This document provides an overview of matrix algebra concepts including:
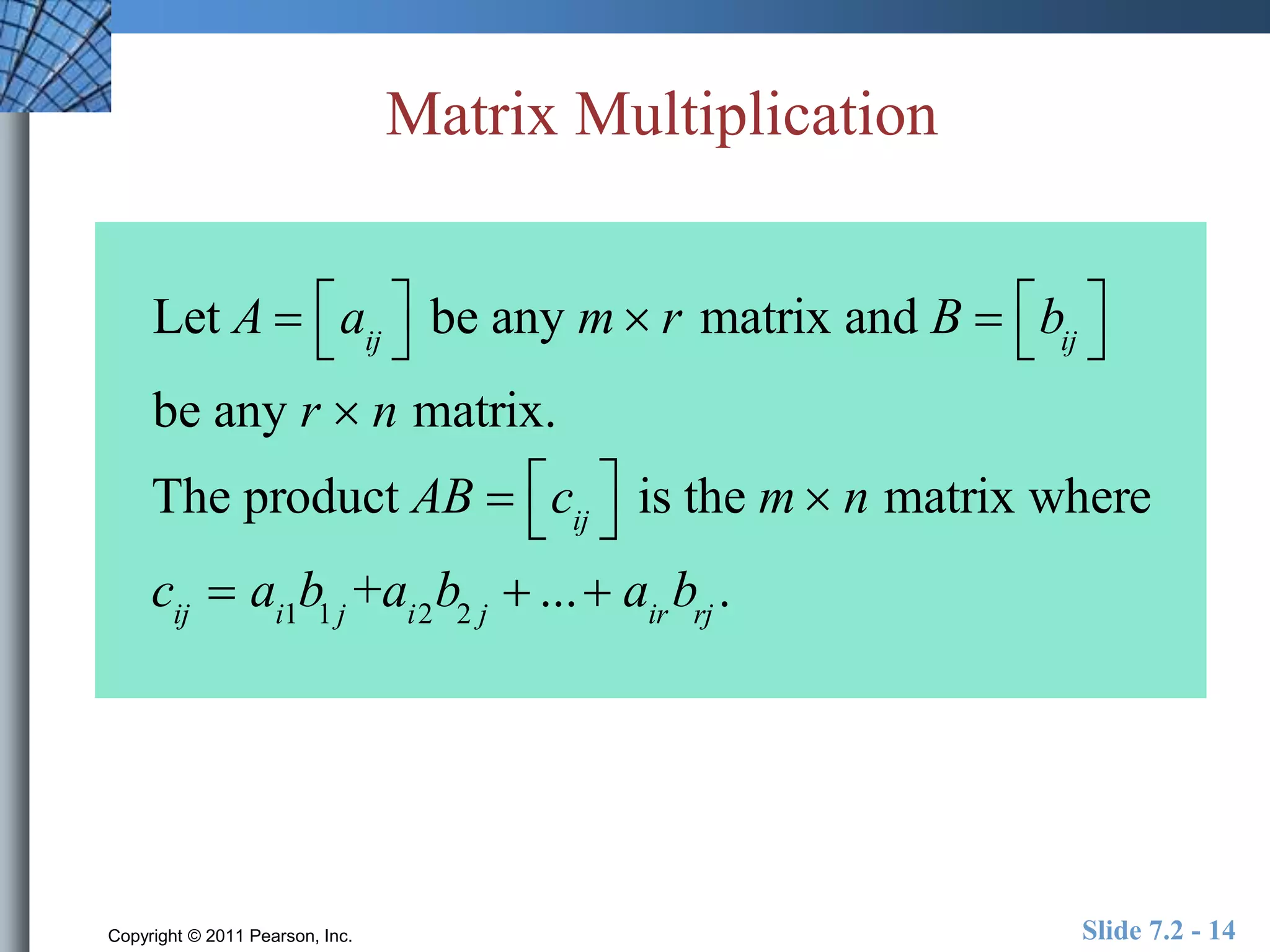
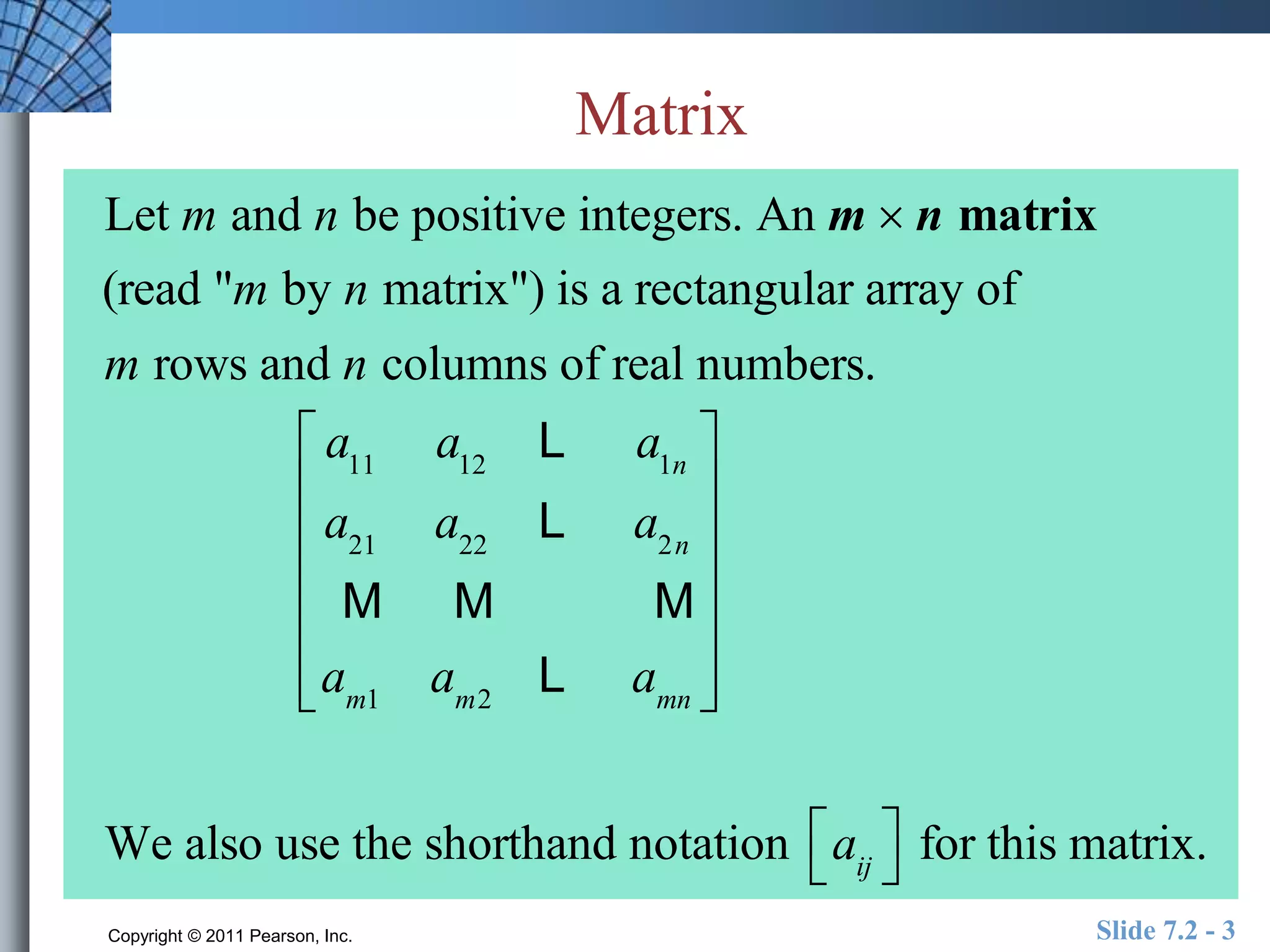
