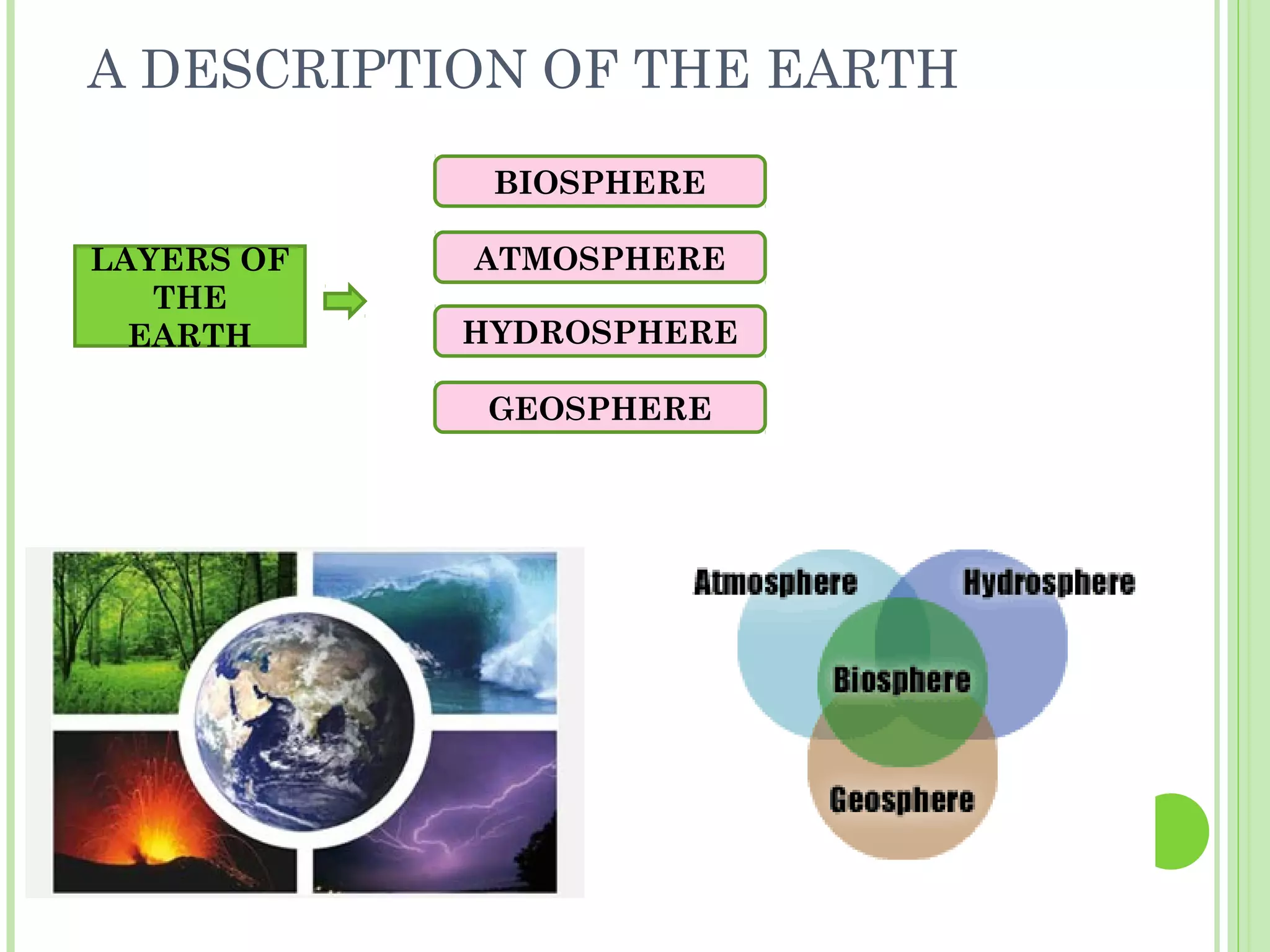
