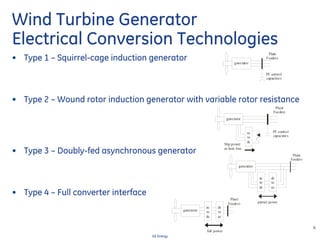
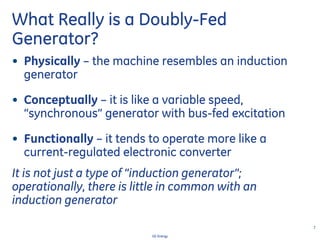
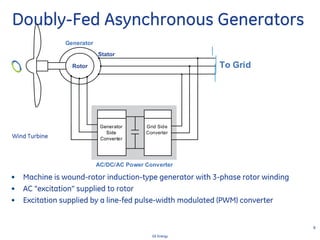
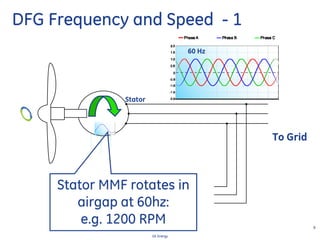
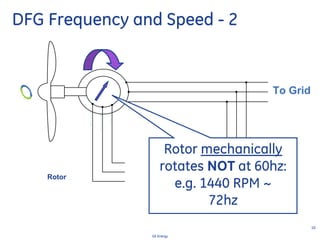
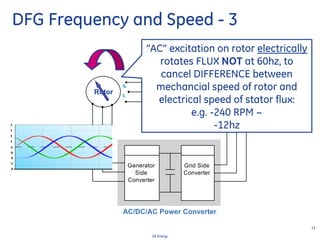
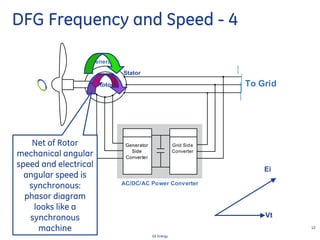
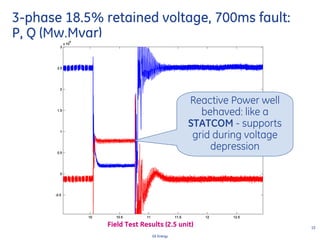
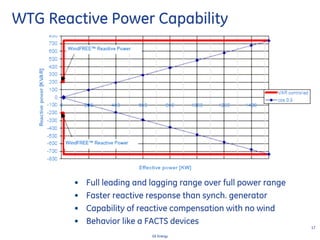
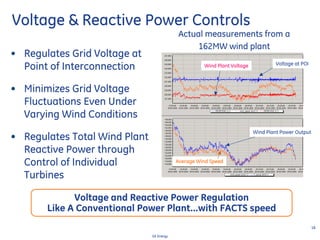
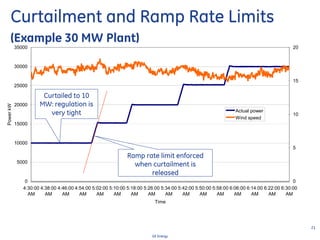
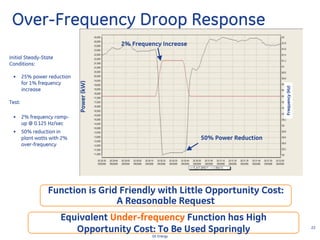
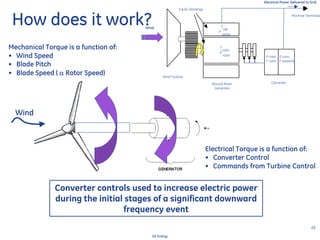
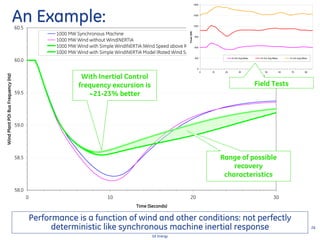
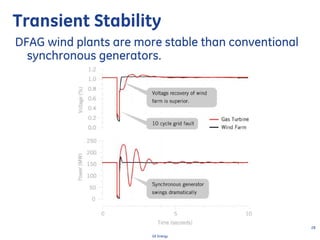
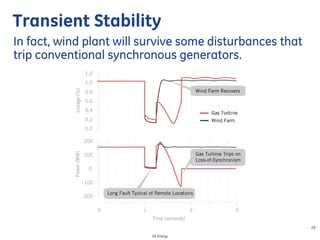
This document discusses how wind turbines can provide grid support functions similar to Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) devices through advanced controls of the power electronics and generator systems. It describes how doubly-fed induction generator wind turbines can regulate voltage and reactive power at the point of interconnection, provide inertial response during frequency disturbances, limit ramp rates during changes in wind speed, and improve transient stability compared to synchronous generators. The document argues that these grid support functions allow high levels of wind power to be integrated onto the grid in a reliable manner without compromising system performance.