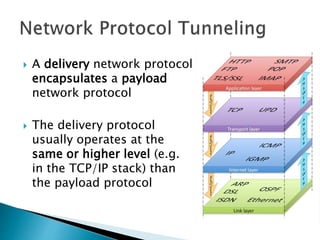
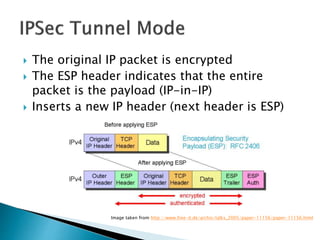
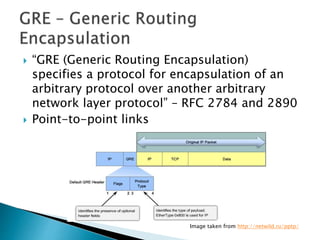
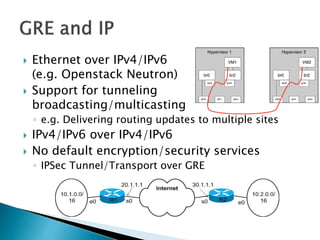
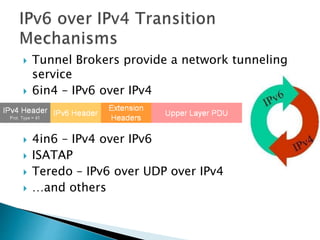
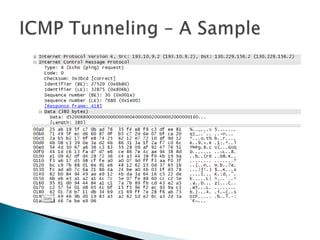
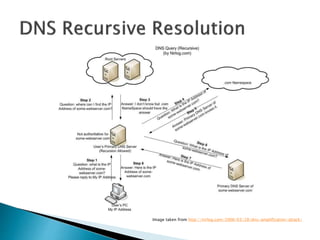
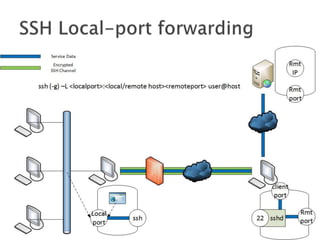
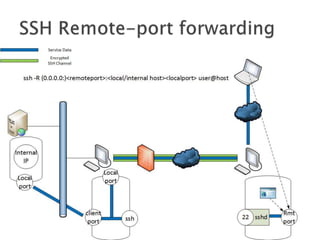
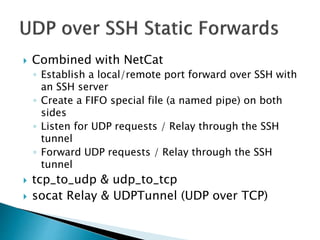
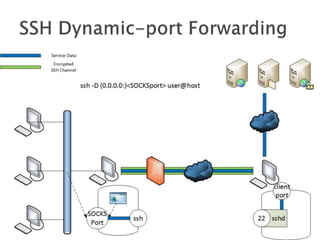
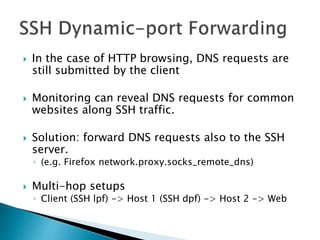
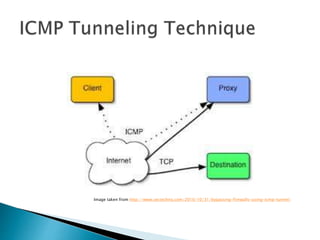
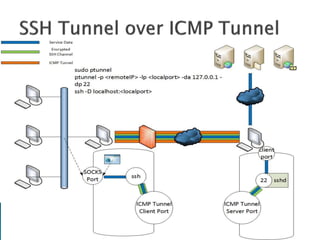
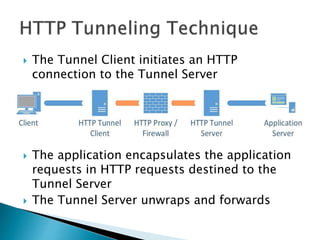
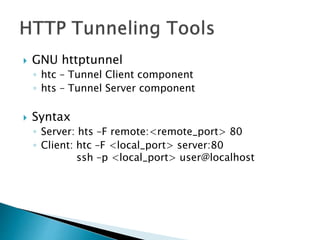
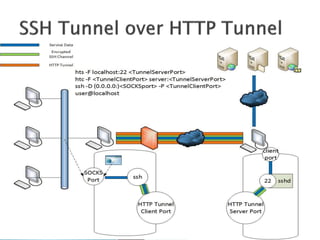
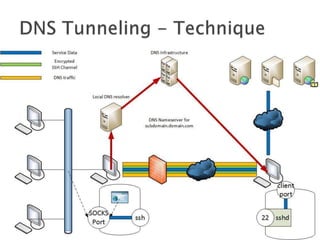
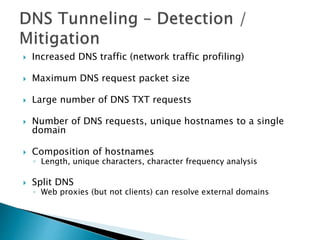
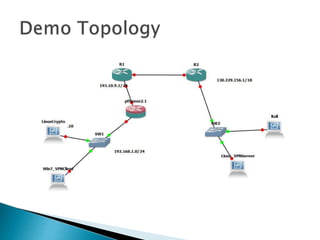
This document discusses network tunneling protocols and tools. It describes how protocols like SSH, GRE, and ICMP can be used to encapsulate other protocols and bypass network restrictions. Examples of network tunneling tools that operate over HTTP, DNS, and ICMP are provided. The document notes both legitimate and malicious uses of tunneling, and outlines challenges in detecting tunneling traffic and payloads.