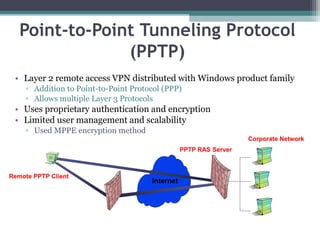
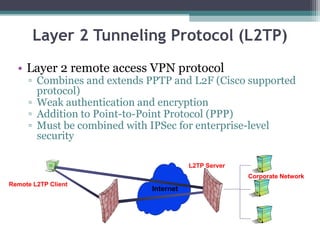
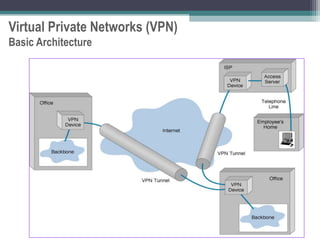
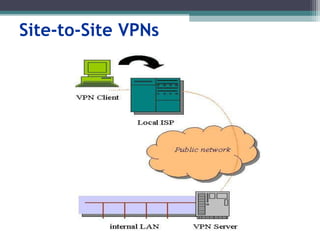
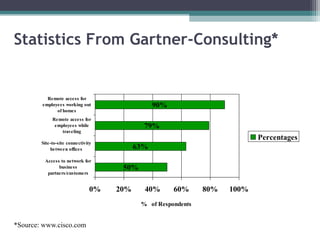
Virtual private networks (VPNs) allow employees to securely access a company's intranet from remote locations over the public Internet. VPNs use encryption and authentication to ensure privacy and prevent unauthorized access. They provide cost savings over traditional private networks by reducing equipment and maintenance costs while improving scalability. Common VPN types include remote access VPNs for employees and site-to-site VPNs for connecting multiple office locations. Key VPN protocols are PPTP, L2TP, and IPSec. VPNs benefit industries requiring remote access or private network connections and their use is growing as more employees work remotely.

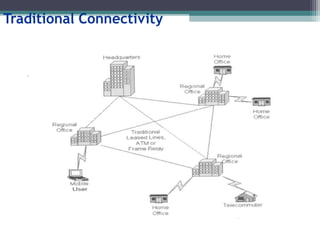



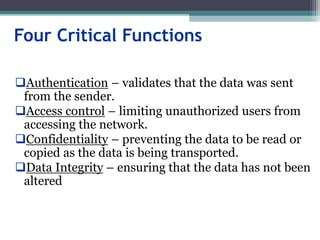

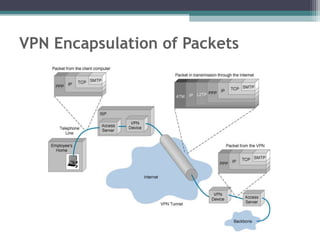
![Tunneling
A virtual point-to-point connection
made through a public network. It transports
encapsulated datagrams.
Encrypted Inner Datagram
Datagram Header Outer Datagram Data Area
Original Datagram
Data Encapsulation [From Comer]
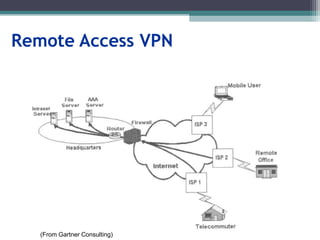
Two types of end points:
Remote Access
Site-to-Site](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vpnppt-220901163748-b5a76d85/85/VPN_ppt-ppt-9-320.jpg)