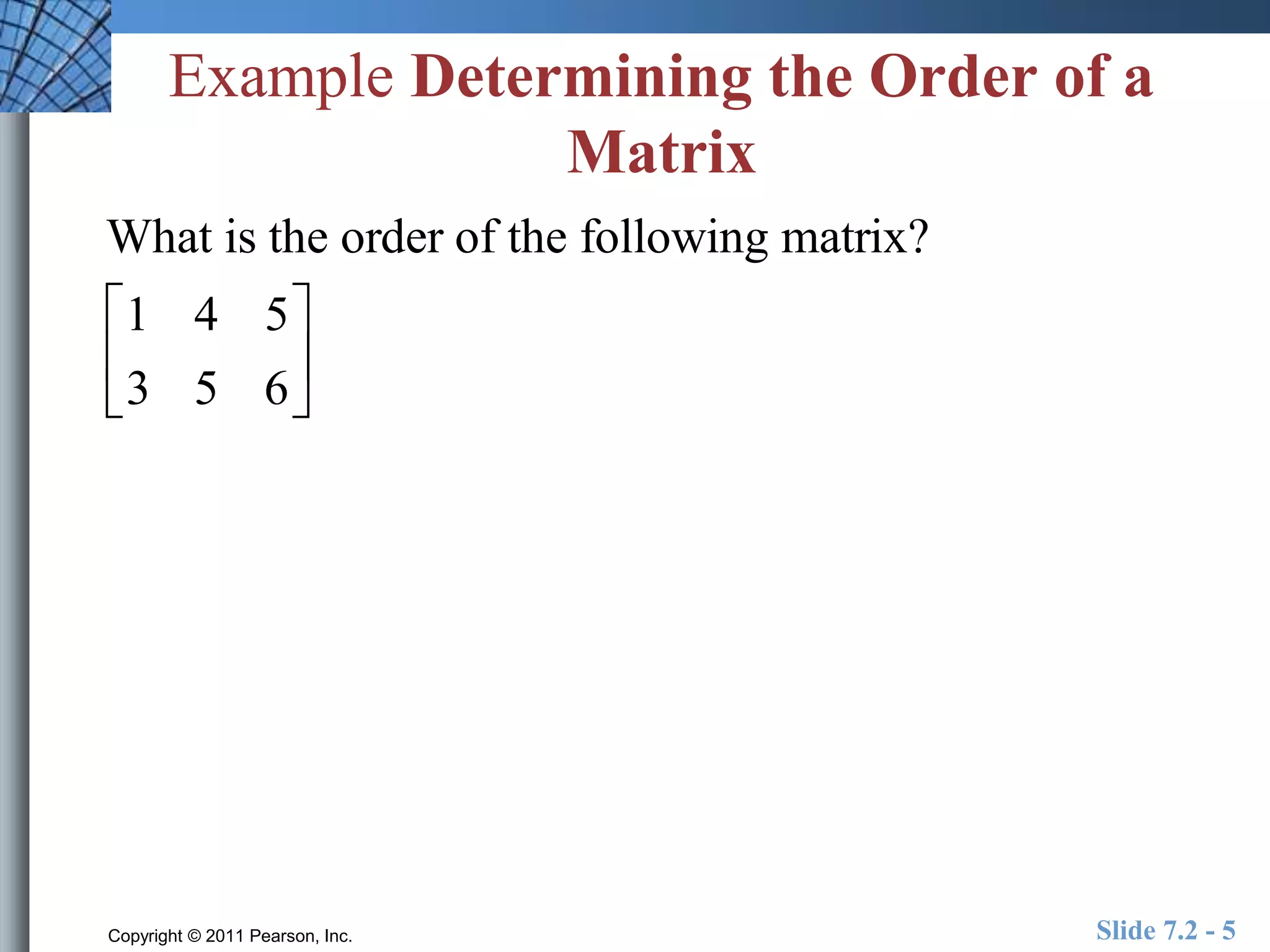
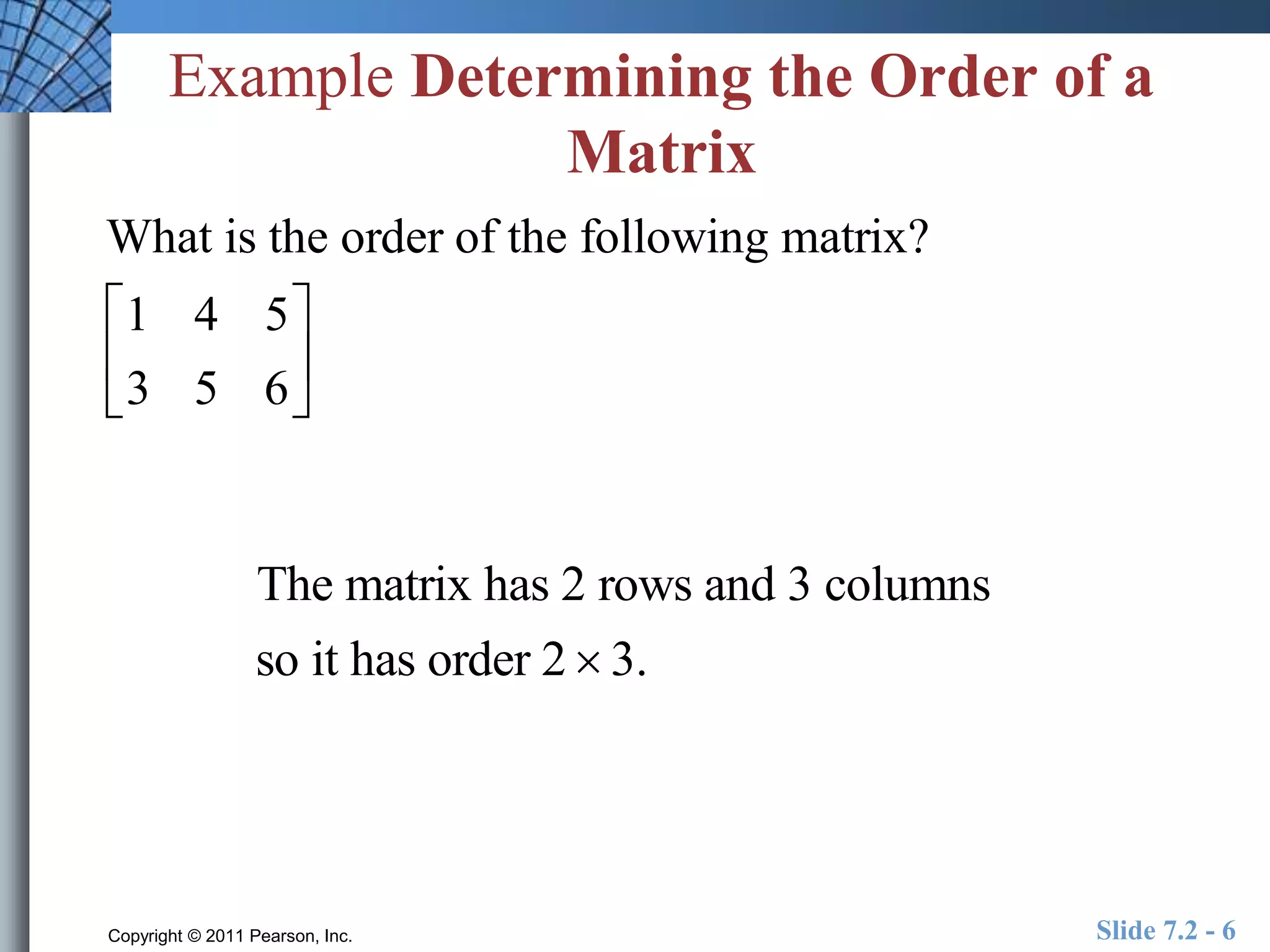
- Matrices are rectangular arrays of numbers with rows and columns.
