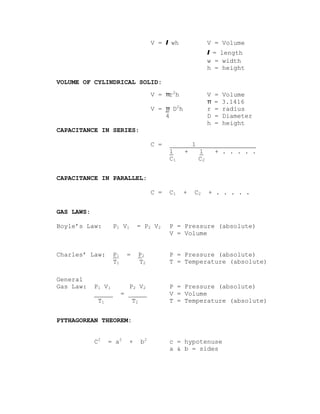
The document contains formulas and information related to HVAC systems. It defines key terms like tons of refrigeration, horsepower, voltage, amperage, resistance, watts, capacitance, gas laws, and geometric formulas. It also includes formulas for calculating areas, volumes, BTUs, airflow, efficiency, and sizing components like ducts, grilles, burners, and nozzles.