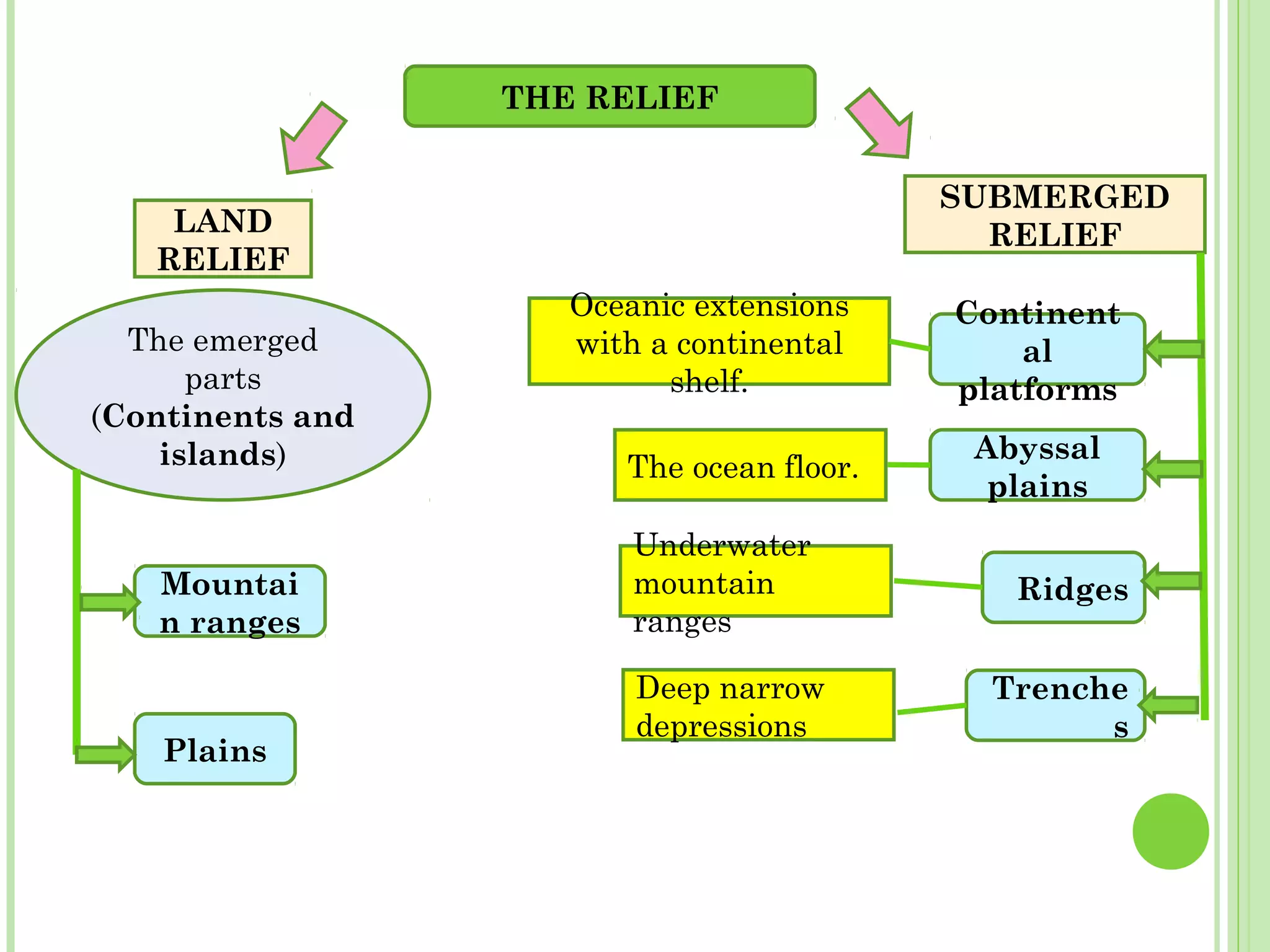
