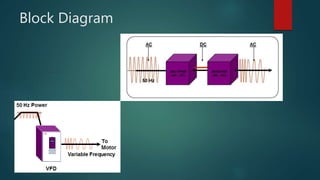
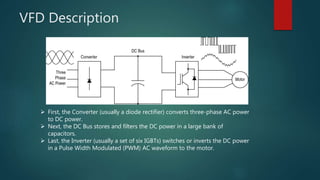
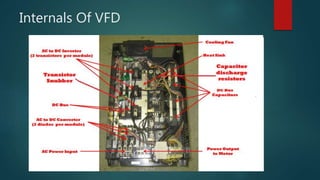
A variable frequency drive (VFD) controls the speed and torque of AC motors by varying the motor input frequency and voltage. It provides benefits like energy savings, better process control, adjustable speed, power factor correction, and overload protection. A VFD converts AC power to DC, stores it in capacitors, and uses pulse width modulation to invert the DC back to a variable frequency AC output to the motor. VFDs feature line reactors to reduce harmonics and are used widely in applications like fans, pumps, textile machinery and water supply to provide significant energy savings over fixed speed drives.