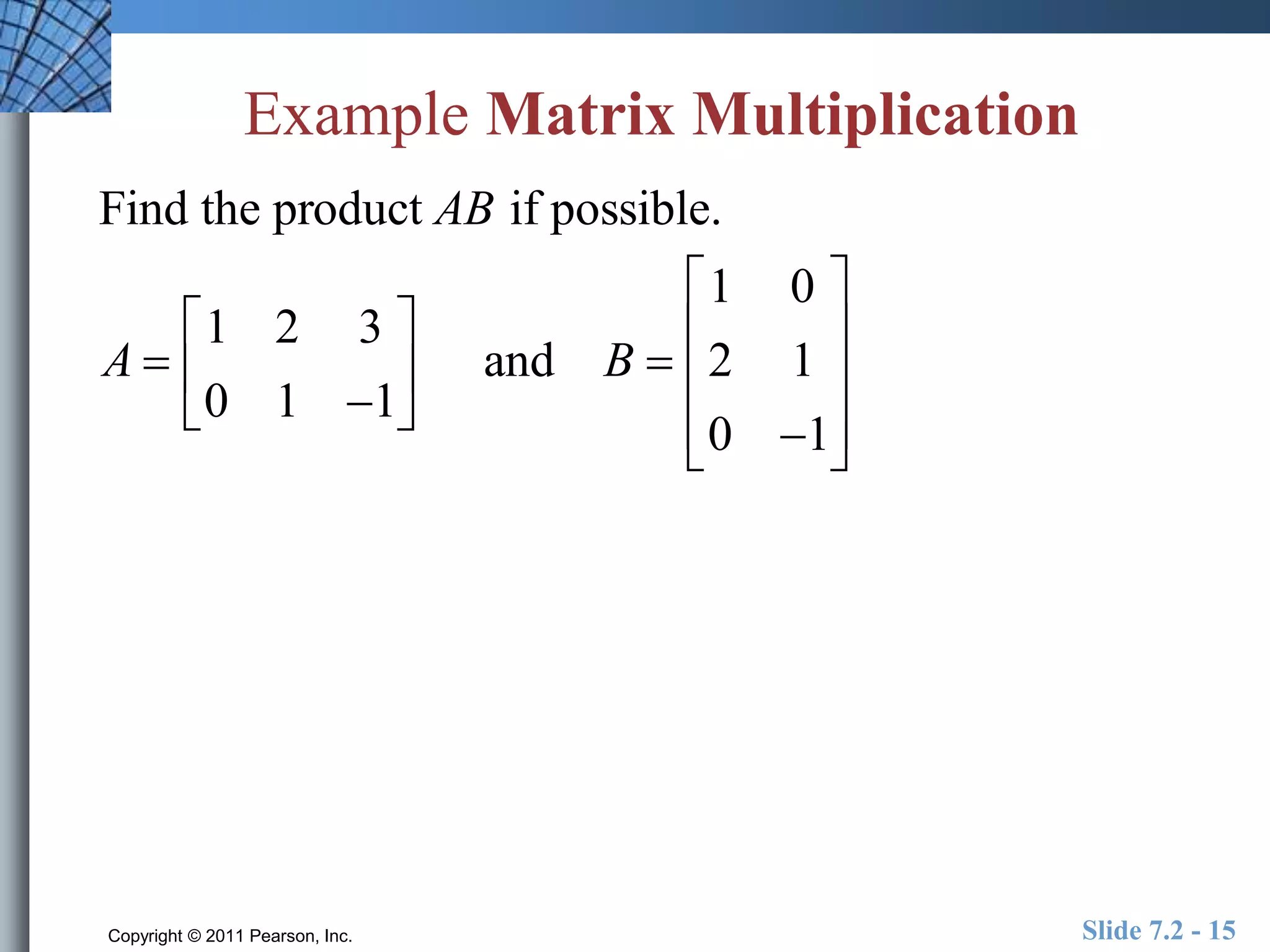
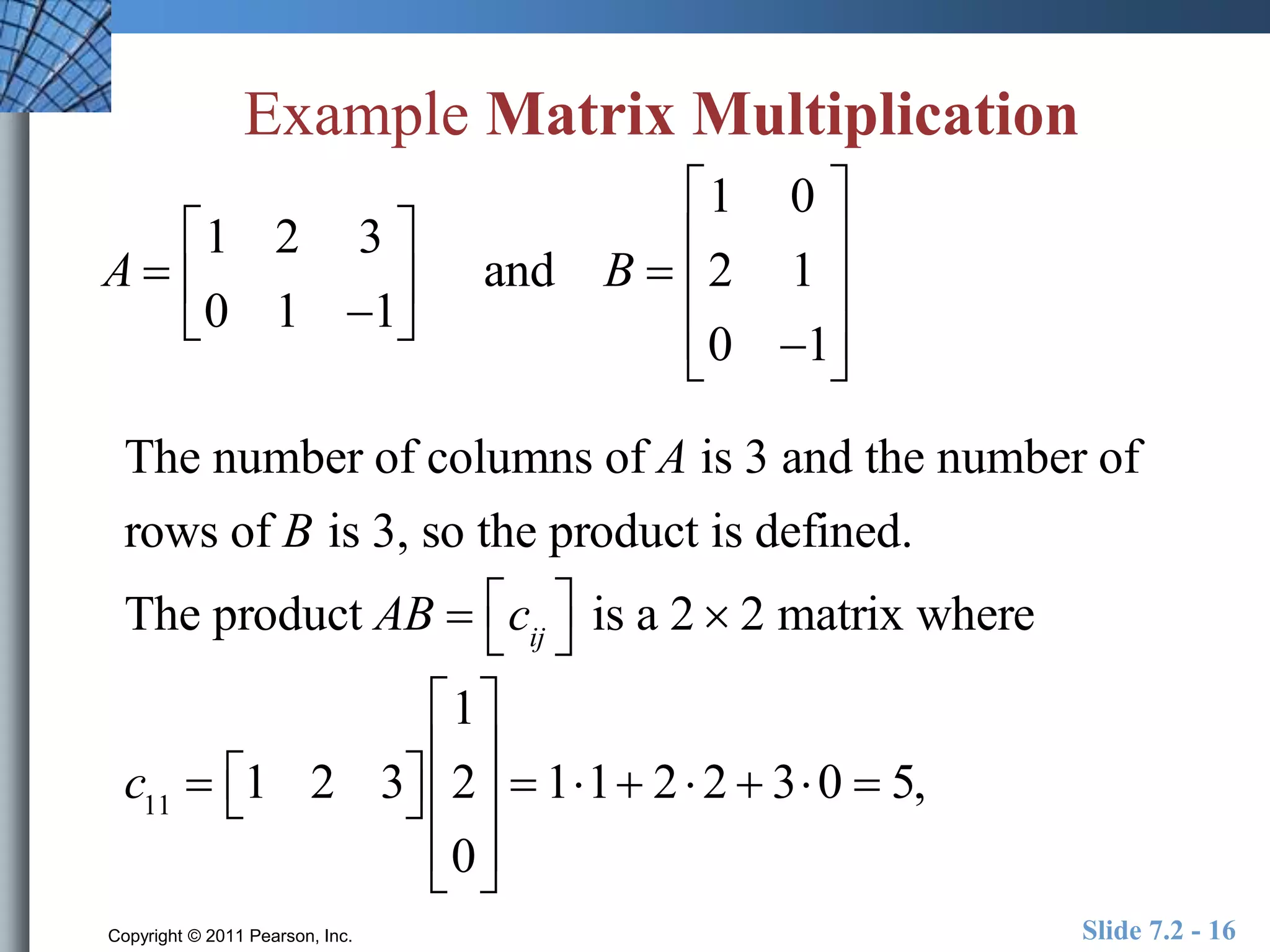
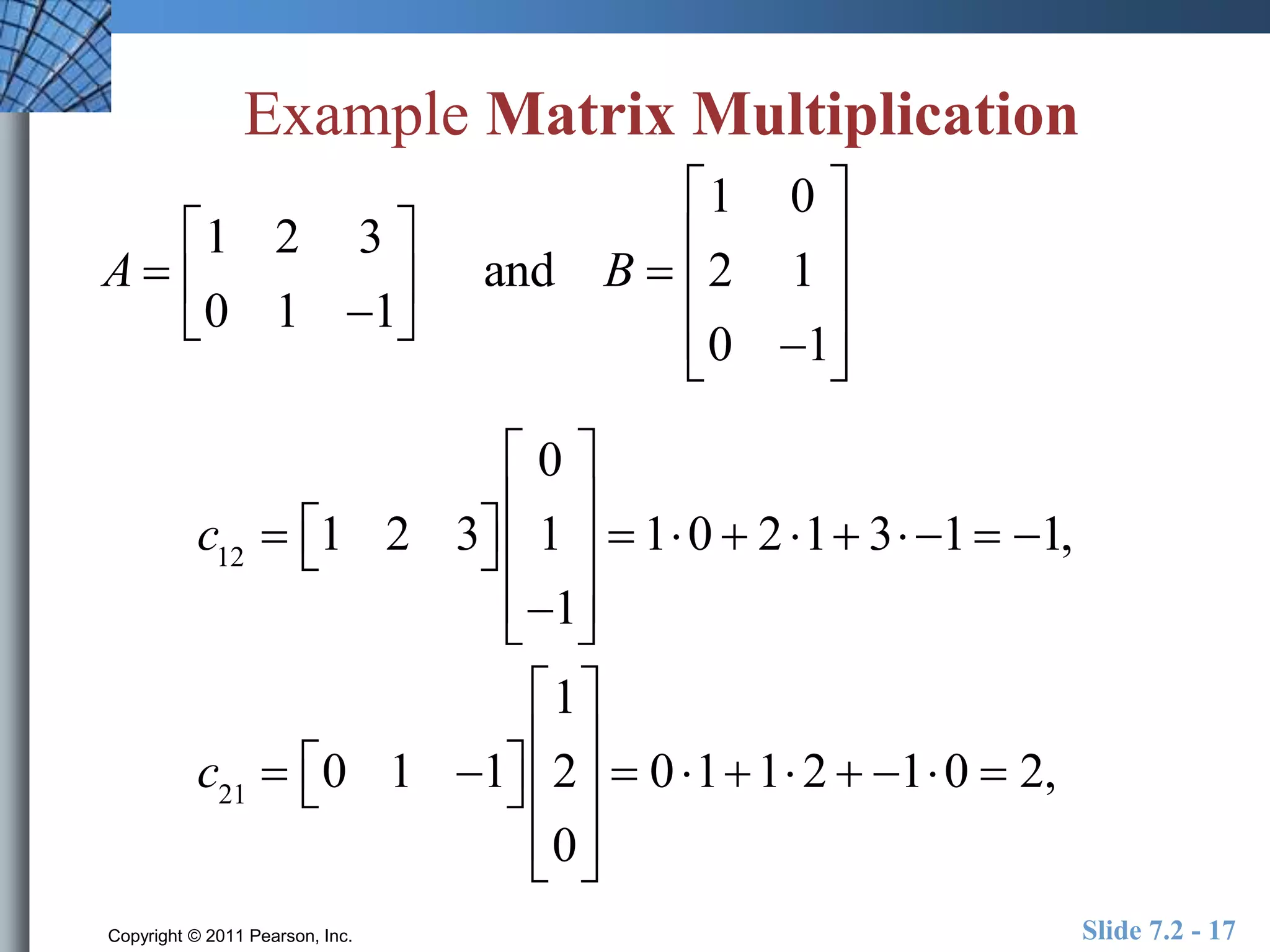
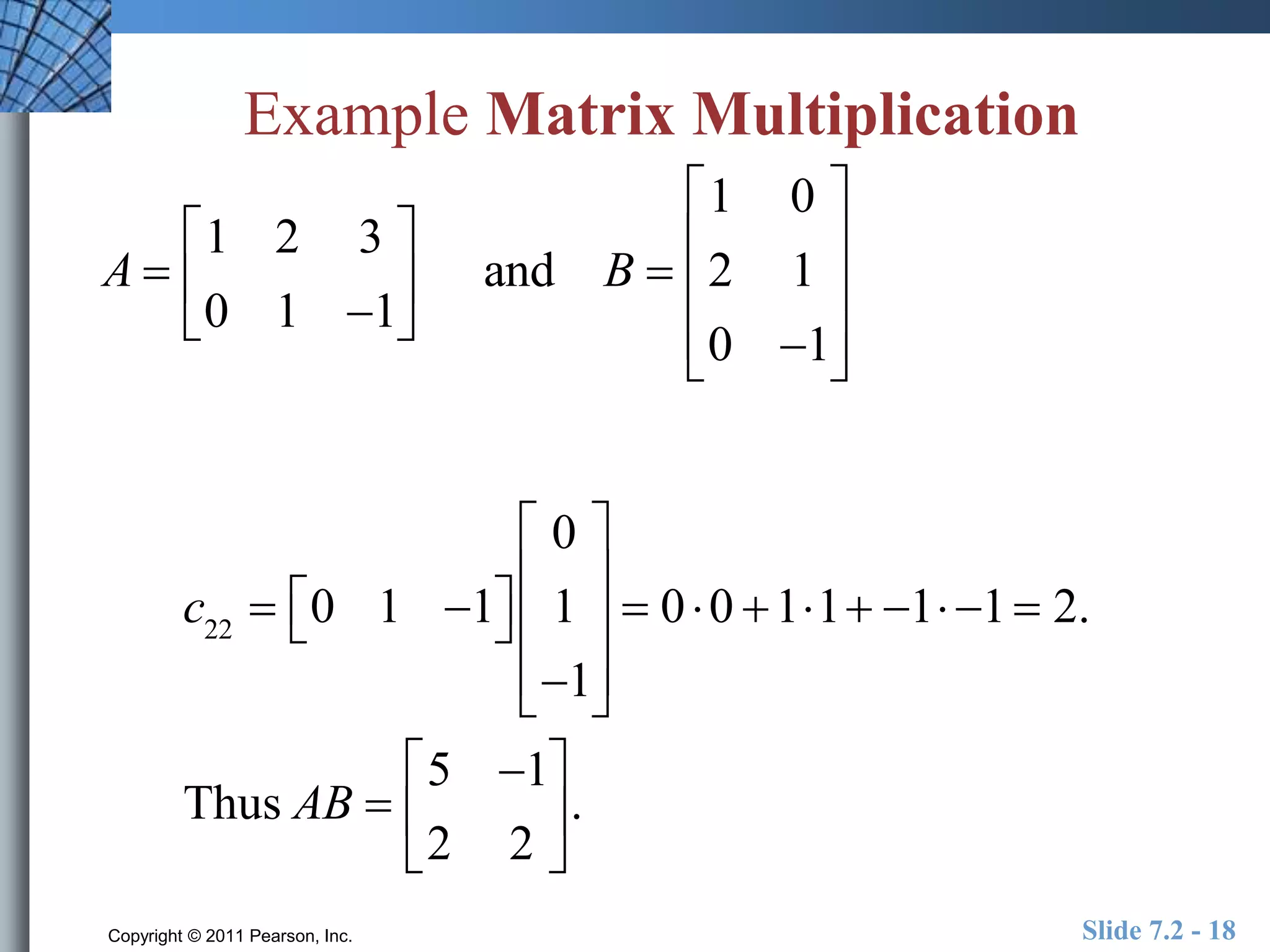
