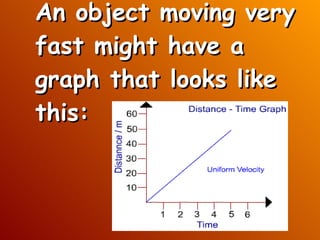
TEKS 6.8B, 6.8C, and 6.8D outline standards related to identifying changes in an object's position, direction, and speed when acted on by unbalanced forces, calculating average speed using distance and time measurements, and measuring and graphing changes in motion. Forces are needed to start or stop an object's motion or change its speed or direction. Speed is calculated by dividing distance by time and can be shown through graphs of changing motion over time. Forces can cause an object's speed to increase, decrease, or stop depending on whether the net force is balanced or unbalanced.