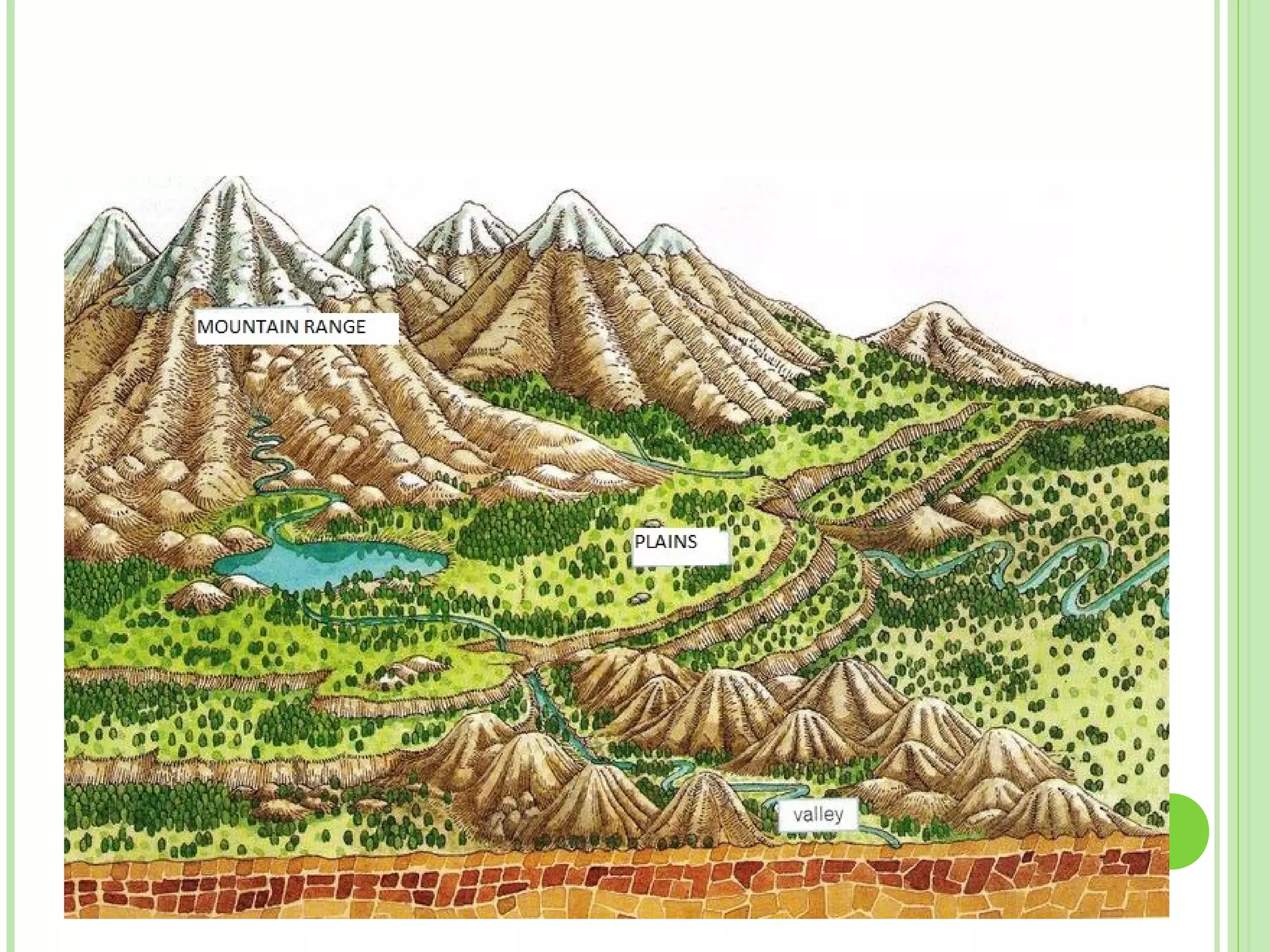
