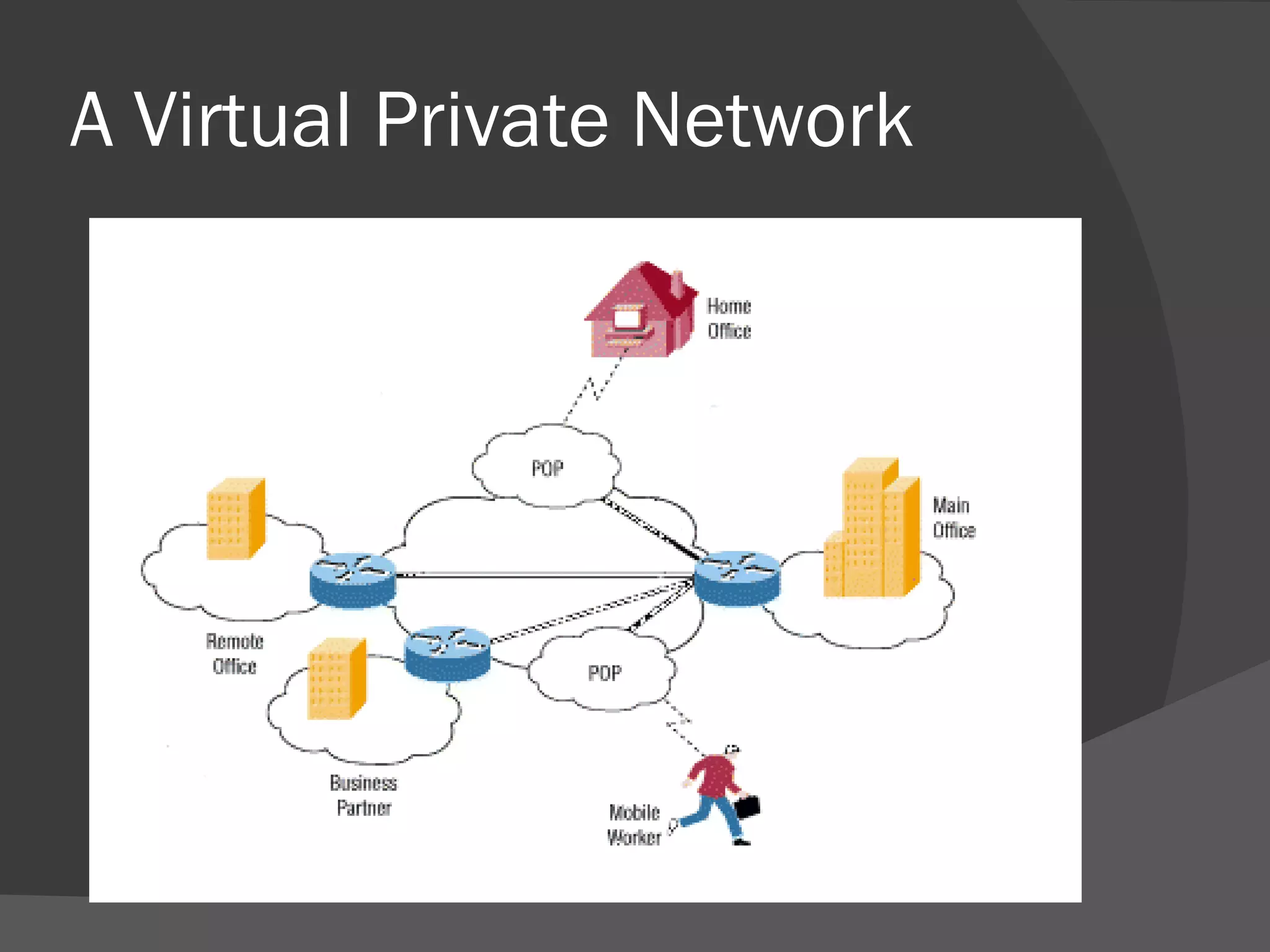
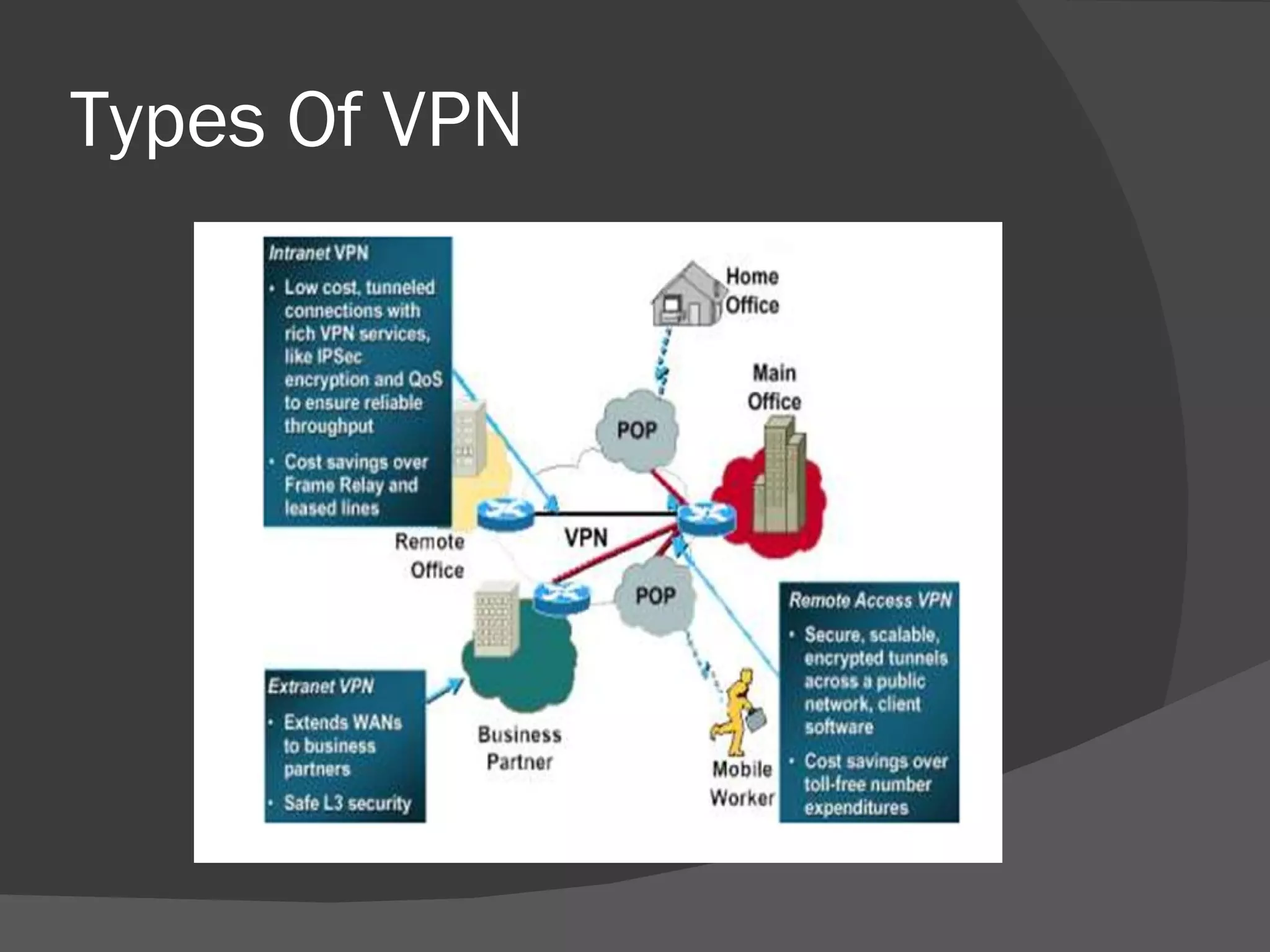
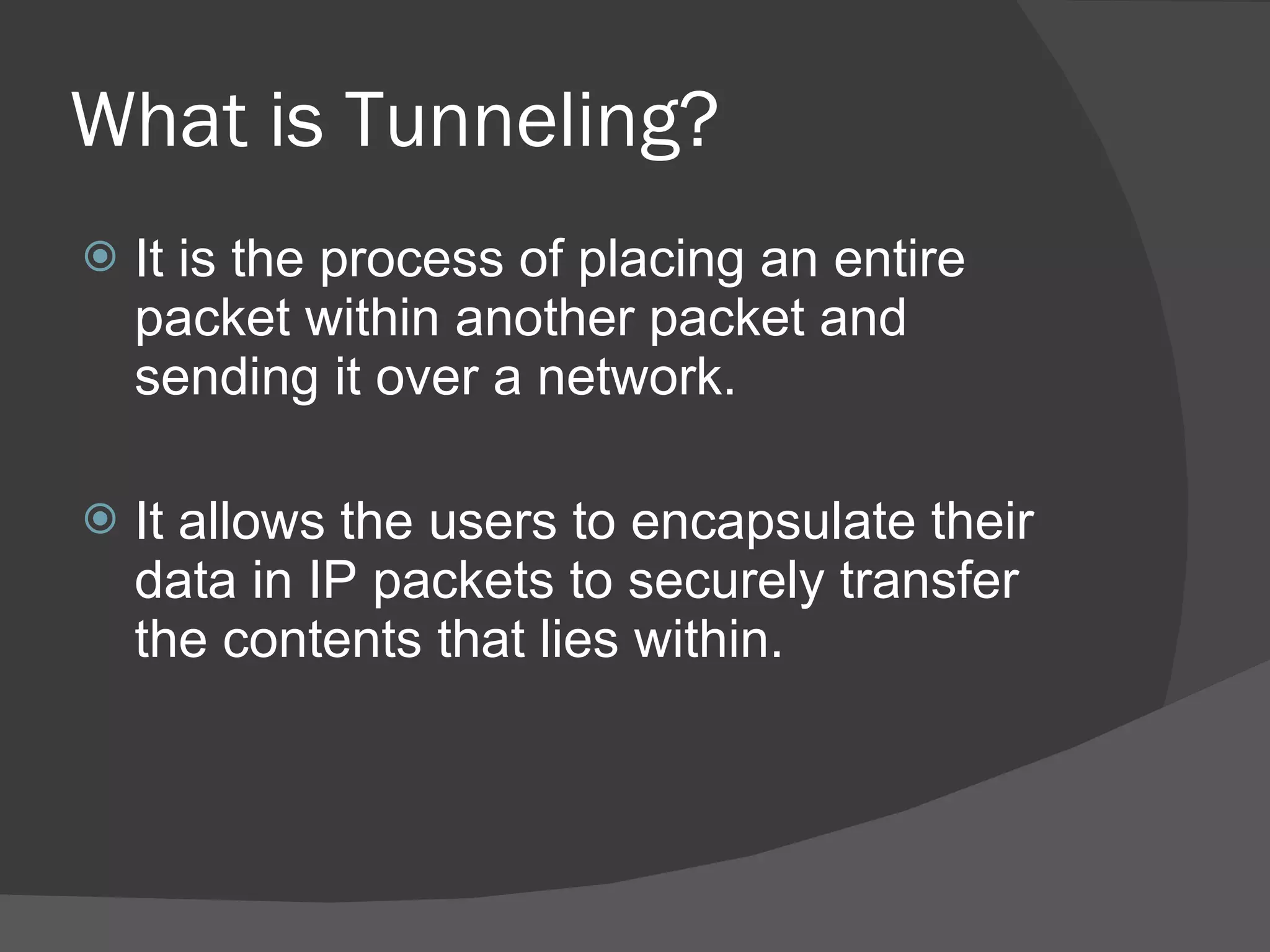
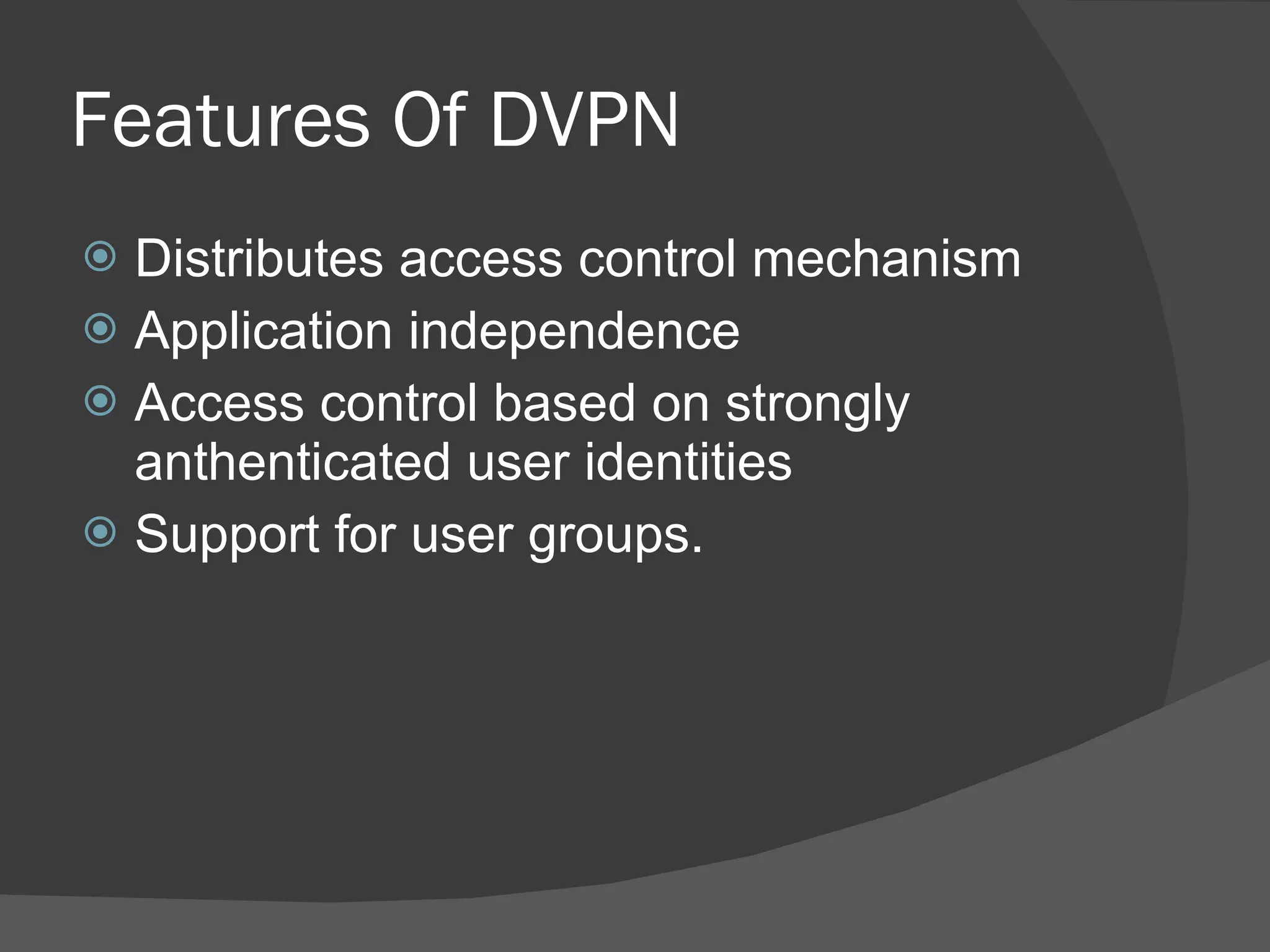
A dynamic virtual private network (DVPN) allows secure connections between remote users and private networks through virtual connections over public networks like the internet. It provides enhanced security, can accommodate changing user communities dynamically, and maintains integrity over user access rights and data security over time regardless of technological changes. Key features include distributed access control, application independence, access control based on authenticated user identities, and support for user groups. DVPNs establish trust in open network environments through flexible yet finely-controlled security.