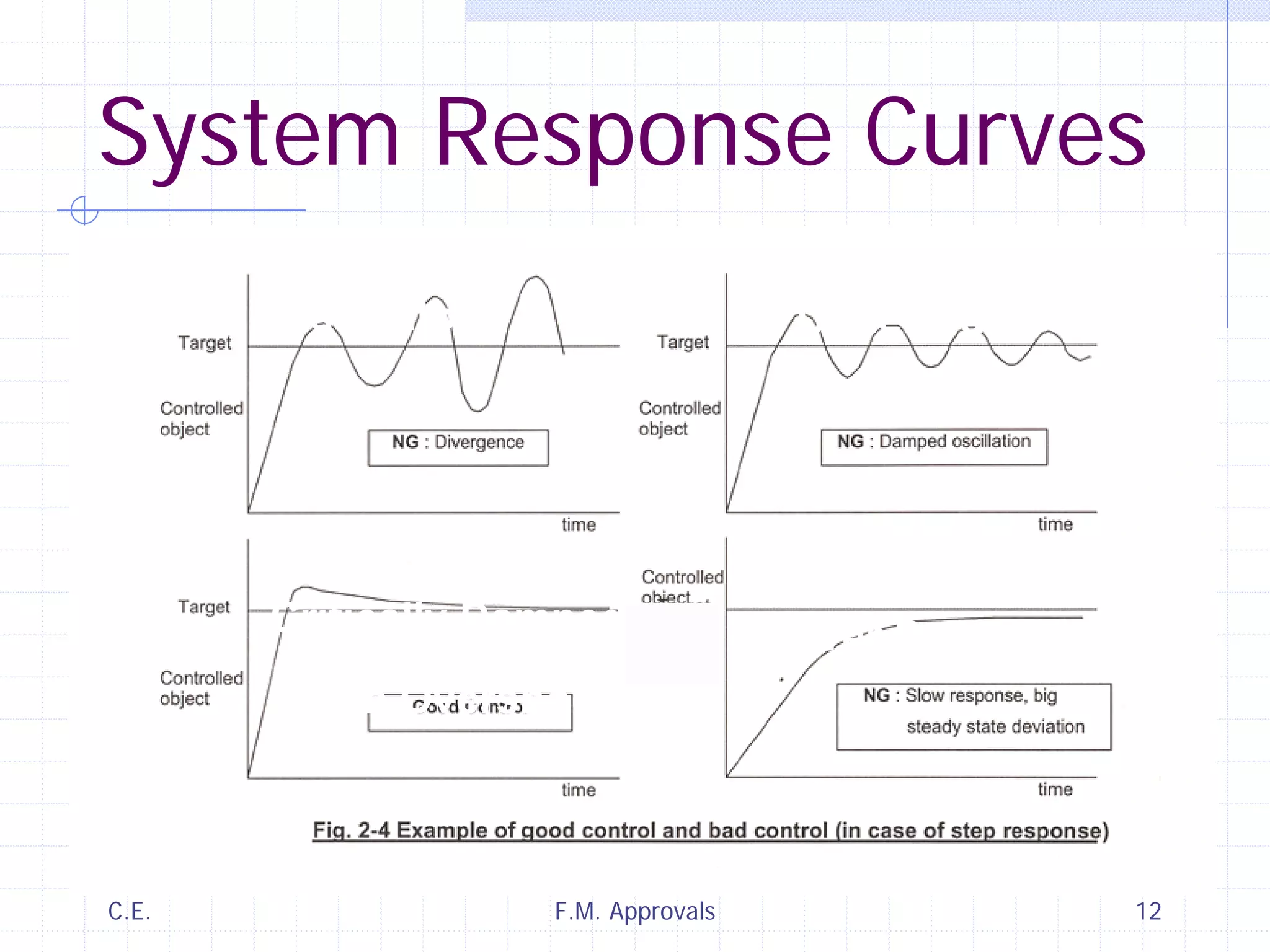
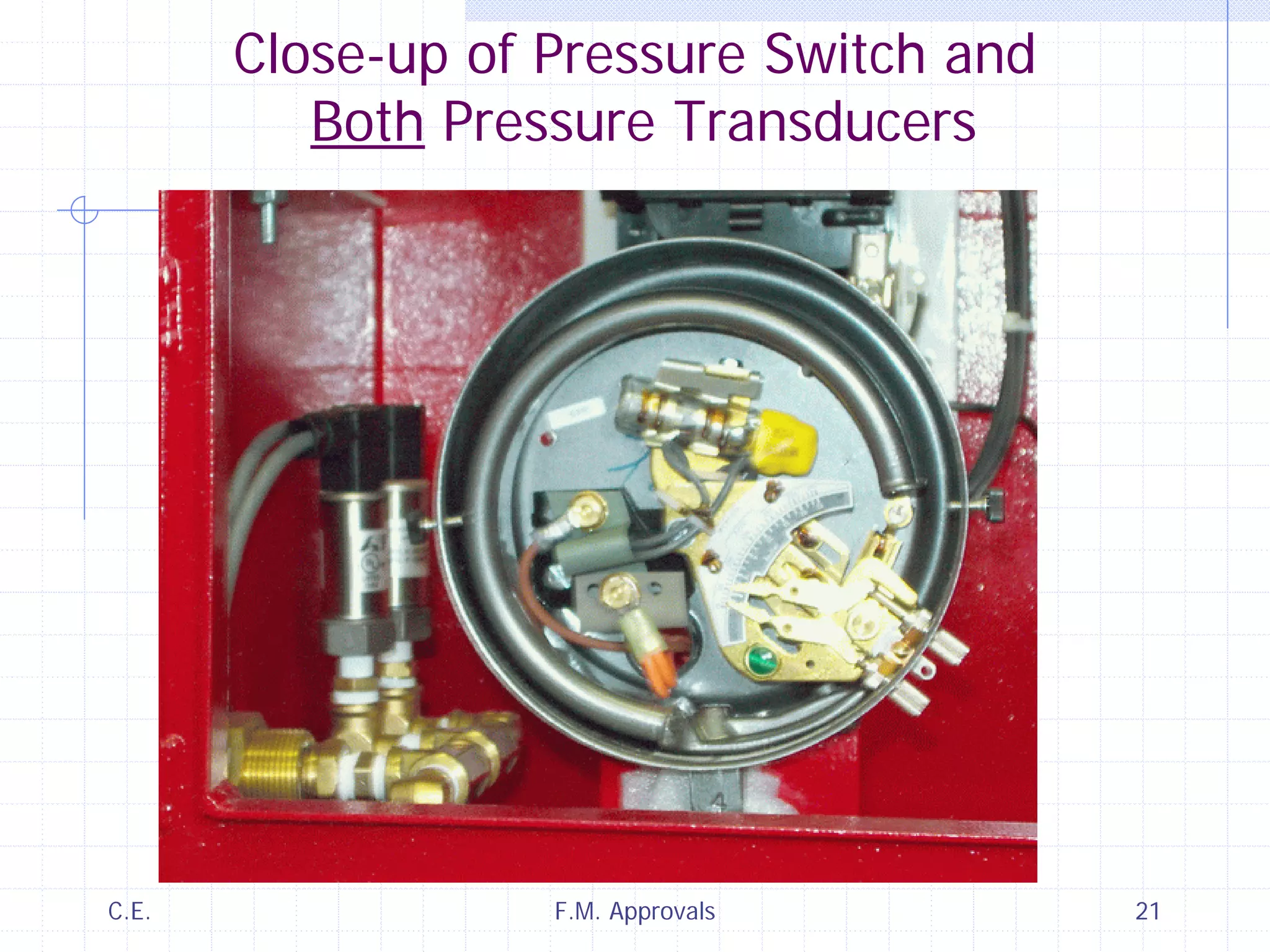
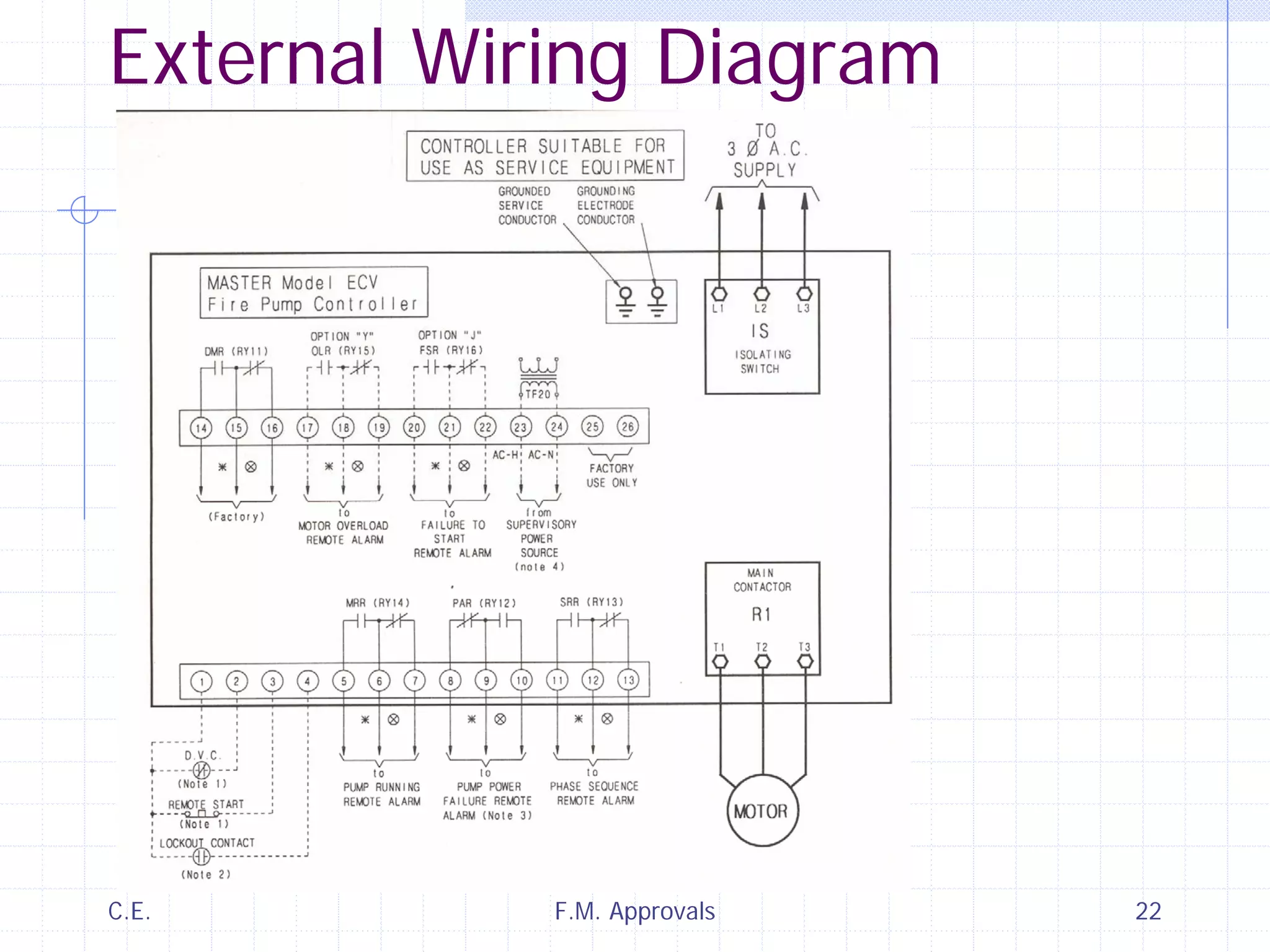
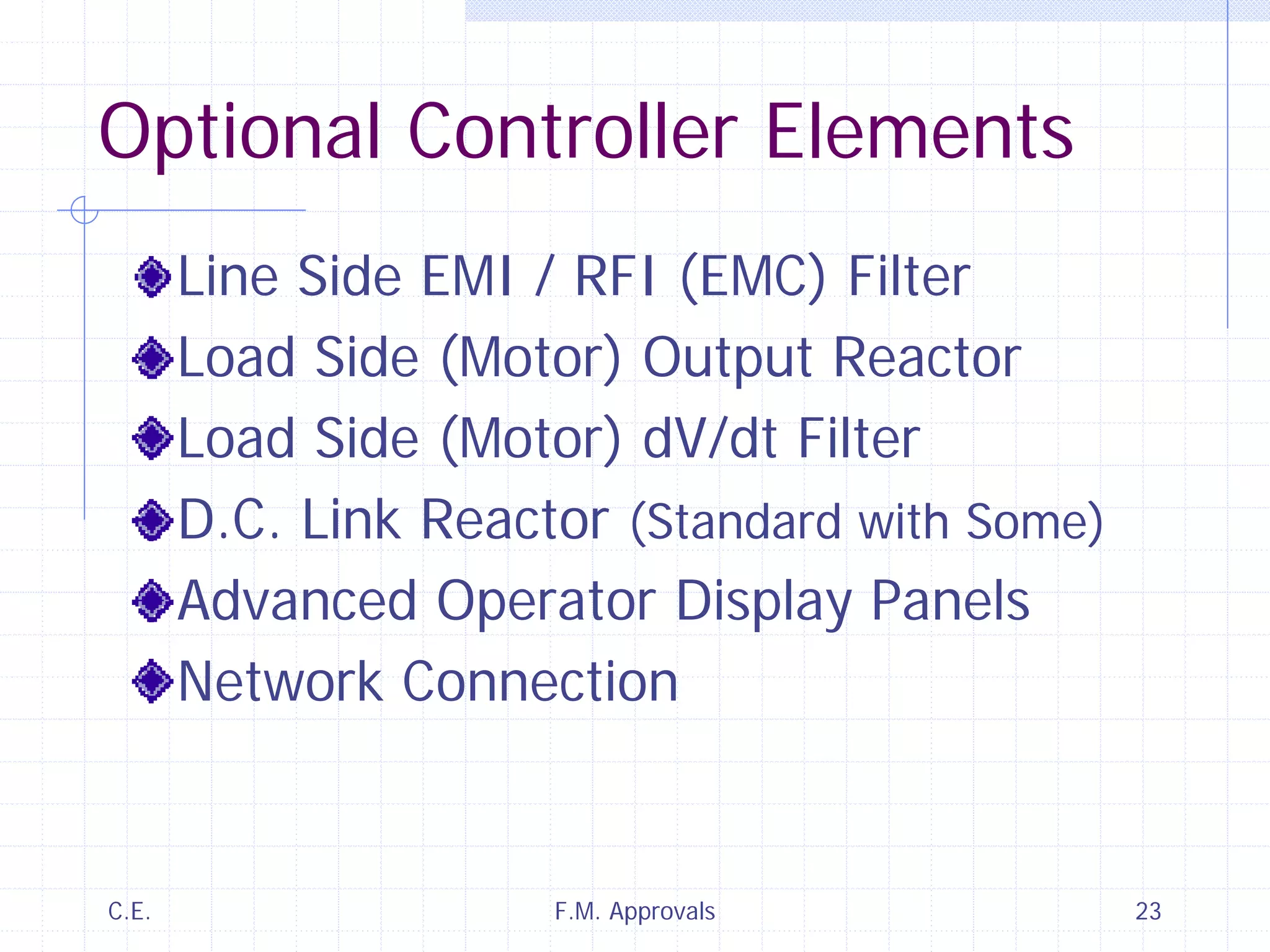