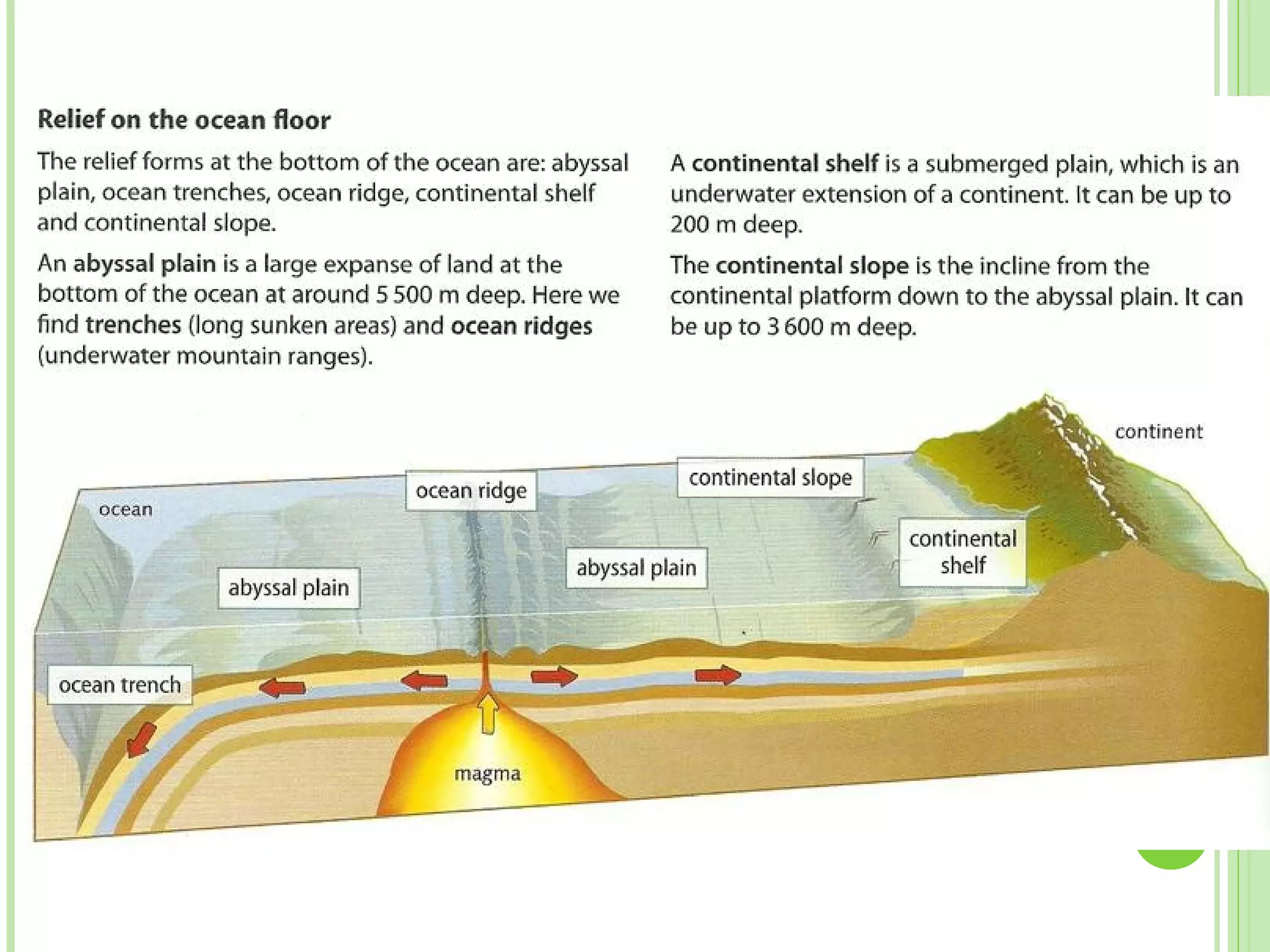
