Embed presentation
Downloaded 527 times









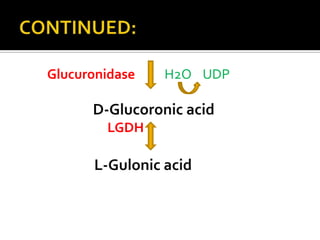

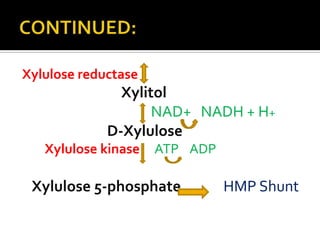




This document summarizes the uronic acid pathway, an alternative pathway for glucose oxidation that occurs in the cytoplasm of liver and adipose tissue. The major function of this pathway is to produce D-glucuronic acid, which is required for detoxification of foreign chemicals and synthesis of mucopolysaccharides. The pathway proceeds through a series of enzymatic steps beginning with glucose and ultimately producing D-glucuronic acid. Regulation of the pathway involves administration of certain drugs that increase production of uronic acid and ascorbic acid. Clinical importance includes essential pentosuria, an inborn error of metabolism caused by deficiency of the enzyme xylitol reductase.