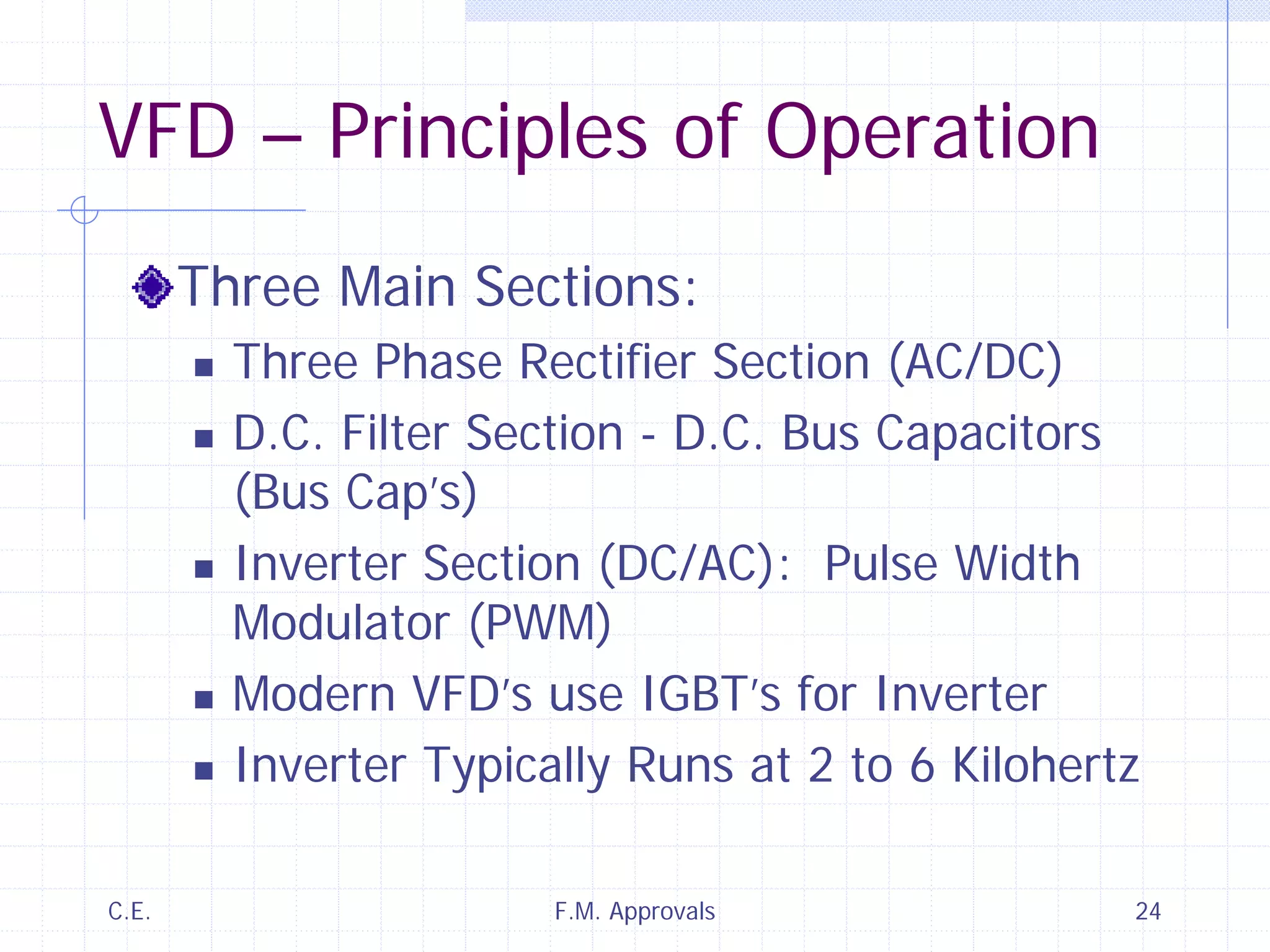
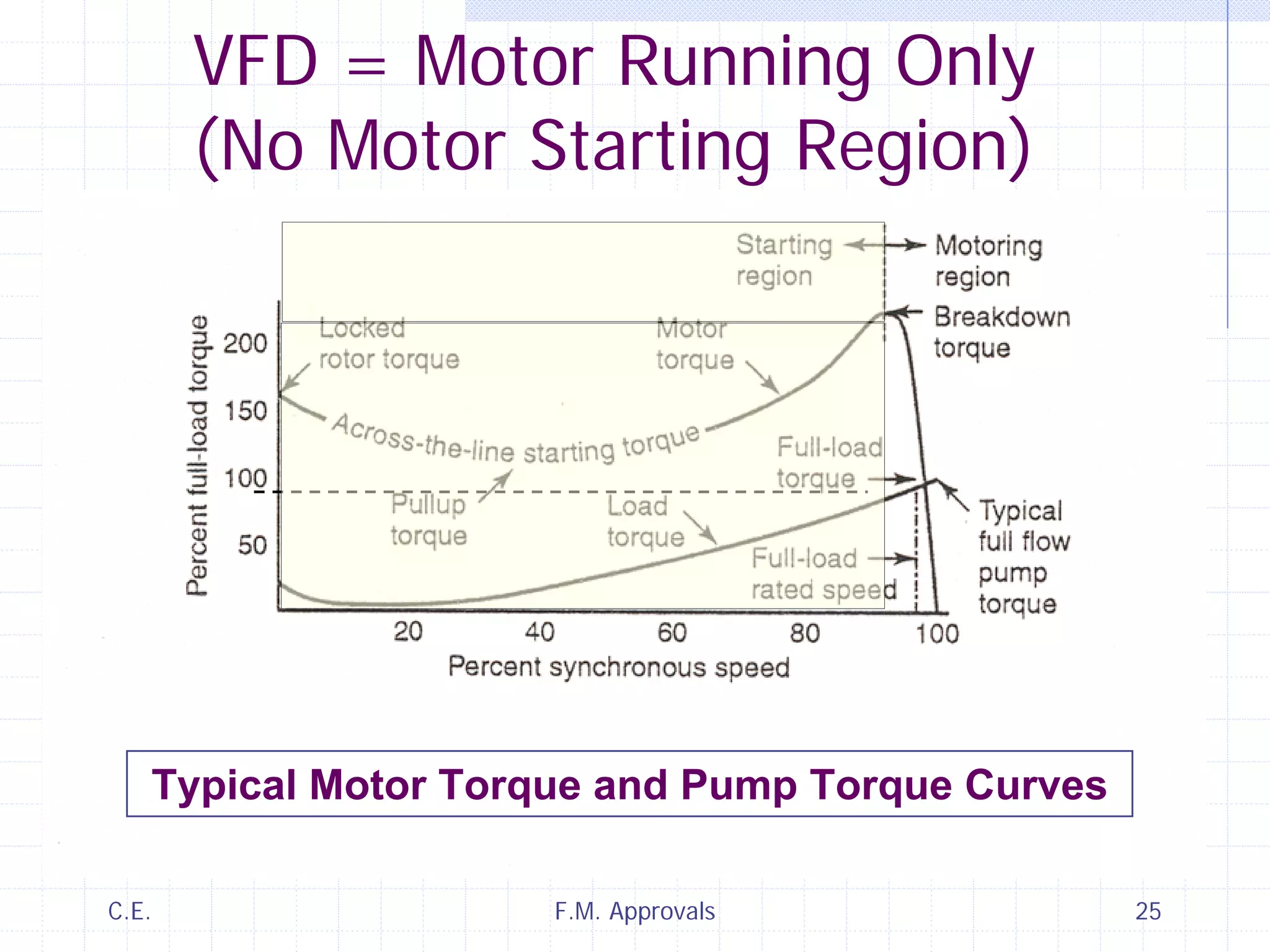
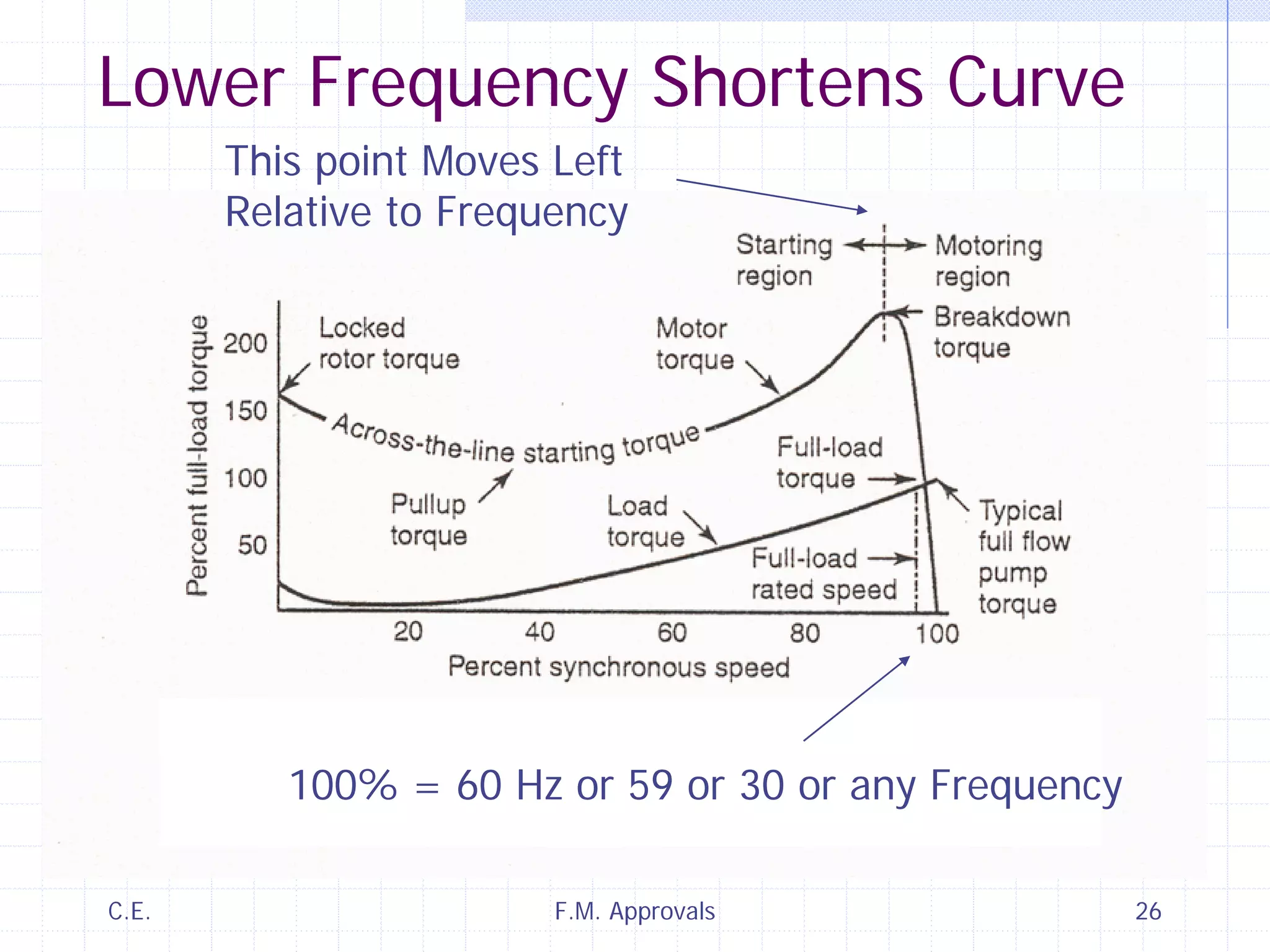
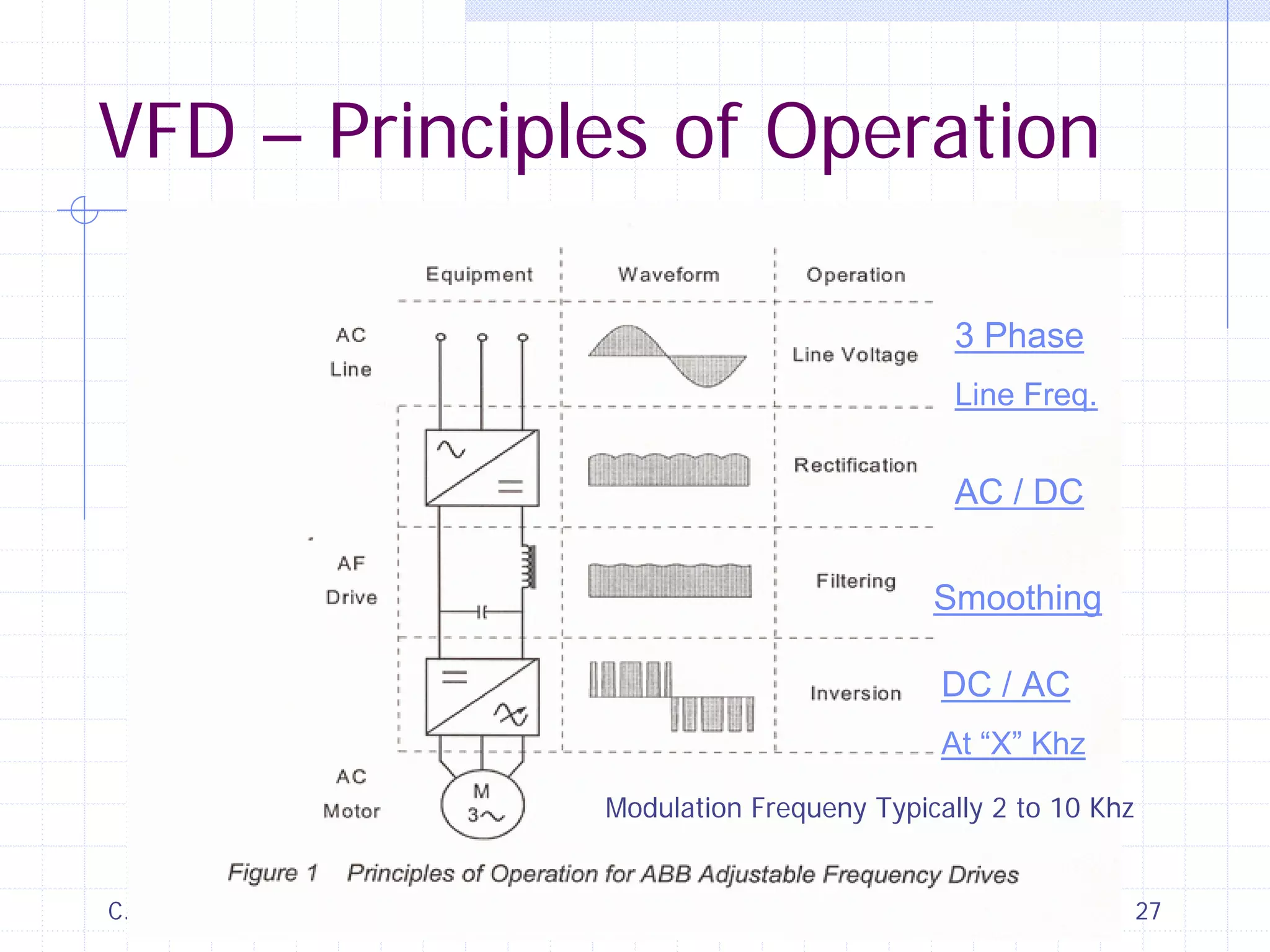
