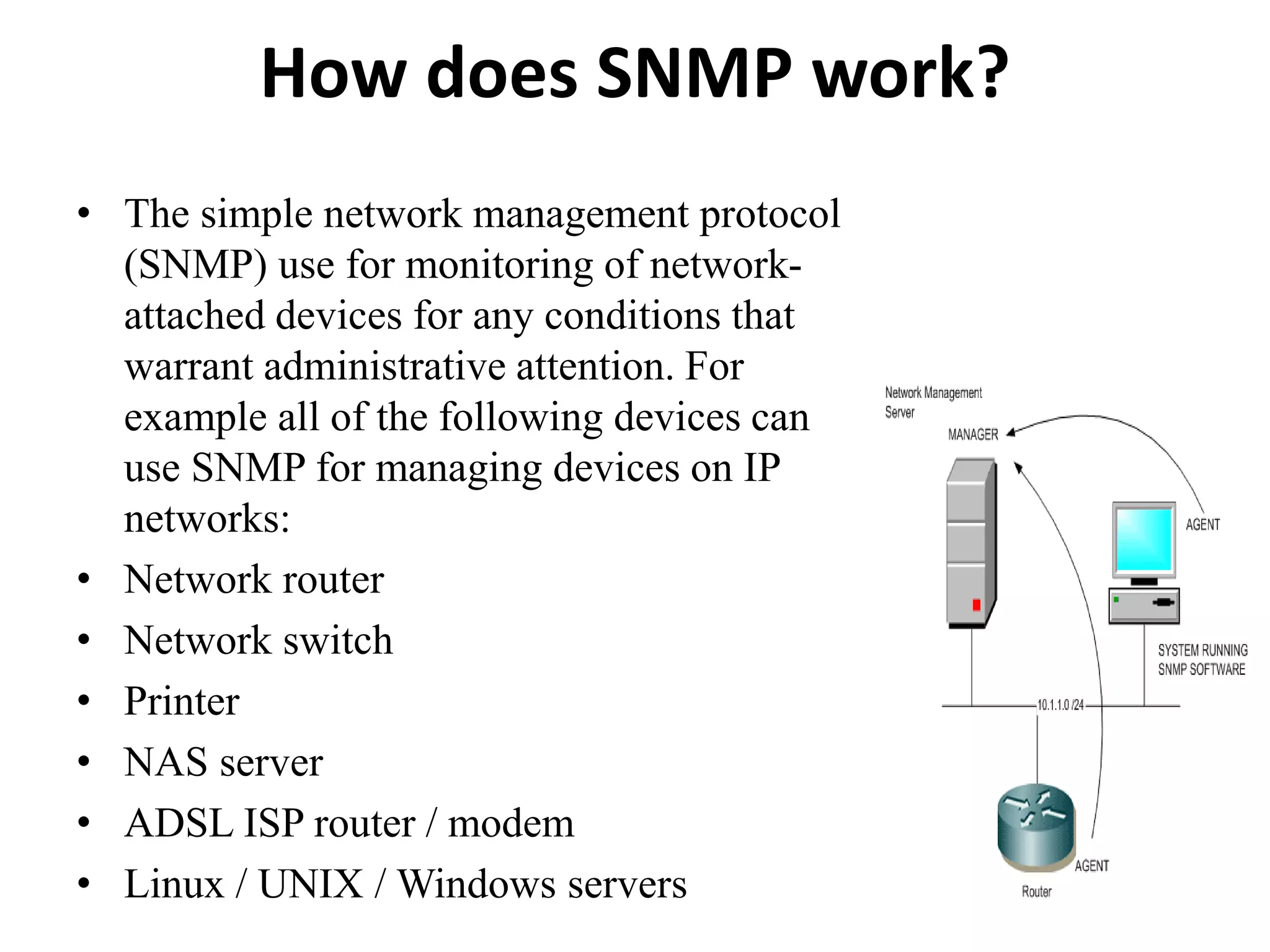
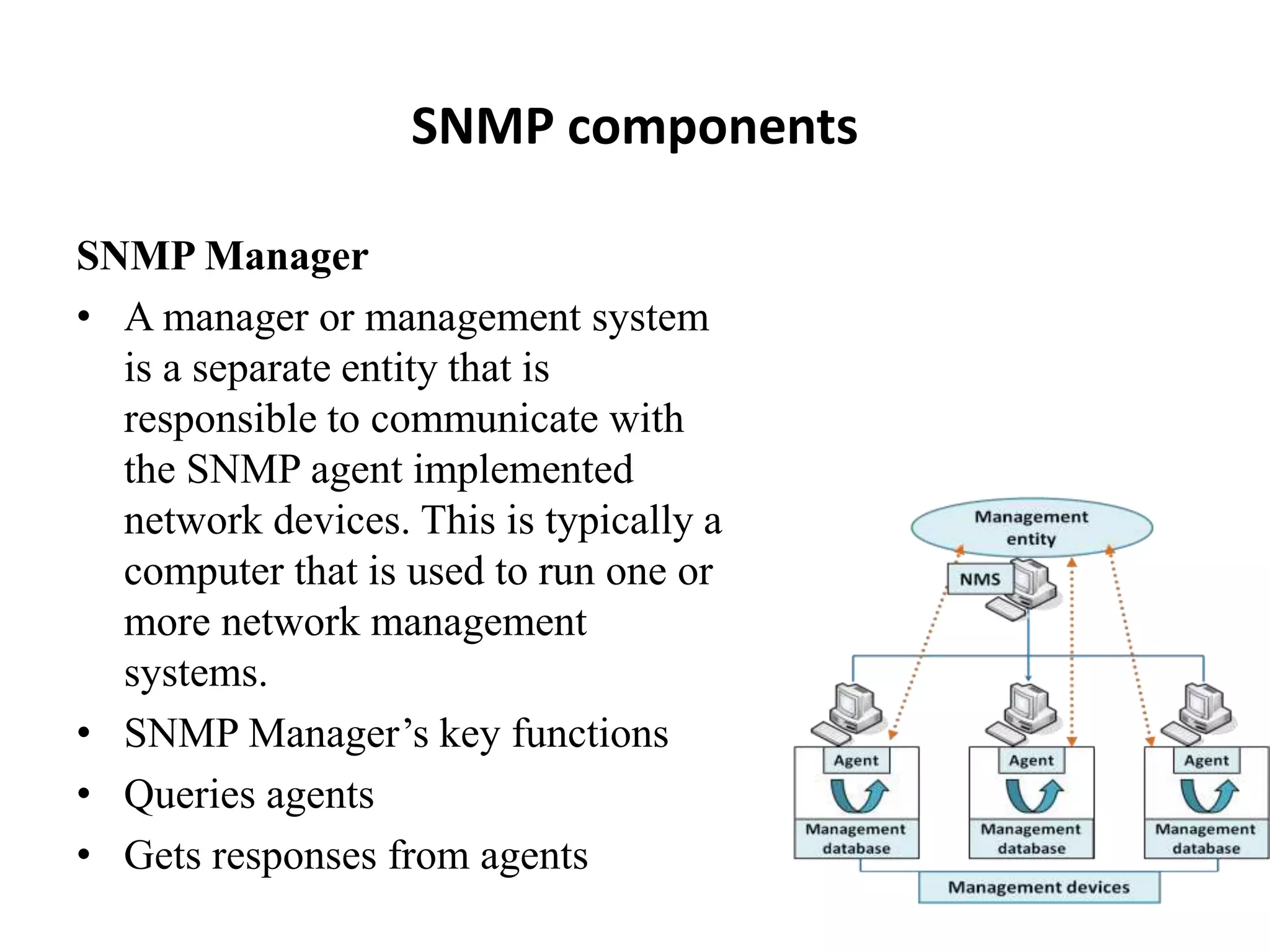
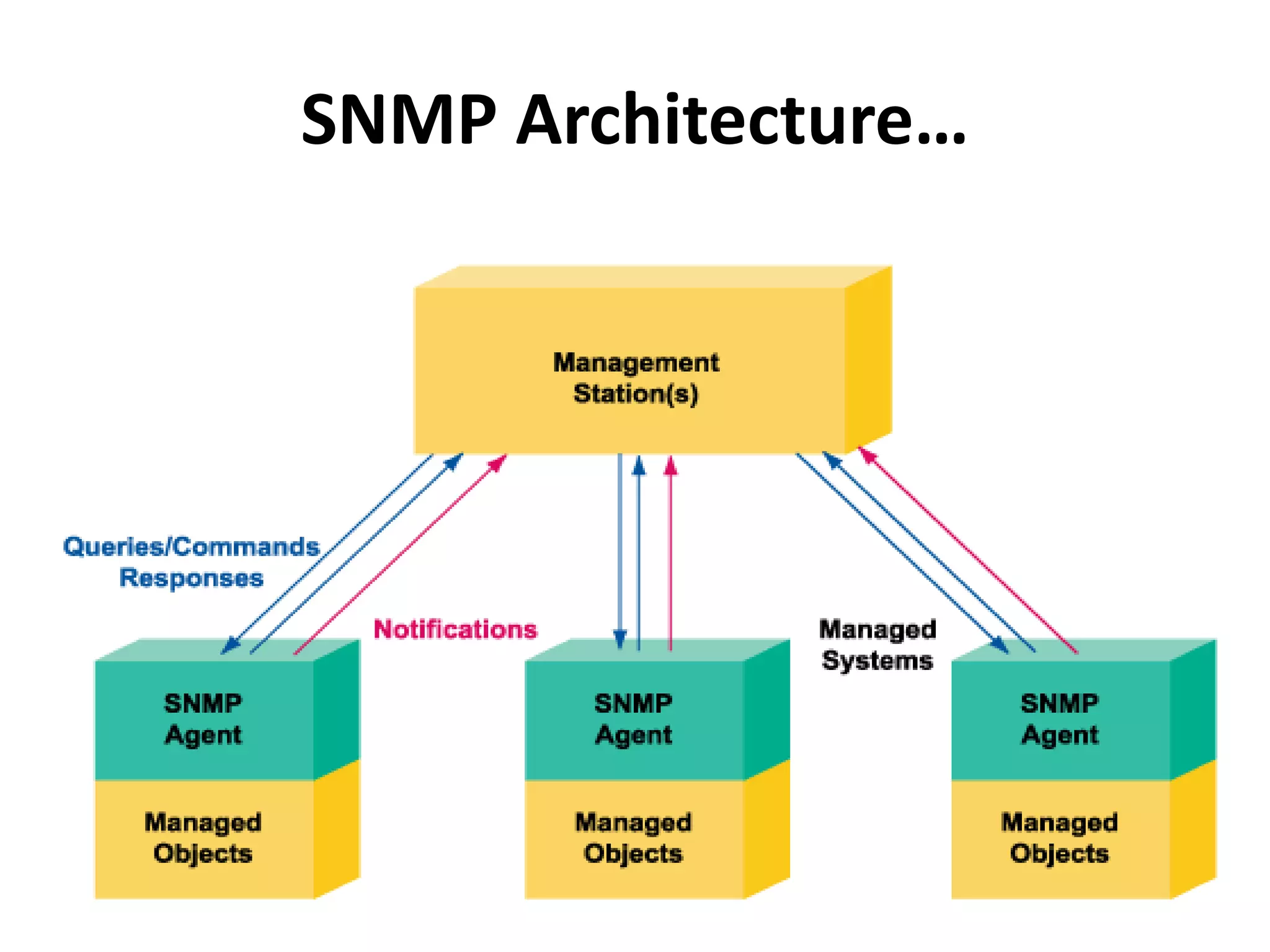
SNMP is a widely used protocol for monitoring network devices and their conditions. It uses a simple client-server architecture with SNMP managers querying SNMP agents running on devices to retrieve information defined in MIBs. SNMP is popular due to its simplicity, though it has limitations in security since it operates over UDP. The document discusses the components of SNMP including managers, agents, MIBs and messages as well as how it works, benefits, limitations and security considerations.