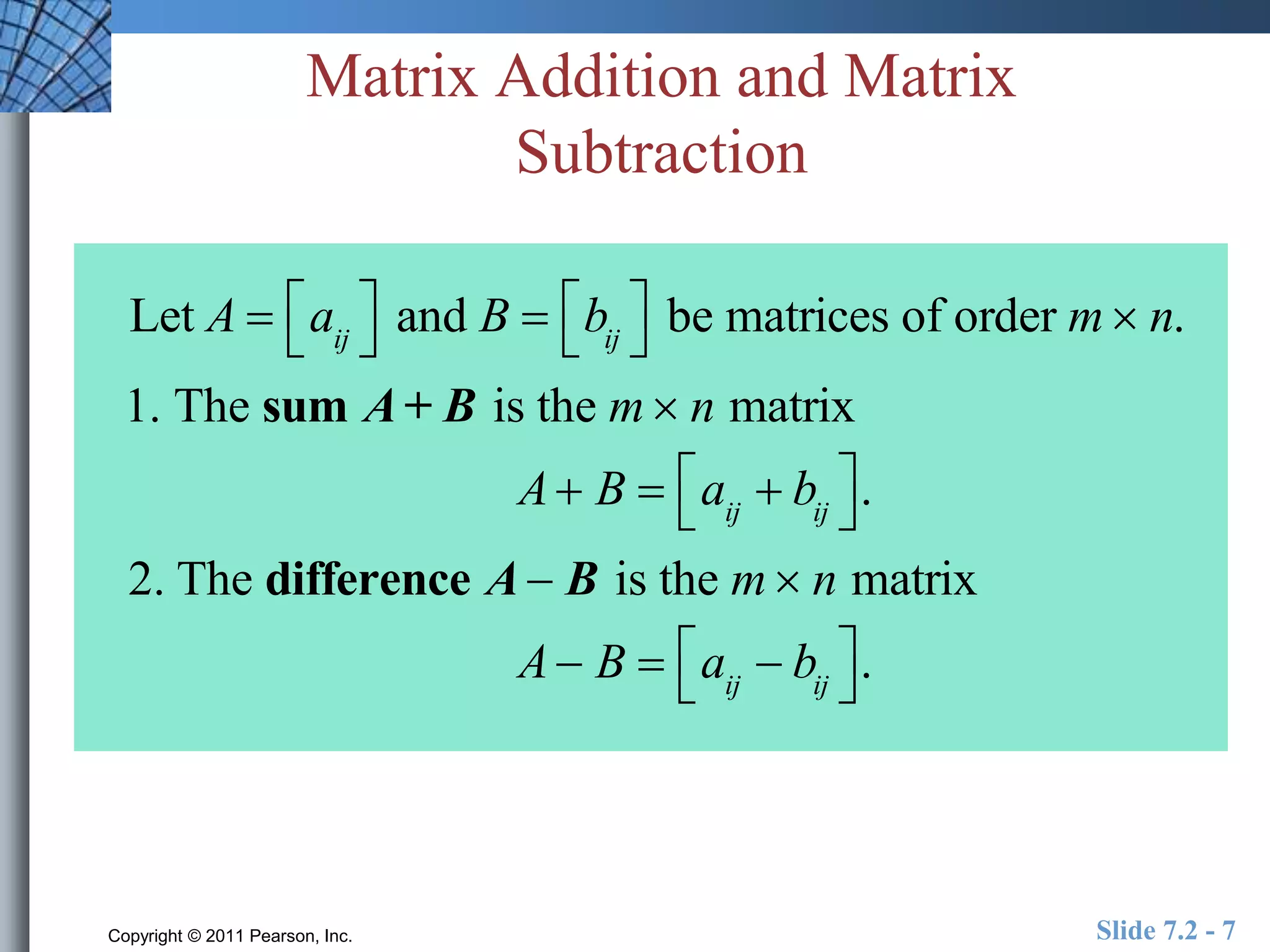
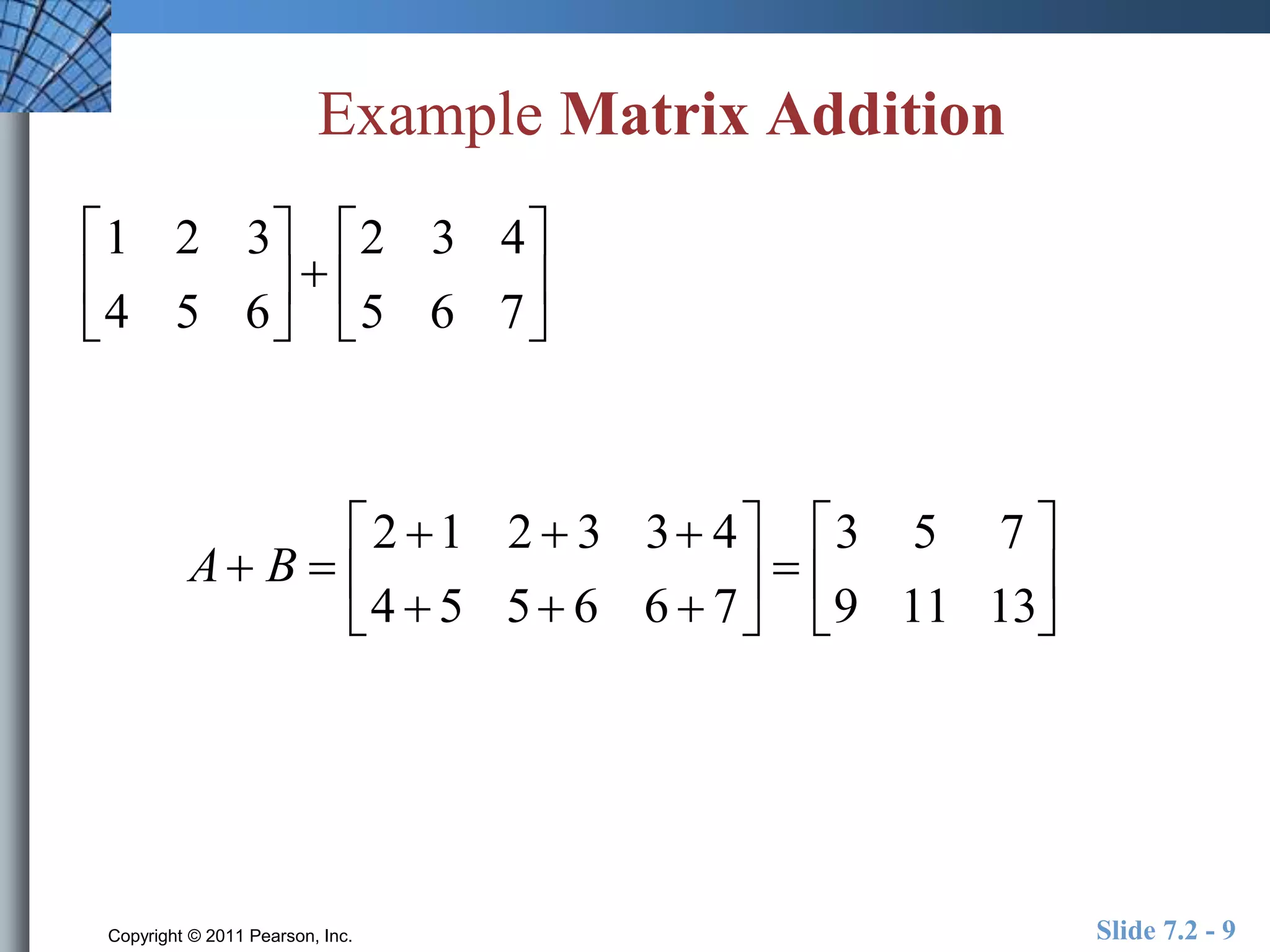
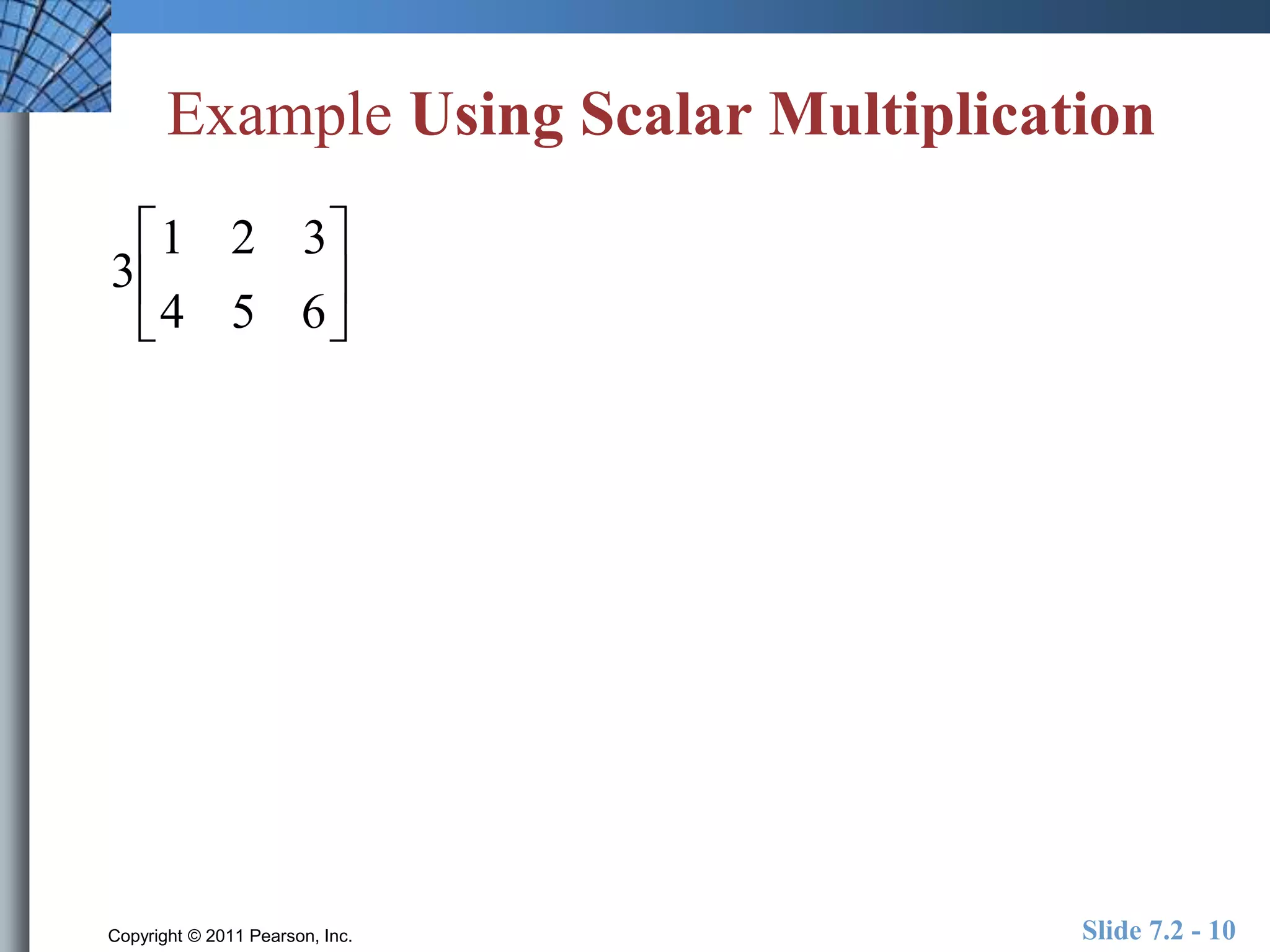
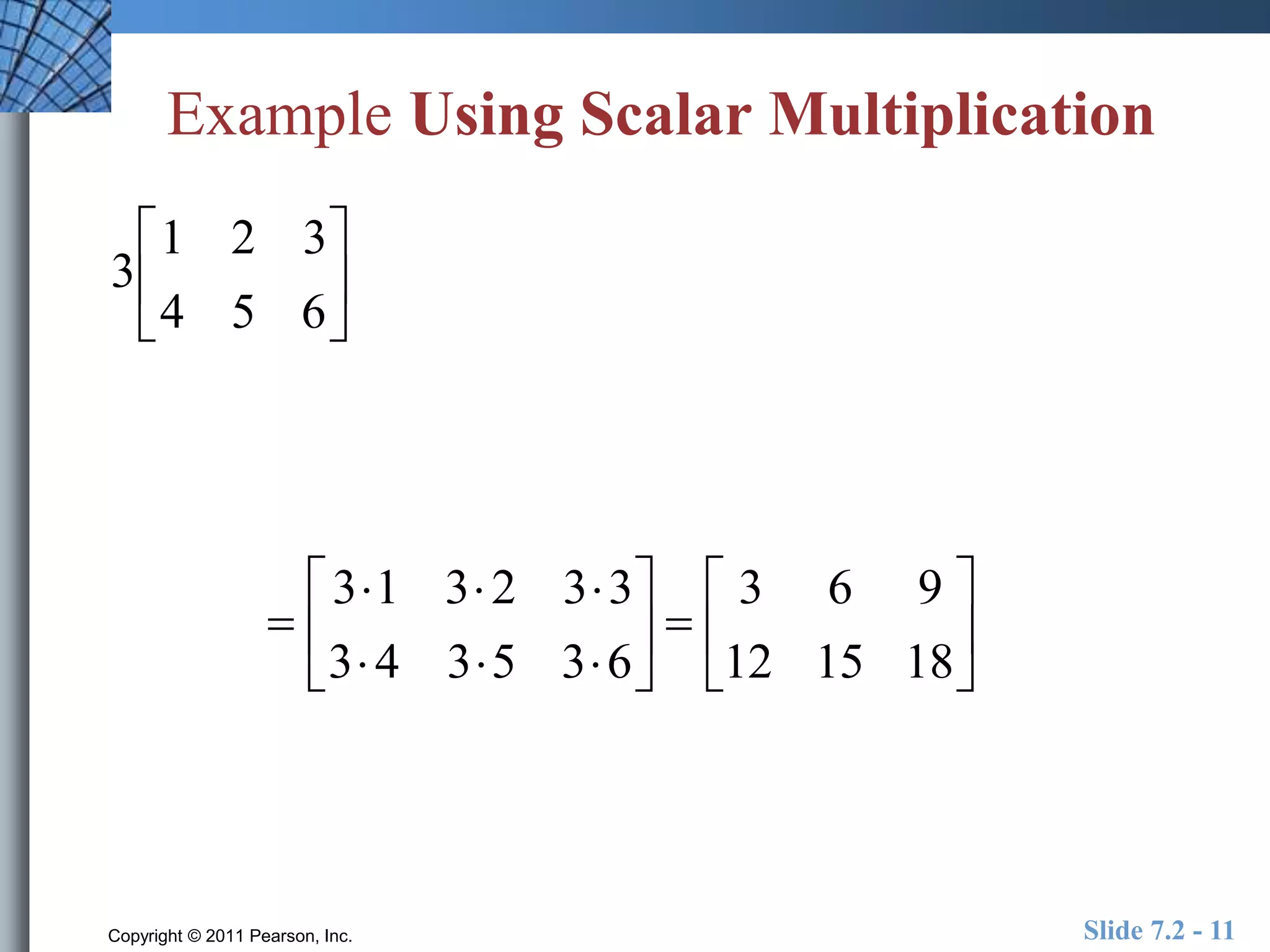
