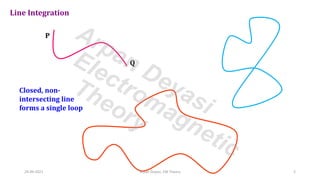
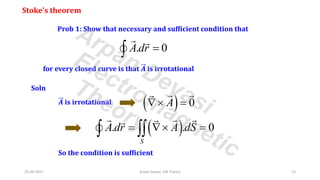
This document discusses vector calculus theorems including Stokes' theorem and the divergence theorem. Stokes' theorem relates the line integral of a vector field around a closed curve to the surface integral of the curl of the vector field over any surface bounded by the curve. The divergence theorem relates the volume integral of the divergence of a vector field over a volume to the surface integral of the vector field over the boundary surface of that volume. The document provides proofs of these theorems and examples of their applications to problems involving conservative vector fields and evaluating integrals.



























![Divergence theorem
( )
.[ ] [ ].
V
S
A B dV A B dS
=
( ) ˆ
. . [ ]
V
S
B A dV B n A dS
=
( ) ˆ
[ ]
V
S
A dV n A dS
=
29-09-2021 Arpan Deyasi, EM Theory 30
Arpan Deyasi
Electromagnetic
Theory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/integration-210929074717/85/Vector-Integration-30-320.jpg)









