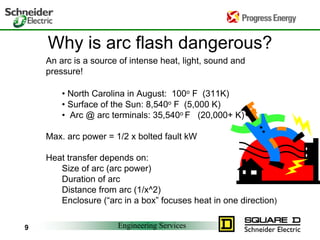
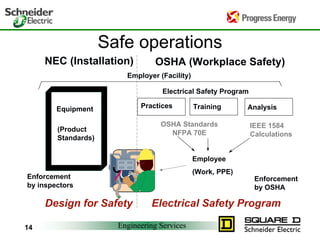
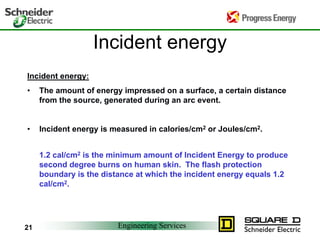
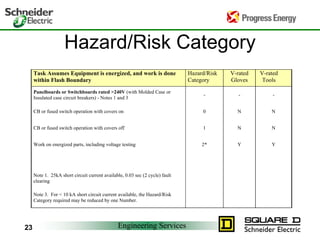
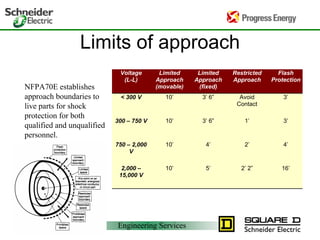
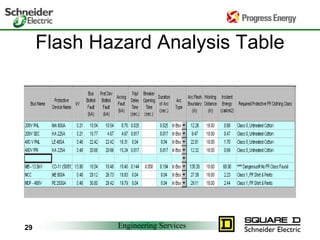
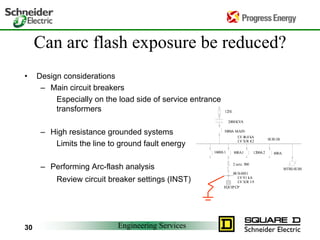
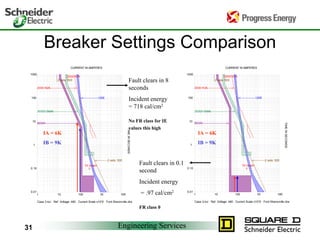
Five to 10 arc flash explosions occur daily in the US, often requiring specialized burn treatment. There are two types of faults that can cause arcs: bolted faults where current flows through a solid connection, and arcing faults where current arcs through ionized air. Arcing faults are more dangerous as the energy is released into the environment. Standards like NFPA 70E and OSHA requirements aim to protect workers by enforcing safety practices like arc flash analyses and requiring personal protective equipment suitable for the estimated incident energy levels. Proper maintenance and use of protective equipment can reduce arc flash exposure hazards.