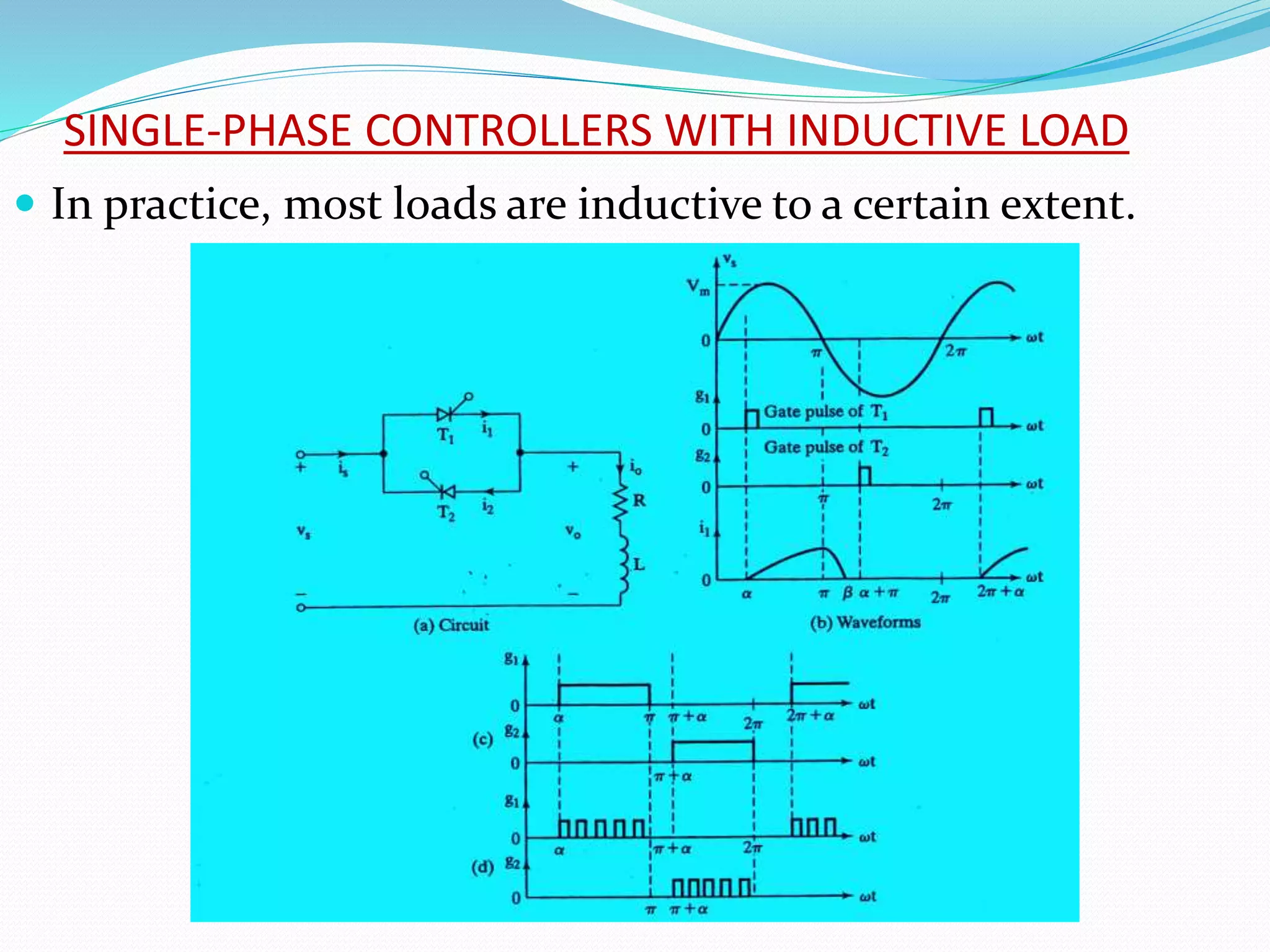
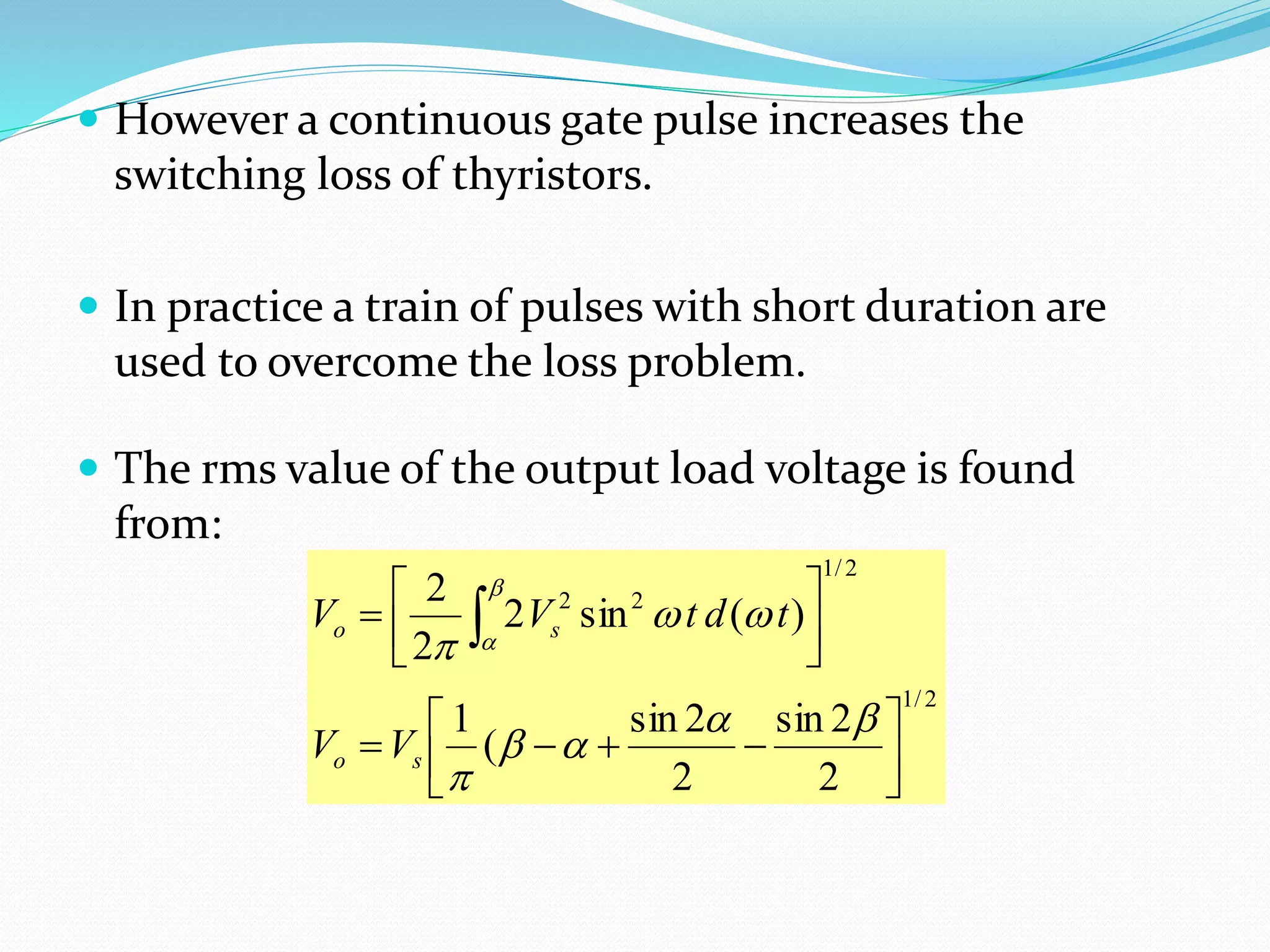
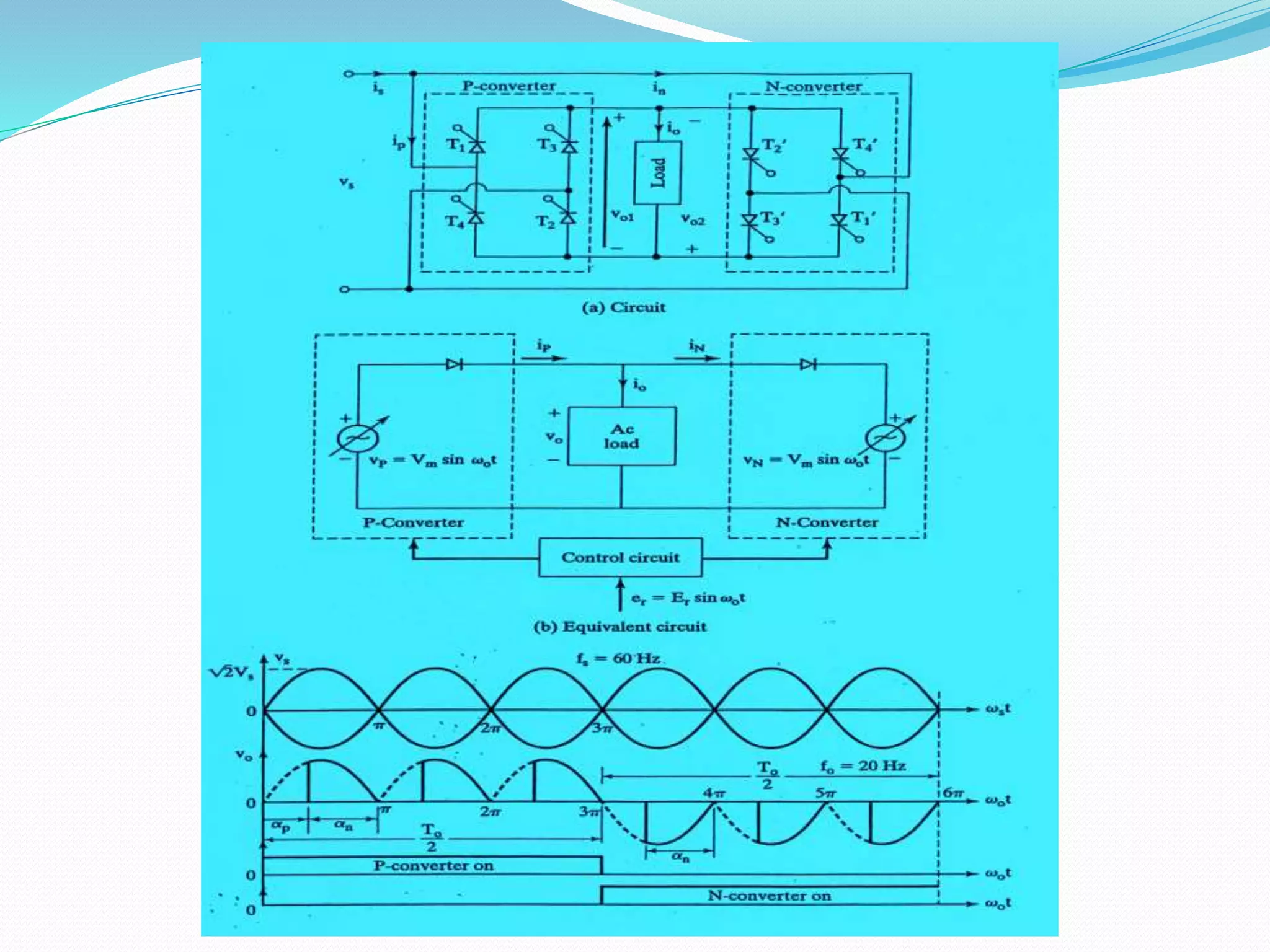
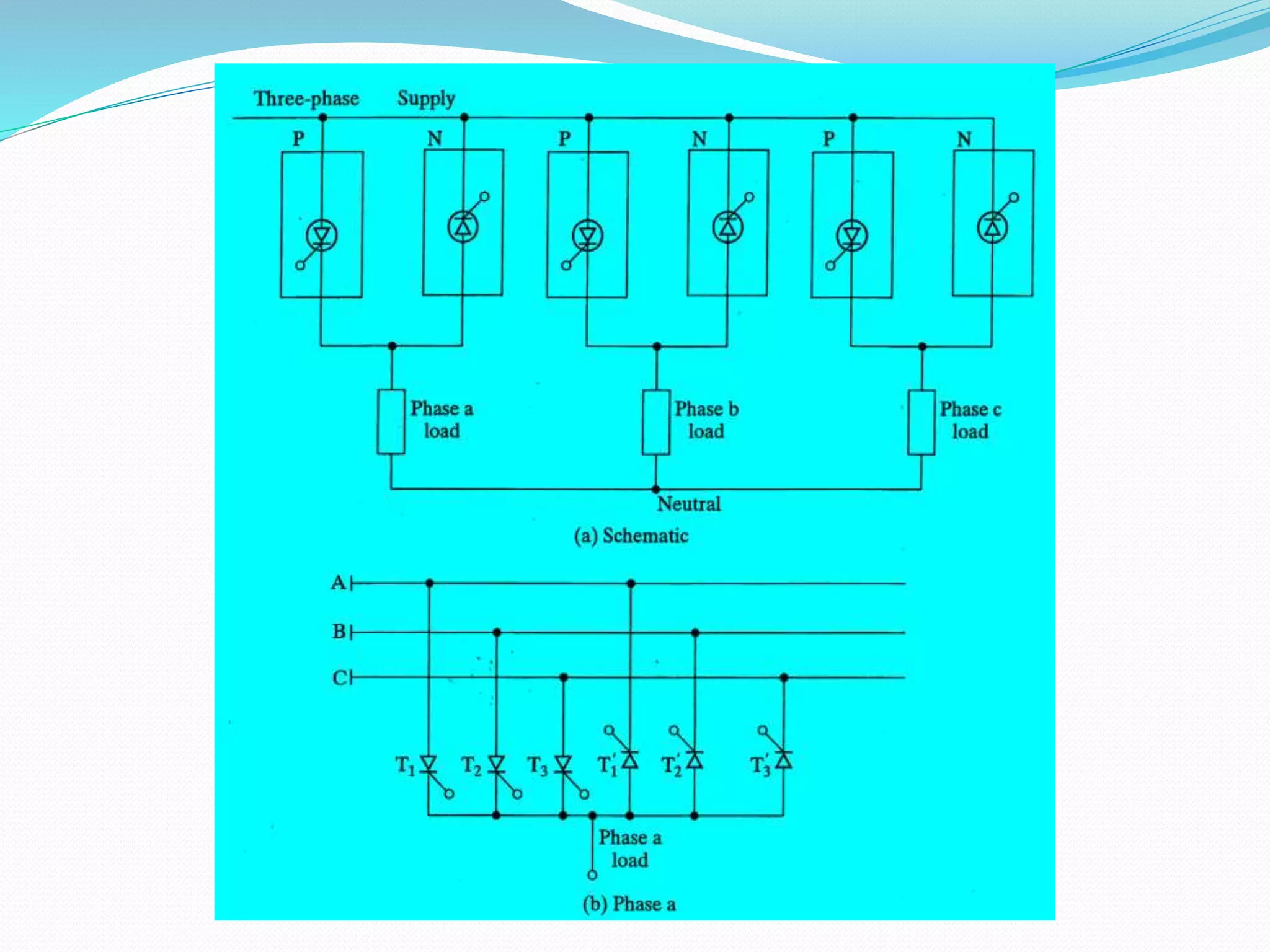
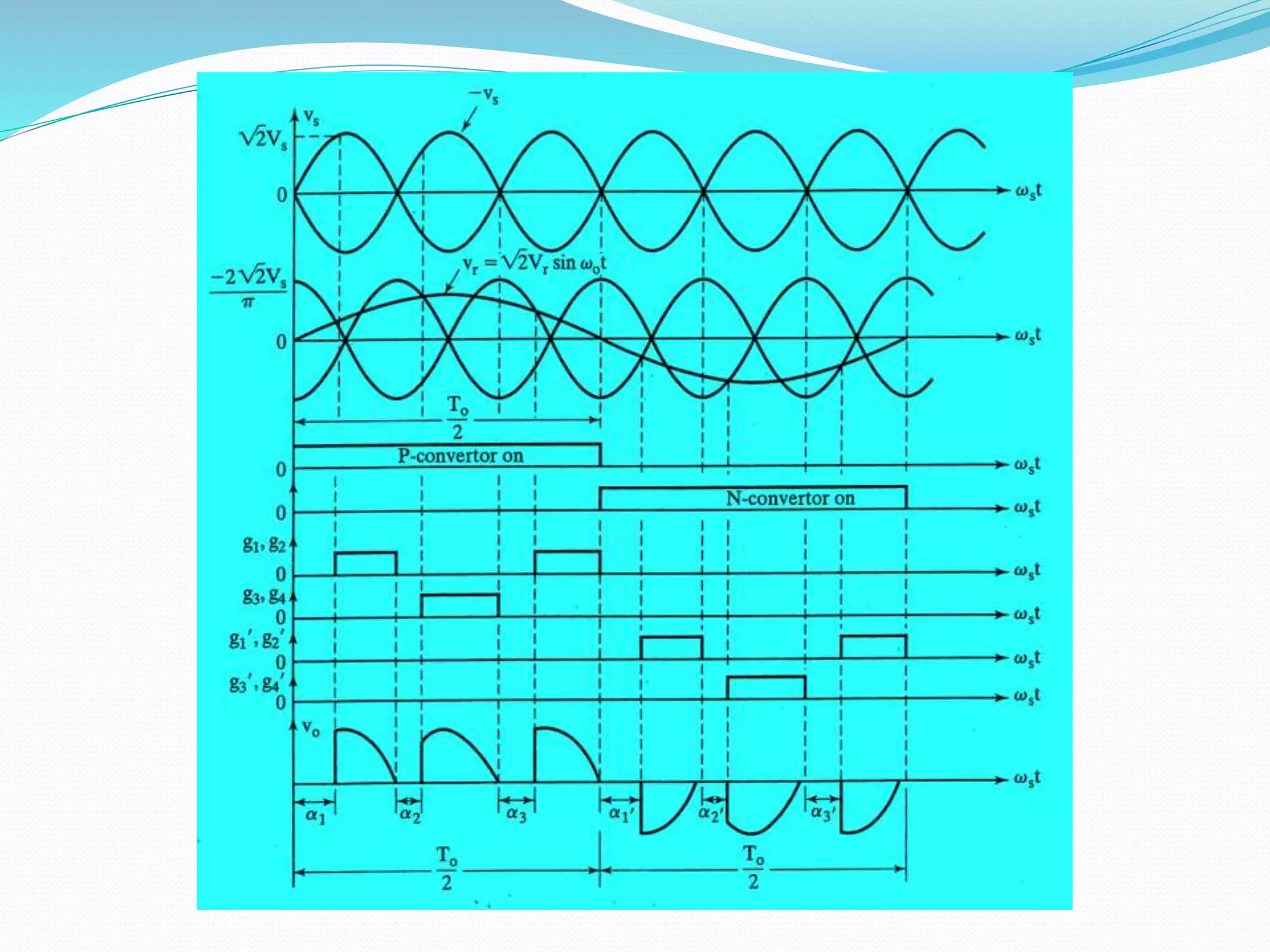
