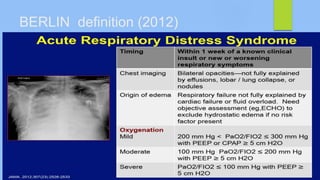
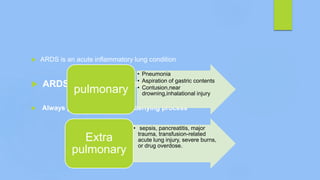
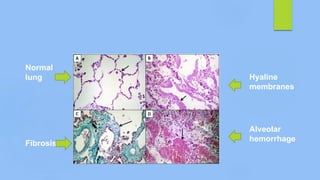
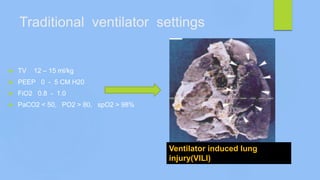
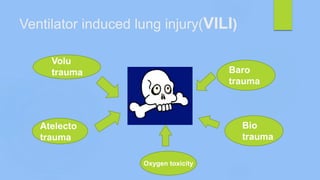
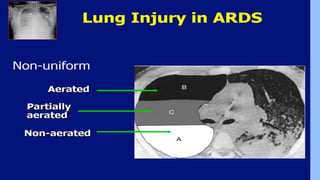
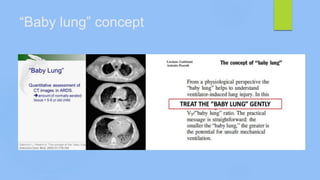
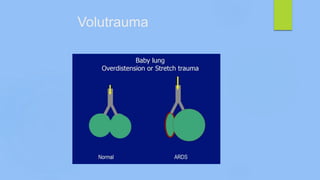
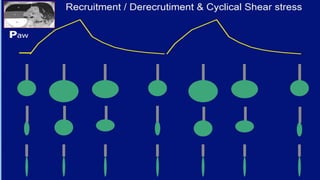
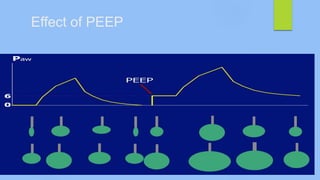
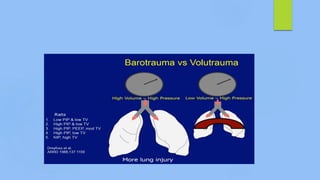
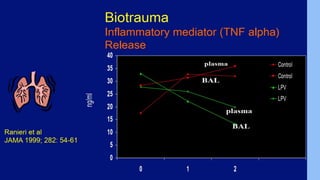
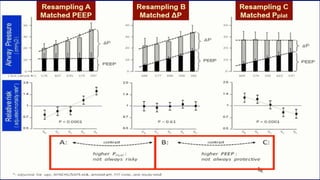
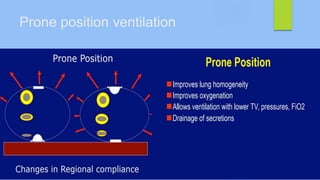
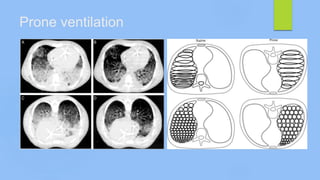
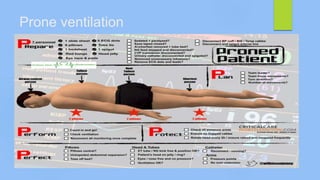
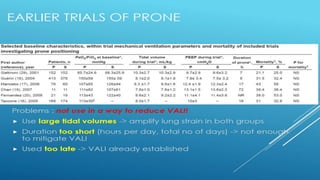
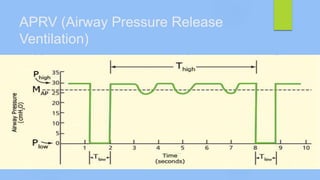
This document discusses ARDS (acute respiratory distress syndrome), including its history, definitions, pathophysiology, and evidence-based treatment strategies. ARDS is characterized by diffuse pulmonary inflammation and reduced lung compliance. Traditional ventilator strategies have been shown to cause ventilator-induced lung injury, so current recommendations focus on lung-protective ventilation with low tidal volumes and high PEEP. Additional rescue therapies for refractory hypoxemia include recruitment maneuvers, proning, and ECMO. Proper diagnosis requires consideration of alternative conditions and use of diagnostic tools like echocardiogram, bronchoscopy, and chest CT scan.