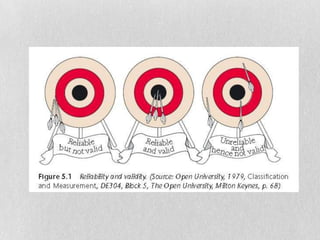
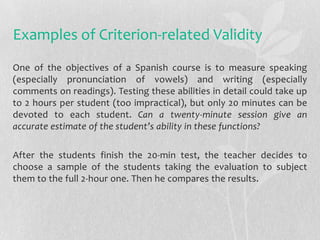
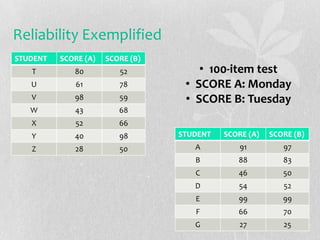
This document discusses validity, reliability, and washback in language testing. Validity refers to a test measuring what it intends to measure, which includes content validity (testing relevant skills and concepts) and criterion-related validity (how test results agree with other assessment results). Reliability means a test is repeatable, which can be measured through reliability coefficients. Washback refers to how a test influences teaching and learning, with the goal of achieving positive washback that encourages effective preparation. Ensuring validity, reliability, and beneficial washback requires careful test construction and use of techniques like setting test specifications, direct testing of objectives, and providing clear scoring criteria.