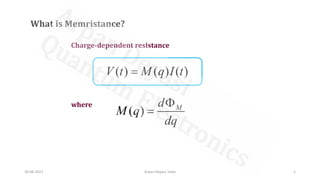
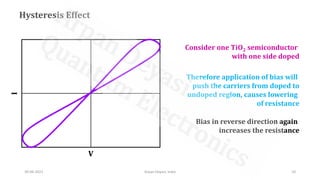
The document discusses memristors, a two-terminal electrical component that remembers the amount of charge that has flowed through it. Memristors can retain their resistance even when power is removed. The document then describes how titanium dioxide memristors work using oxygen vacancies in the material to change resistance based on the direction and amount of current flow, giving it non-volatile memory capabilities. Finally, advantages of memristors are mentioned like faster operation, lower power usage, and potential applications in AI and neuromorphic computing.