- Fire pumps are centrifugal pumps selected to operate between 90-140% of rated capacity and less than 150% to avoid overpressure.
- Pump rooms require 1-hour fire rated separation, emergency lighting, ventilation, and drainage.
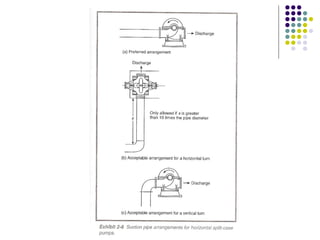
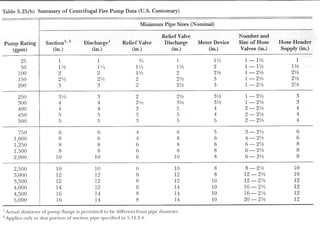
- Suction and discharge piping must be sized properly and have the correct fittings like gauges, valves, and relief valves. Jockey pumps maintain system pressure.
- Electric and diesel fire pump controllers prioritize system operation over equipment protection to ensure reliable fire suppression.