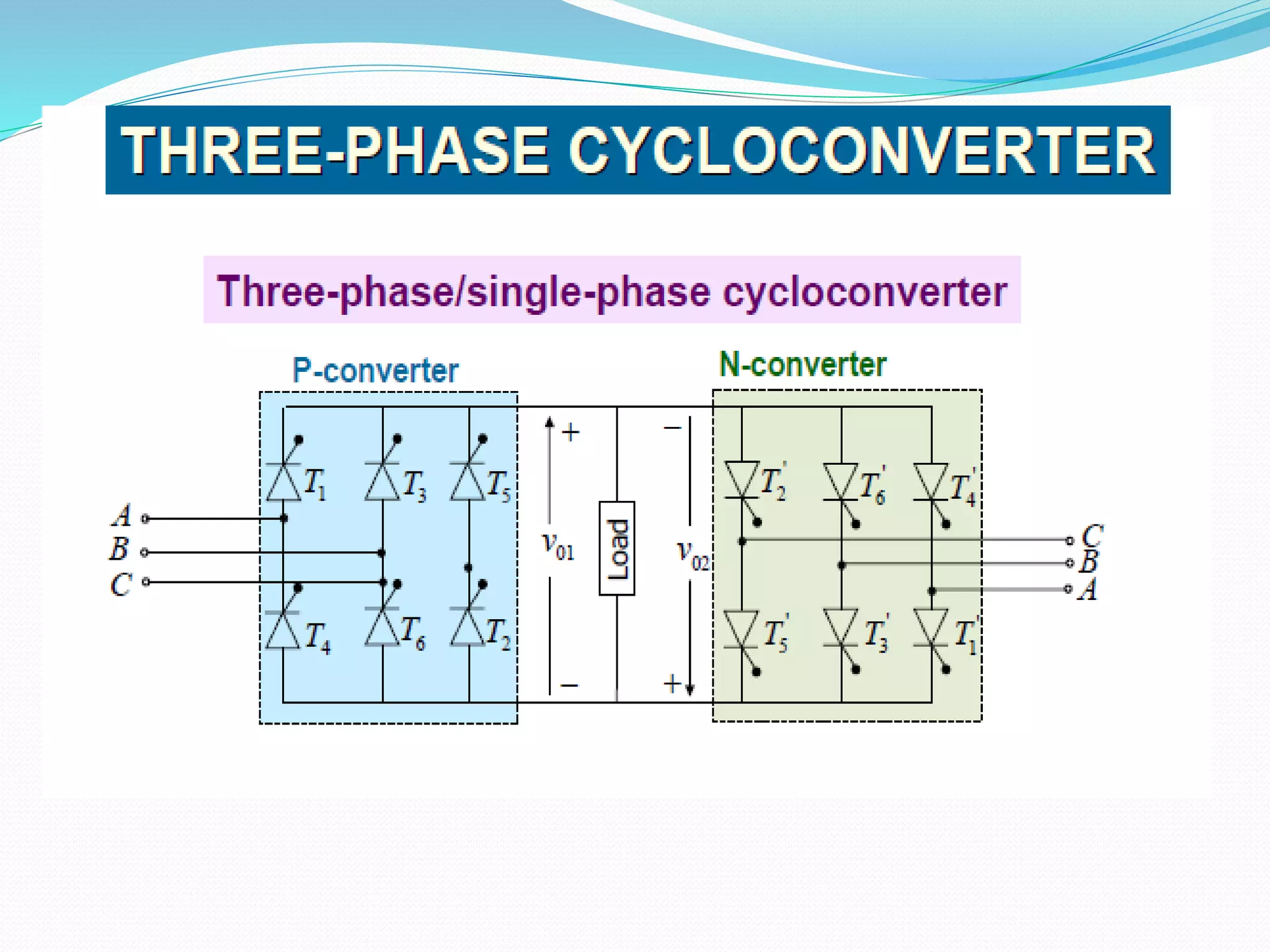
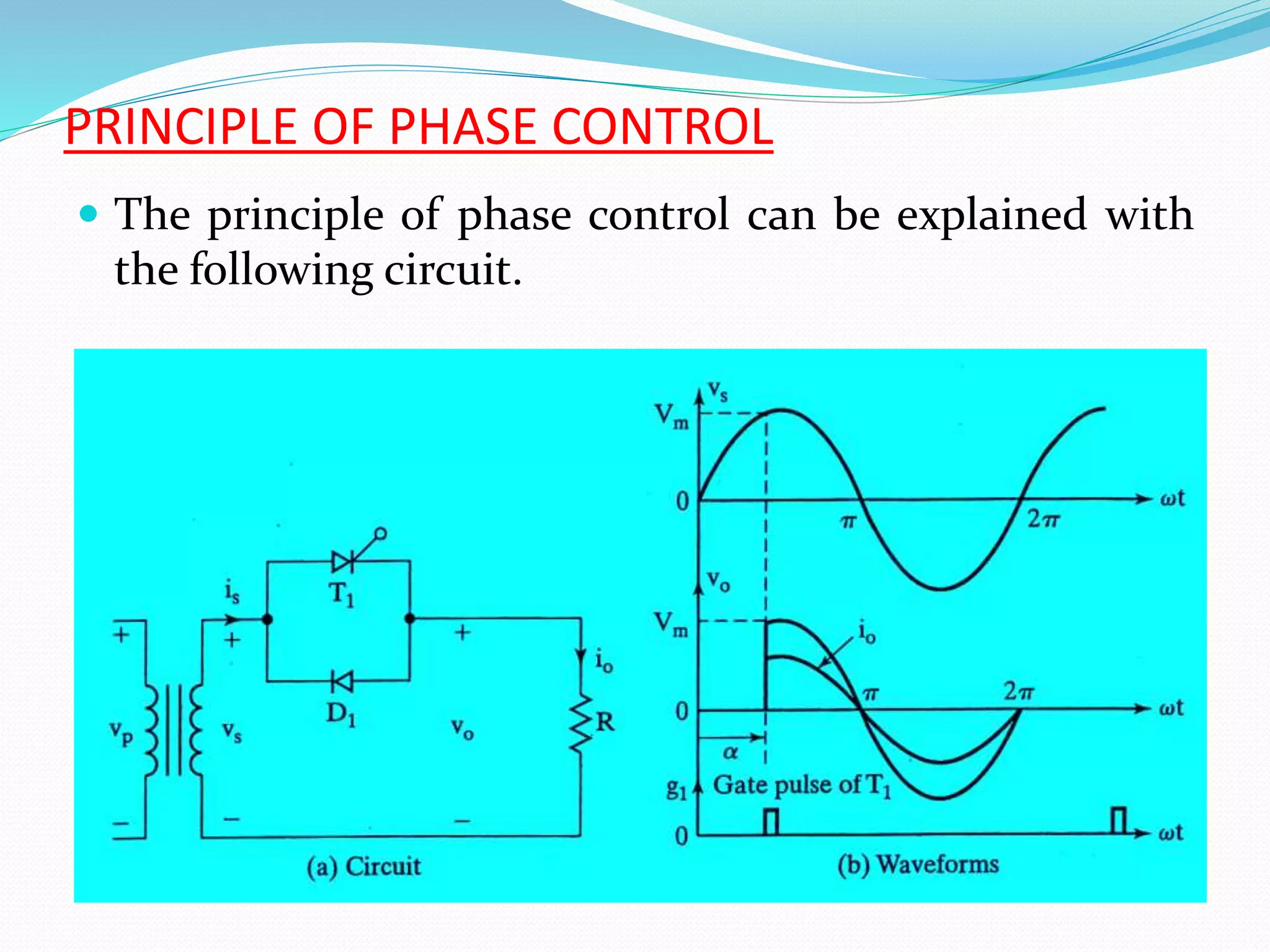
This document discusses different types of AC voltage controllers. It begins by introducing AC voltage controllers and how they can control power flow into a load by varying the RMS value of the load voltage using thyristors. It then describes the main types of AC voltage controllers classified by input supply type and control method. Applications such as lighting, heating and motor speed control are also outlined. The document proceeds to explain the principles and techniques of on-off control and phase control. Circuit diagrams are provided to illustrate single phase and three phase controller configurations. The document concludes by briefly discussing cycloconverters which can provide a variable output voltage and frequency.











![ The rms value of the output voltage is :
The average value of the output voltage is:
2/1
2/122
2
22
)]
2
2sin
2(
2
1
[
)]}(sin2)(sin2[
2
1
{
so
sso
VV
tdtVtdtVV
)1(cos
2
2
)](sin2)(sin2[
2
1 2
s
o
ssdc
V
V
tdtVtdtVV](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-5-190801102319/75/Unit-5-AC-AC-Cycloconverter-13-2048.jpg)