- Matrix operations include addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, and multiplication.
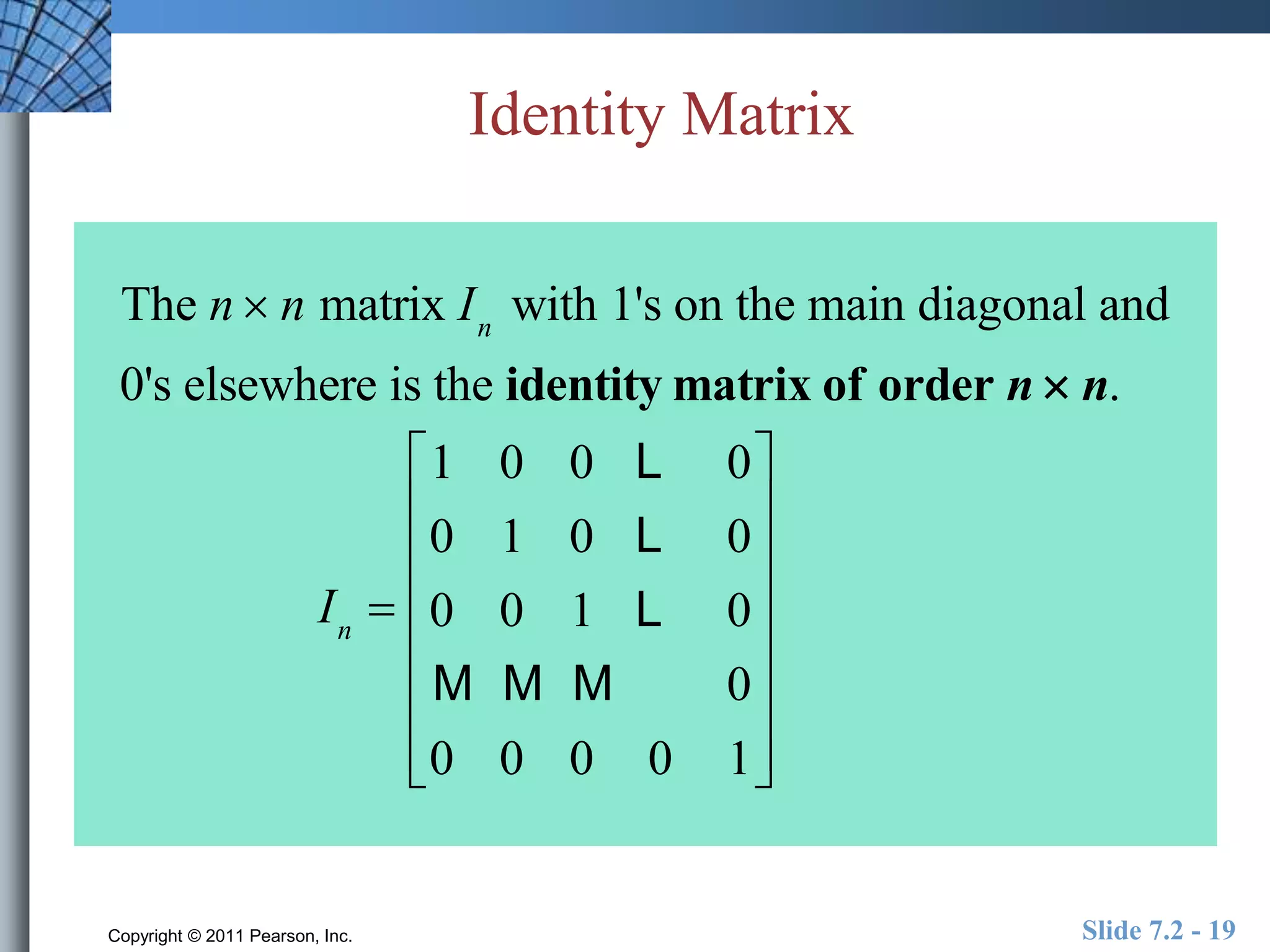
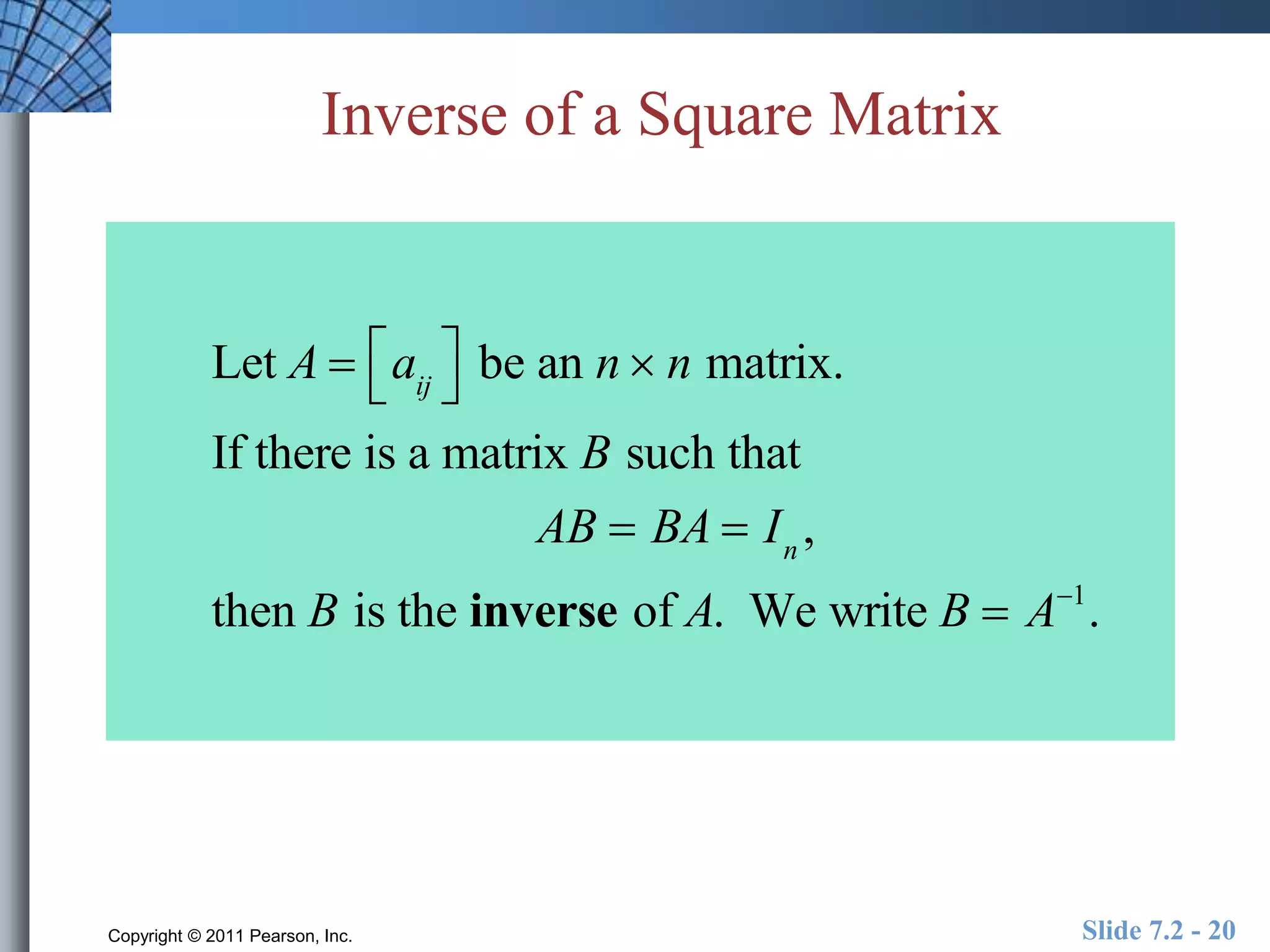
