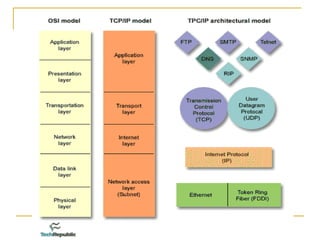
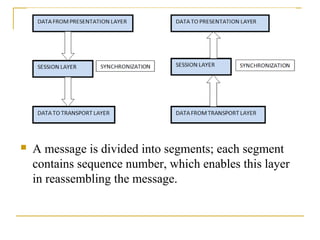
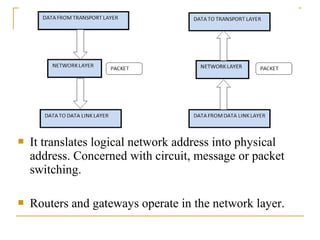
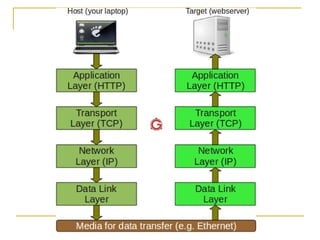
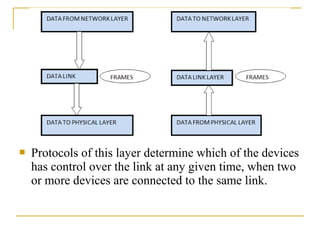
The document provides an overview of the TCP/IP protocol suite, detailing its layers: the application, transport, network, data link, and physical layers. Each layer's functions and protocols, such as HTTP, FTP, and TCP/IP, are described, with emphasis on error detection, data routing, and transmission reliability. It highlights the roles of different protocols in ensuring effective communication and data transfer across networks.