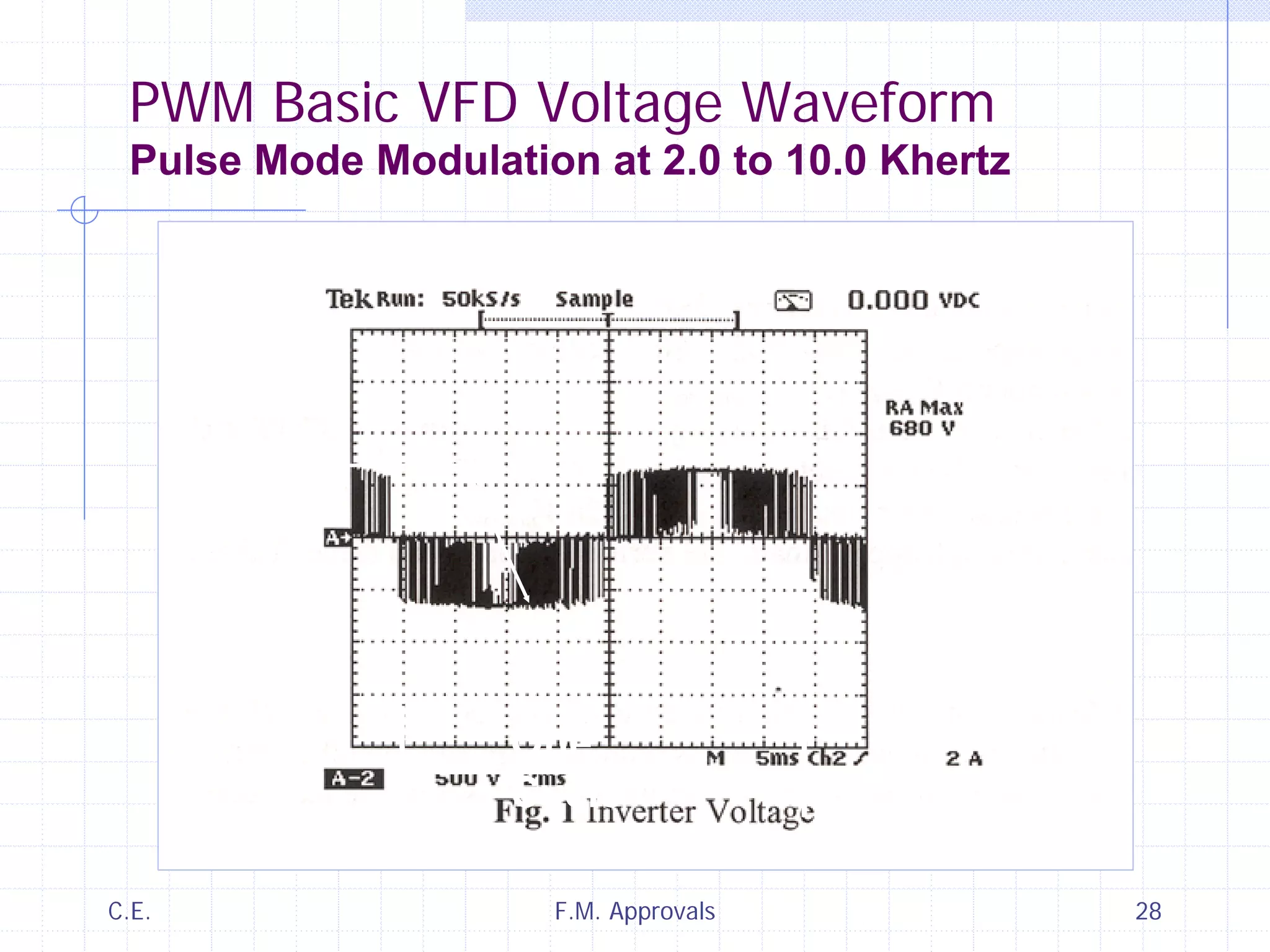
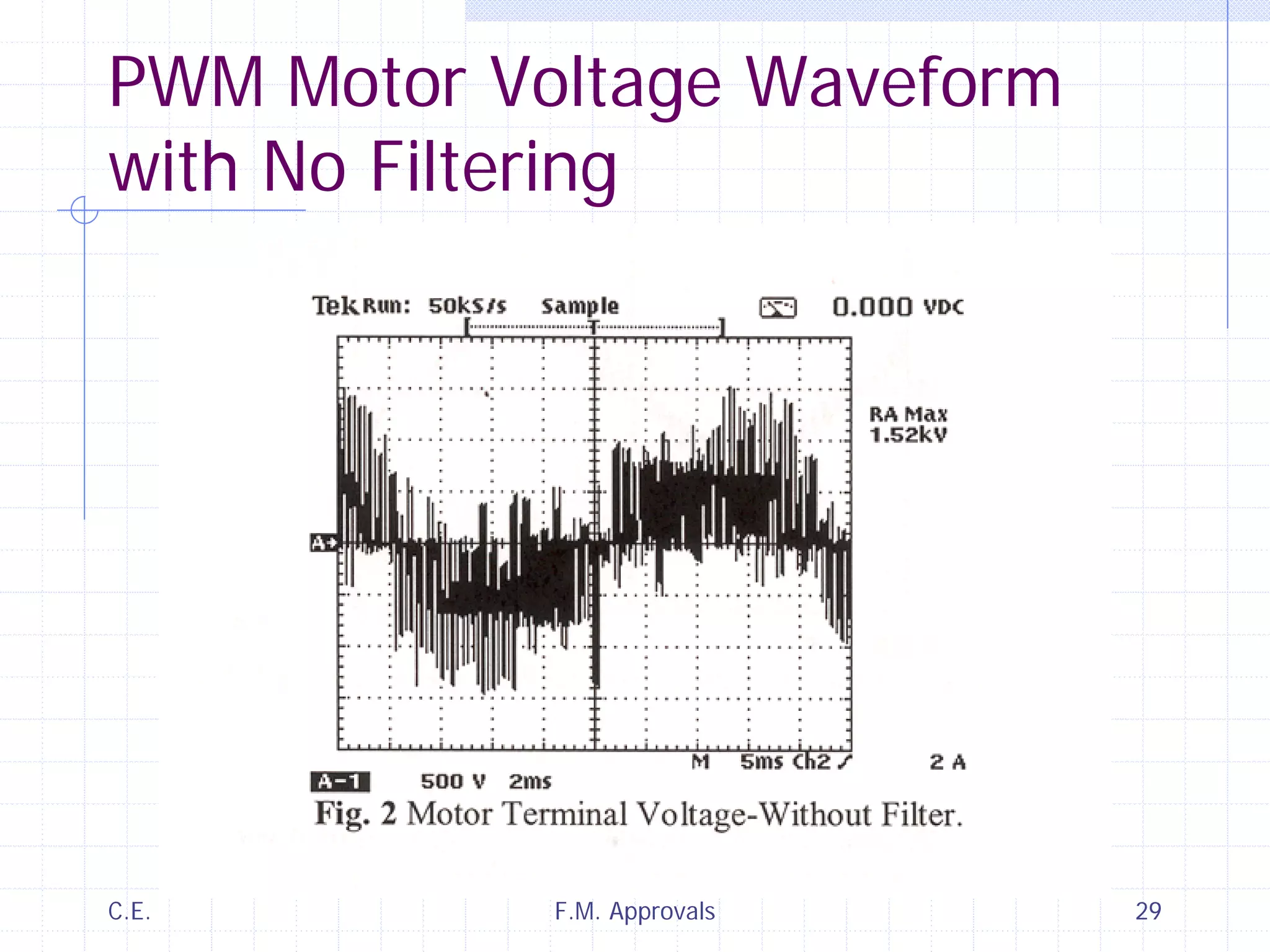
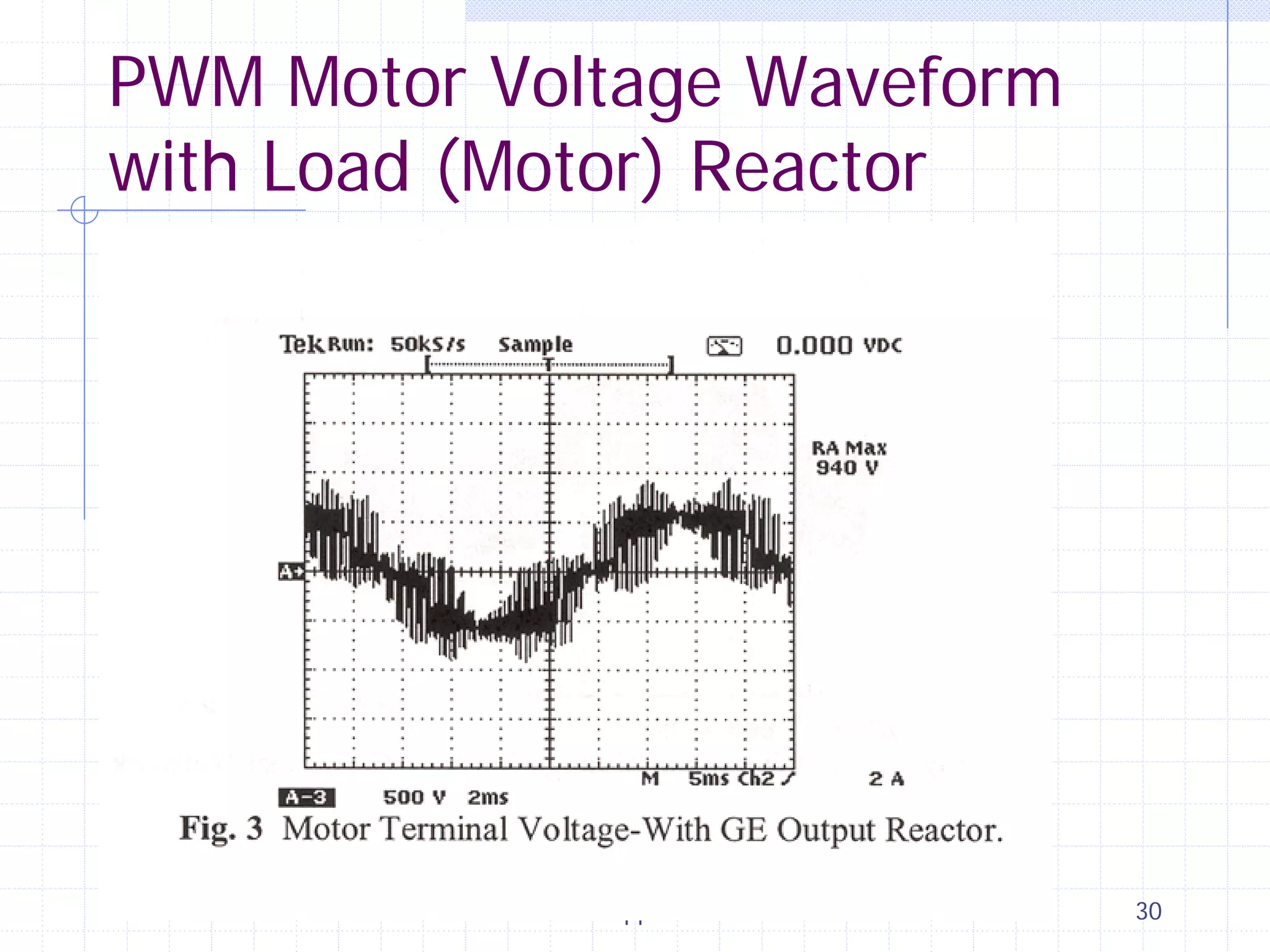
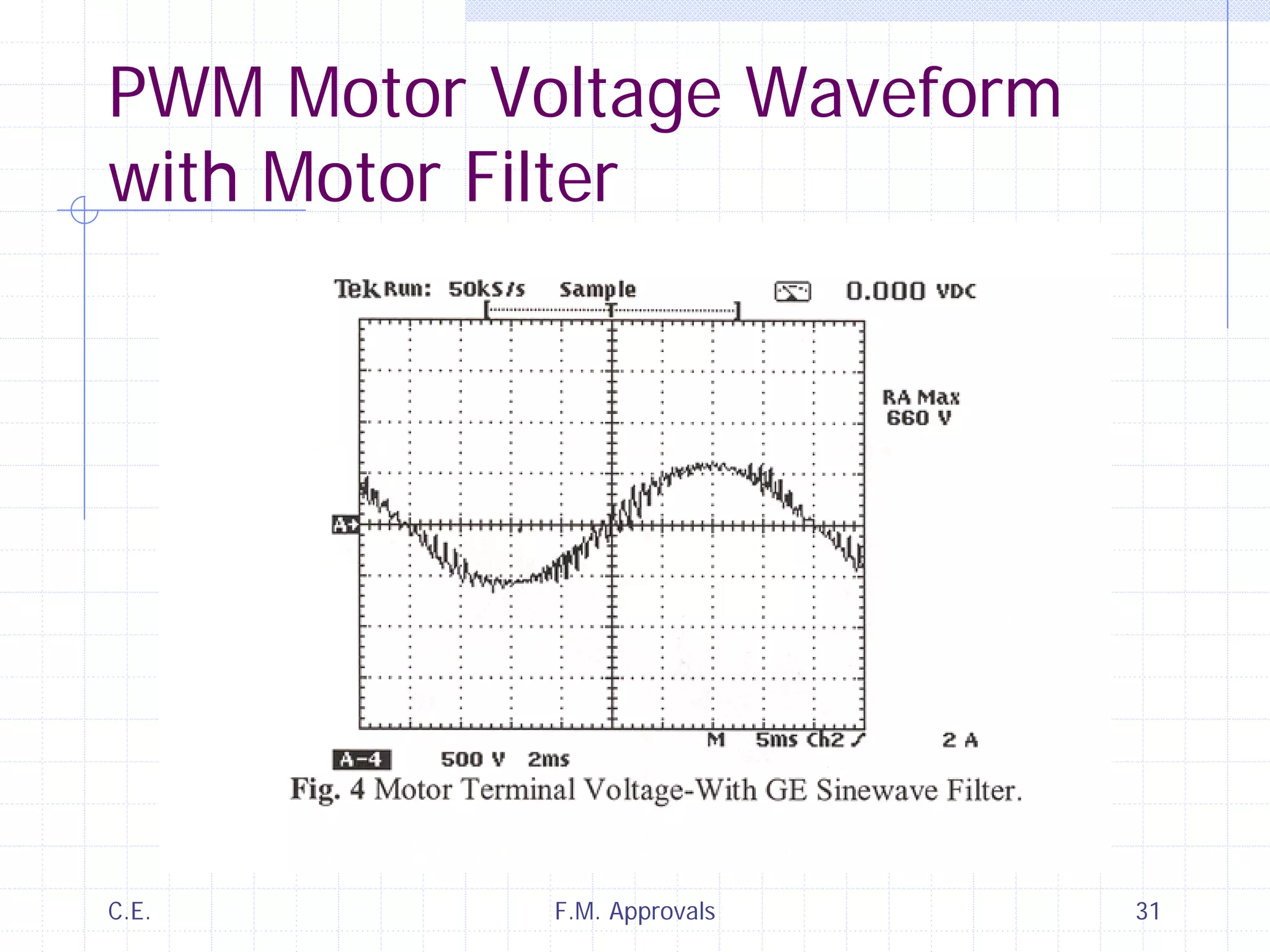
