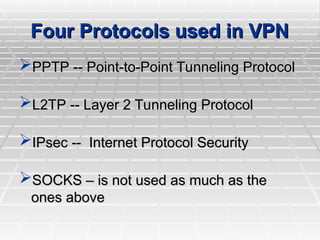
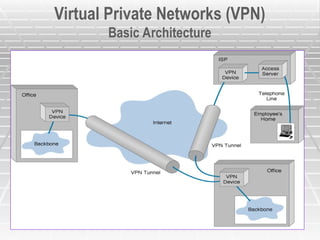
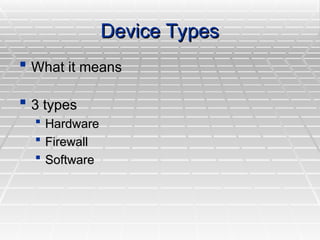
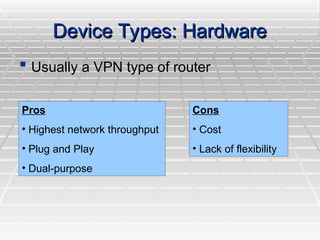
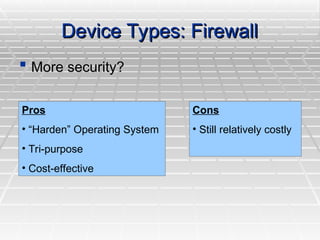
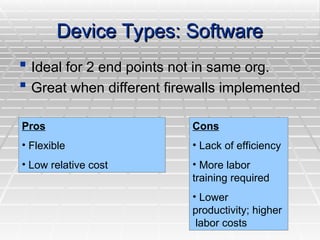
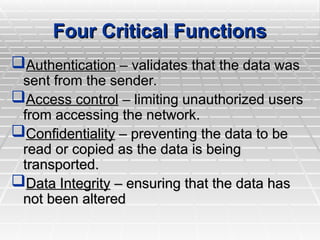
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) allows secure connections over public telecommunications networks like the internet, enabling remote access to private intranets while reducing costs and enhancing flexibility. It operates on principles of authentication, access control, confidentiality, and data integrity, utilizing various protocols and encryption methods. The document discusses types of VPN implementations and applications across industries, along with their advantages and disadvantages.






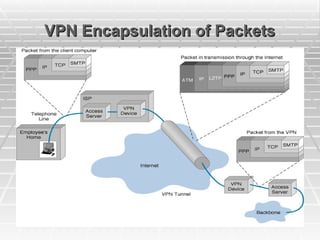
![Tunneling
Tunneling
A virtual point-to-point connection
A virtual point-to-point connection
made through a public network. It transports
made through a public network. It transports
encapsulated datagrams.
encapsulated datagrams.
Encrypted Inner Datagram
Datagram Header Outer Datagram Data Area
Original Datagram
Data Encapsulation [From Comer]
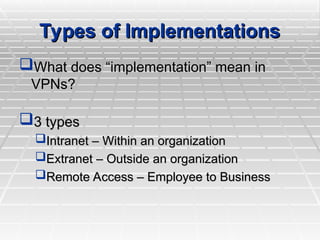
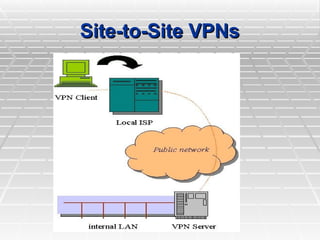
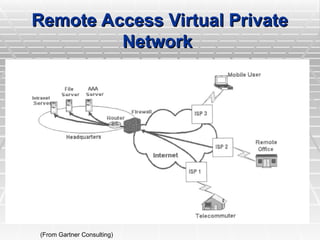
Two types of end points:
Remote Access
Site-to-Site](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/97751669-vpn-presentation-250131173435-b74f2d1d/85/VPN-Presentation-presenation-about-VPN-to-learn-more-9-320.jpg)