- Special matrices include the zero matrix, identity matrix, and inverse matrices.
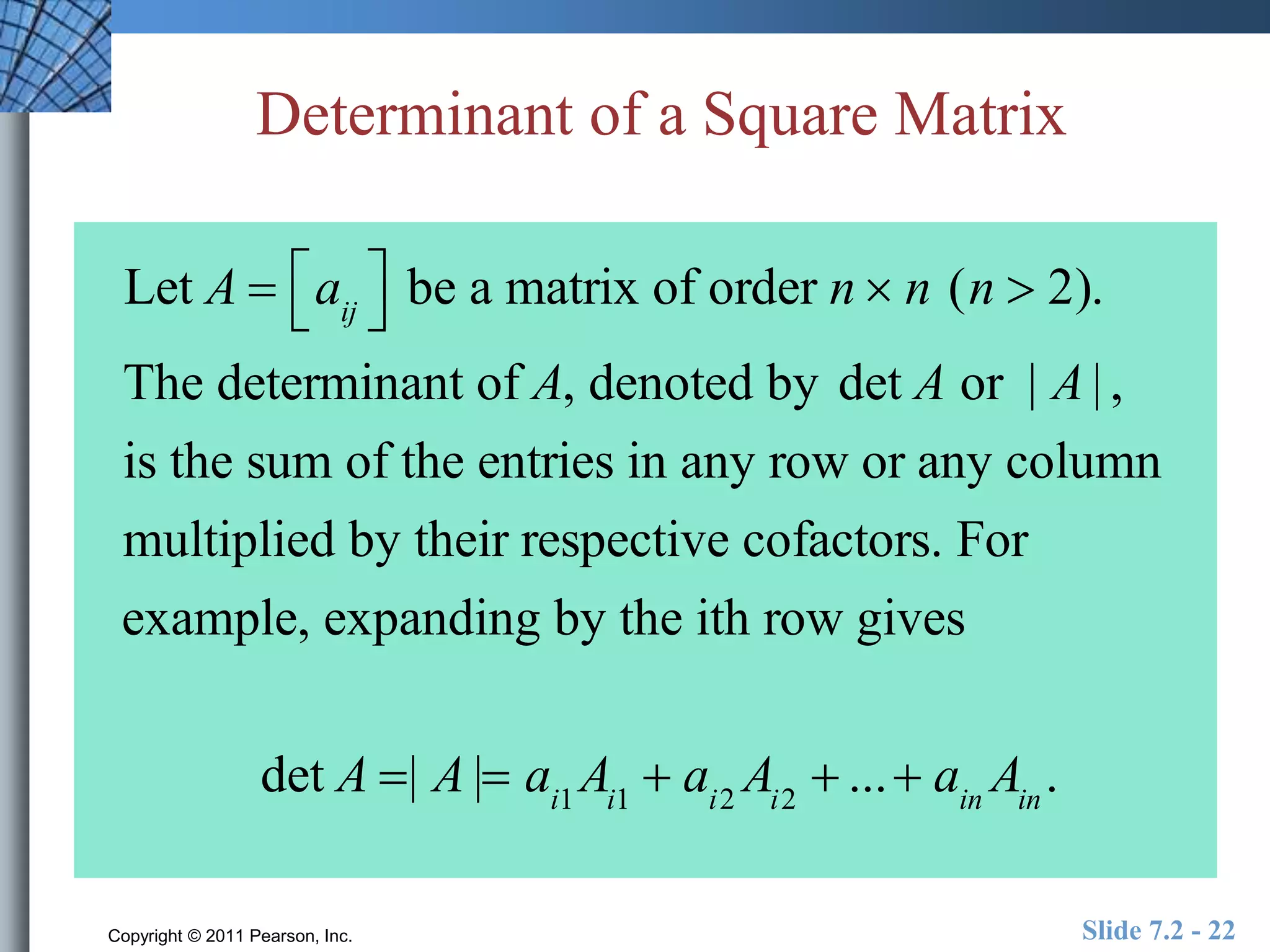
- The determinant of a square matrix is important for determining if the matrix has an inverse.




![The Zero Matrix
The m n matrix 0 [0] consisting entirely of
zeros is the zero matrix.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson, Inc. Slide 7.2 - 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit7-140908143808-phpapp01/75/Unit-7-2-12-2048.jpg)