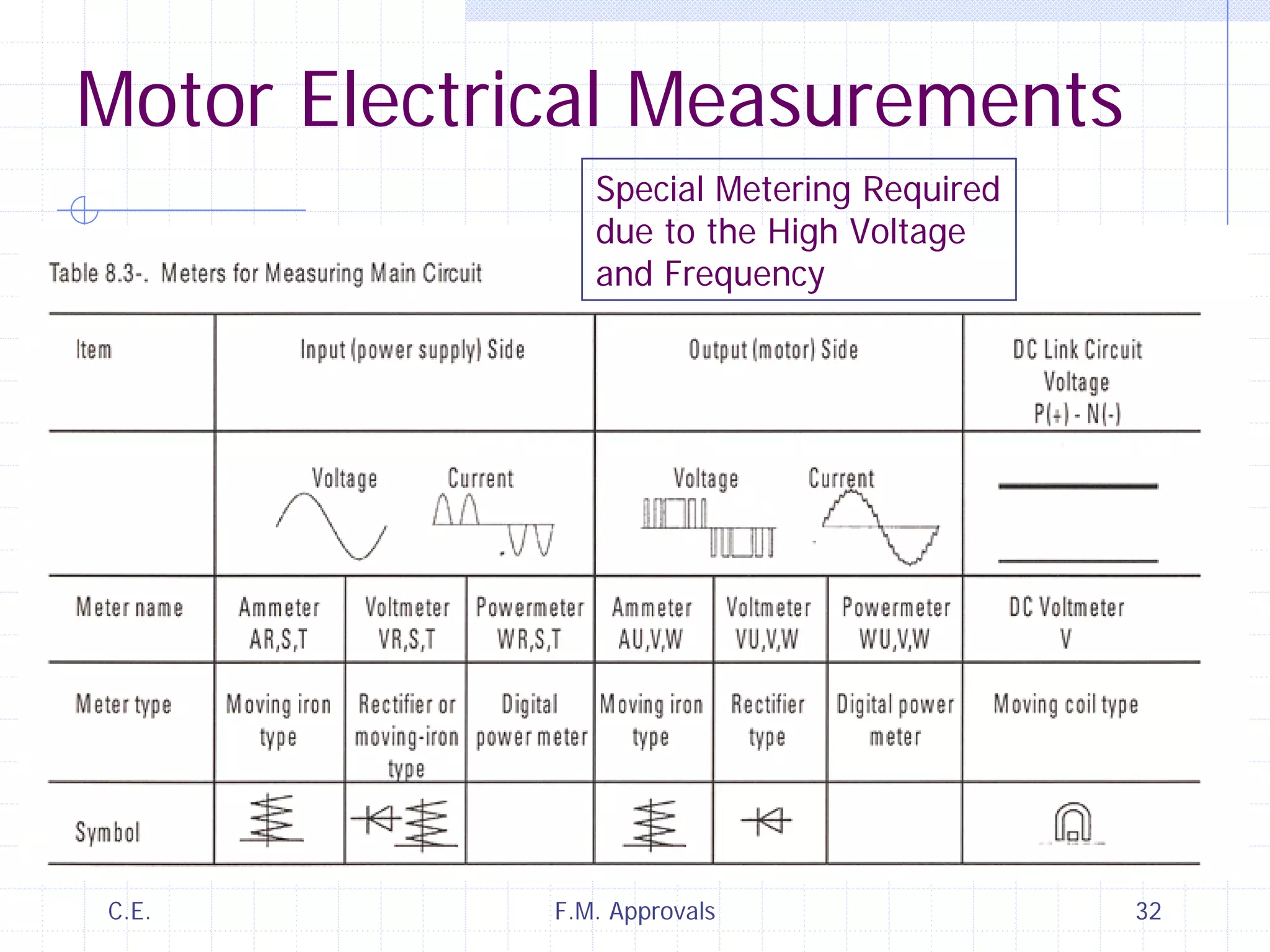
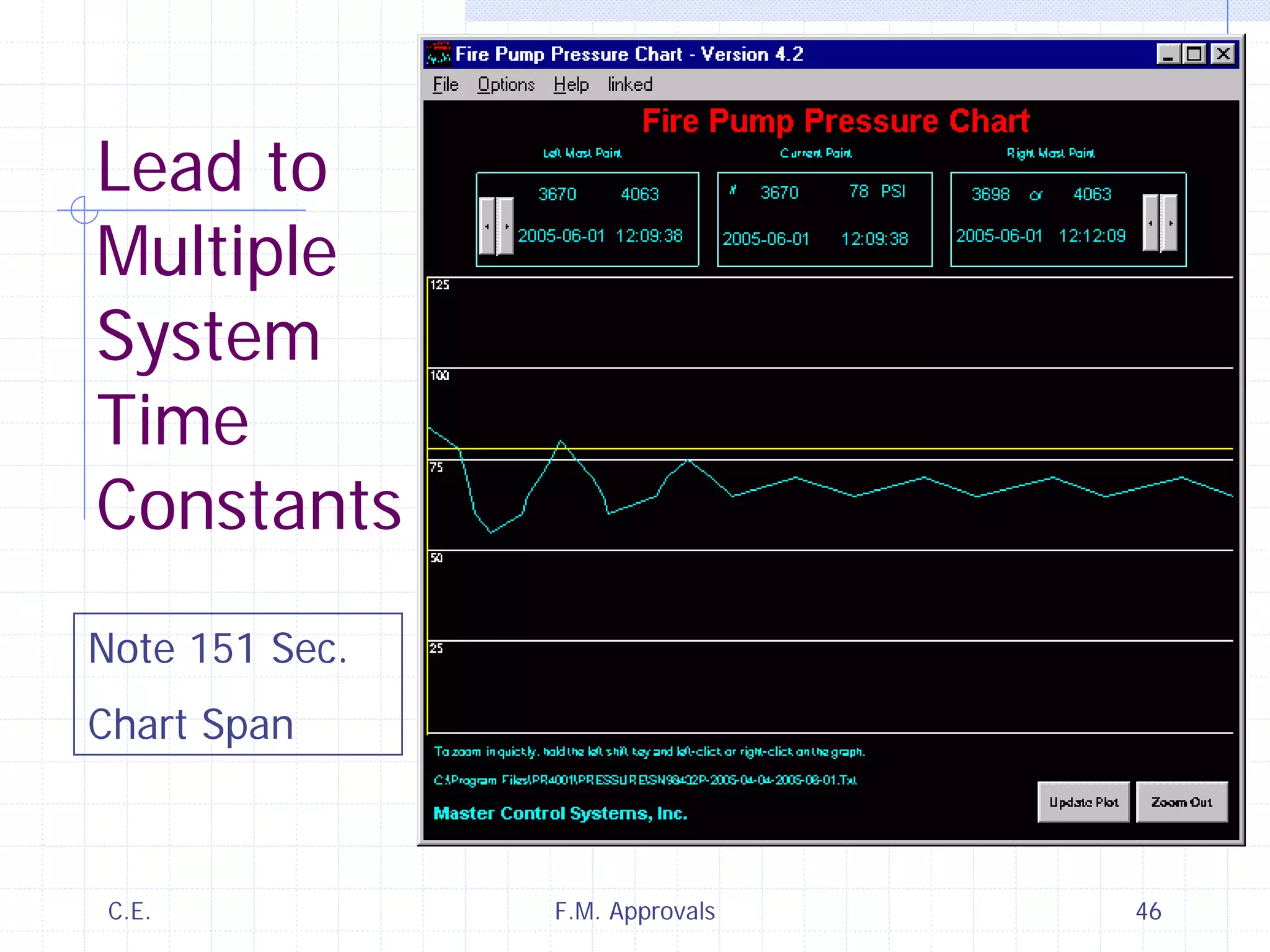
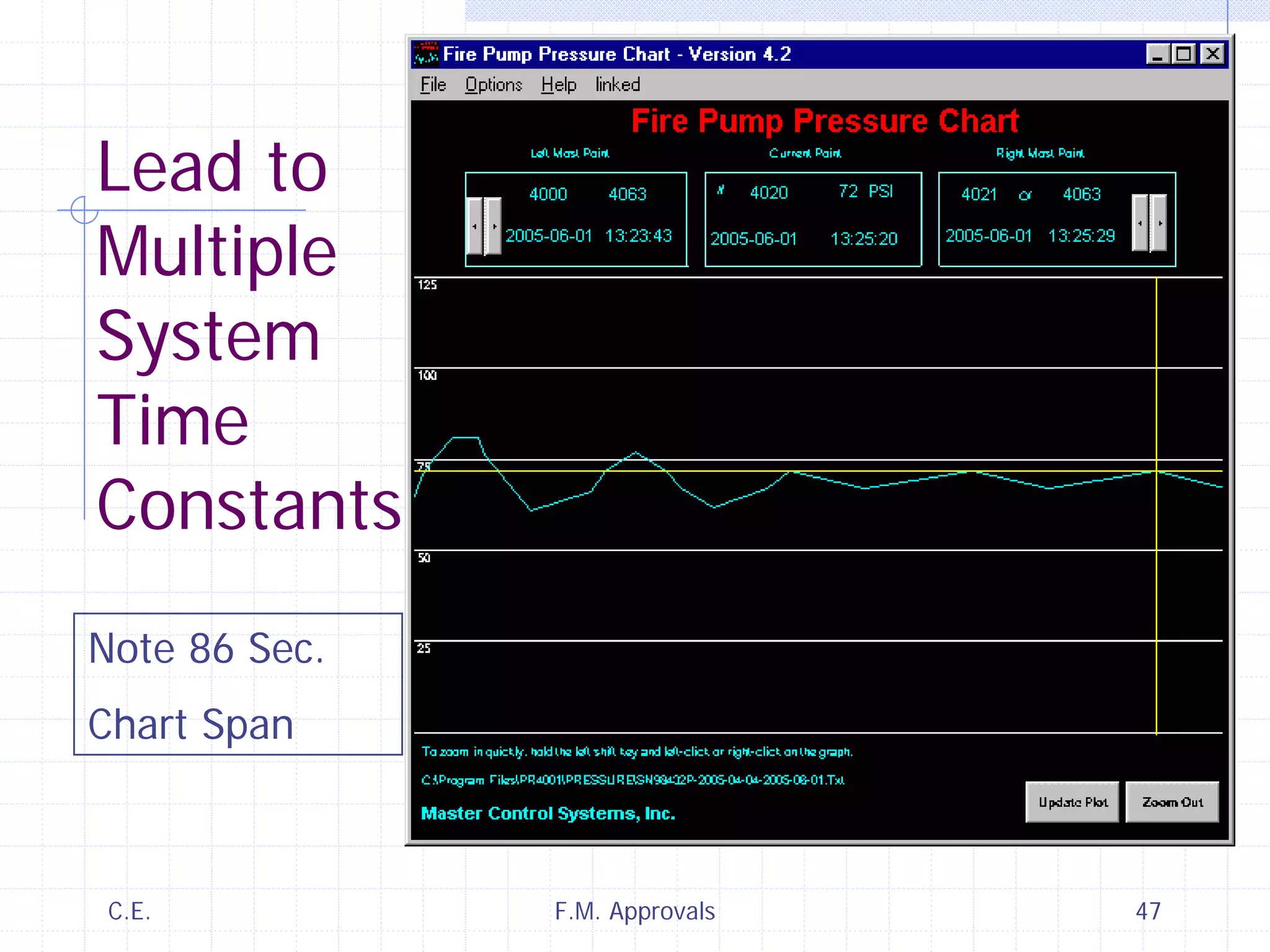
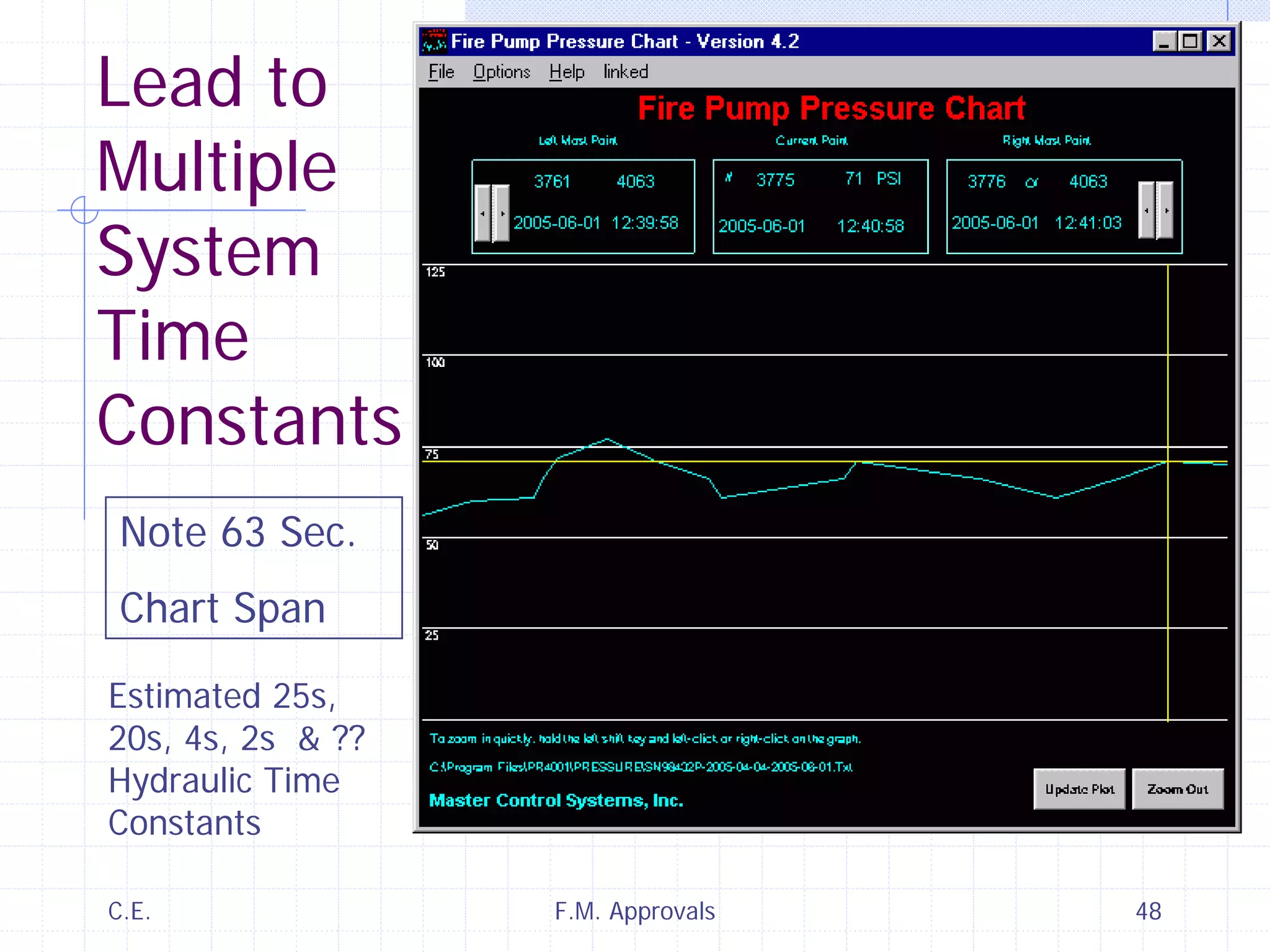
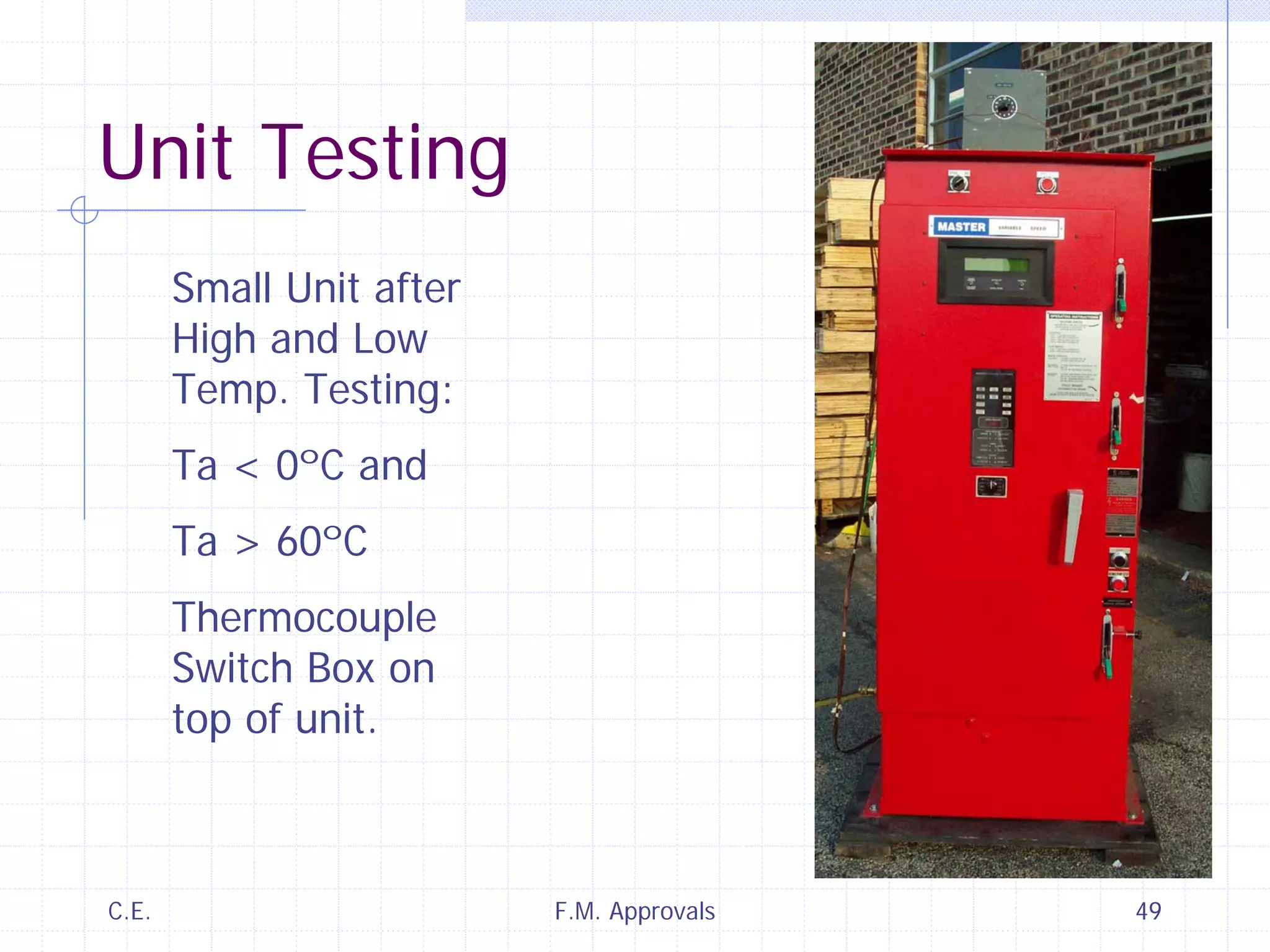
This document discusses variable speed fire pump controllers. It covers the components and operation of variable frequency drives (VFDs) and the requirements for a fire pump controller system using a VFD. Key points include an overview of VFD elements and operation, requirements for the controller system including isolation contactors and pressure monitoring, considerations for motor starting characteristics and coordination, and design factors such as cooling and pollution rating. Application-specific topics like hydraulic system tuning are also addressed.