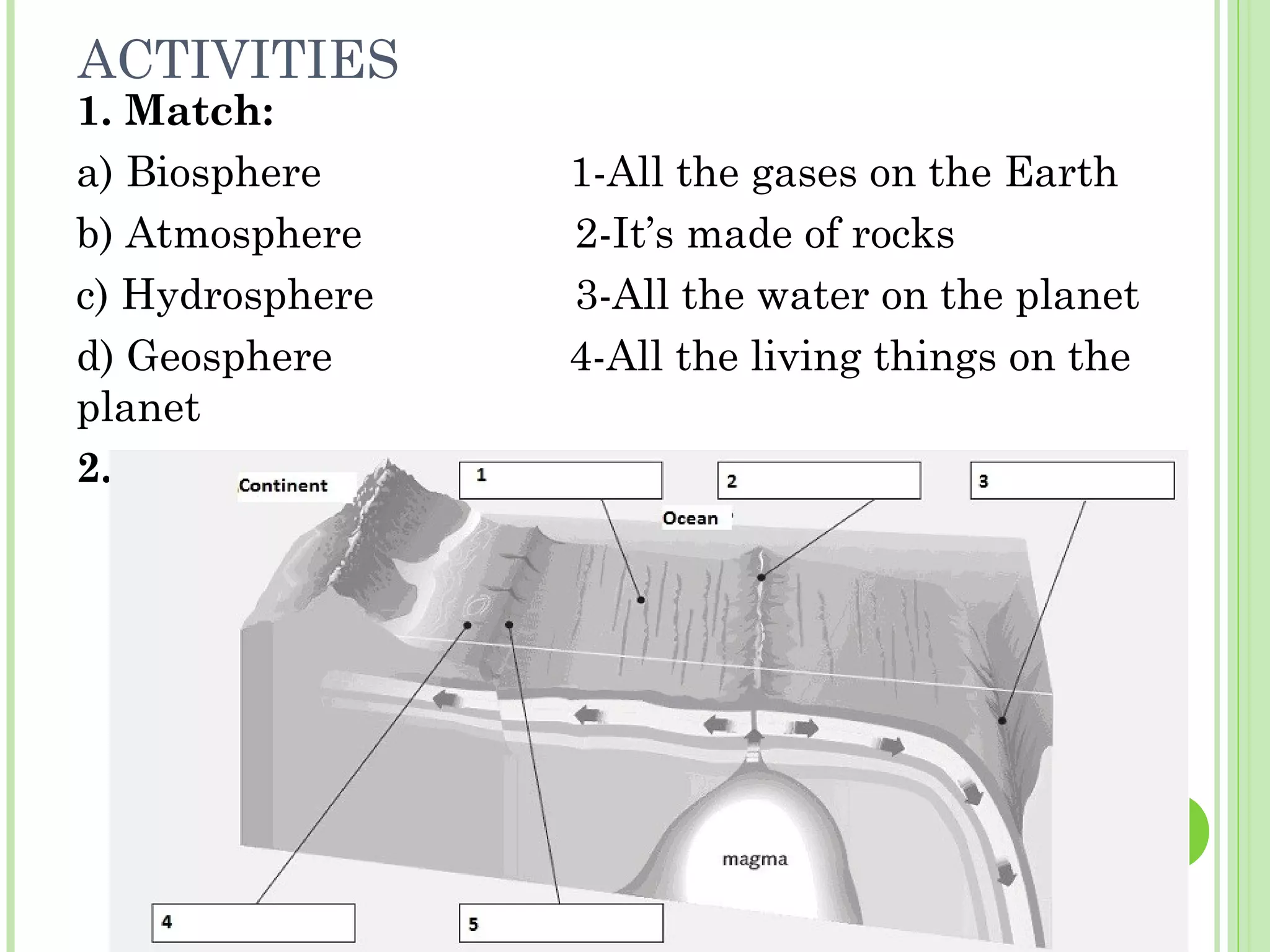
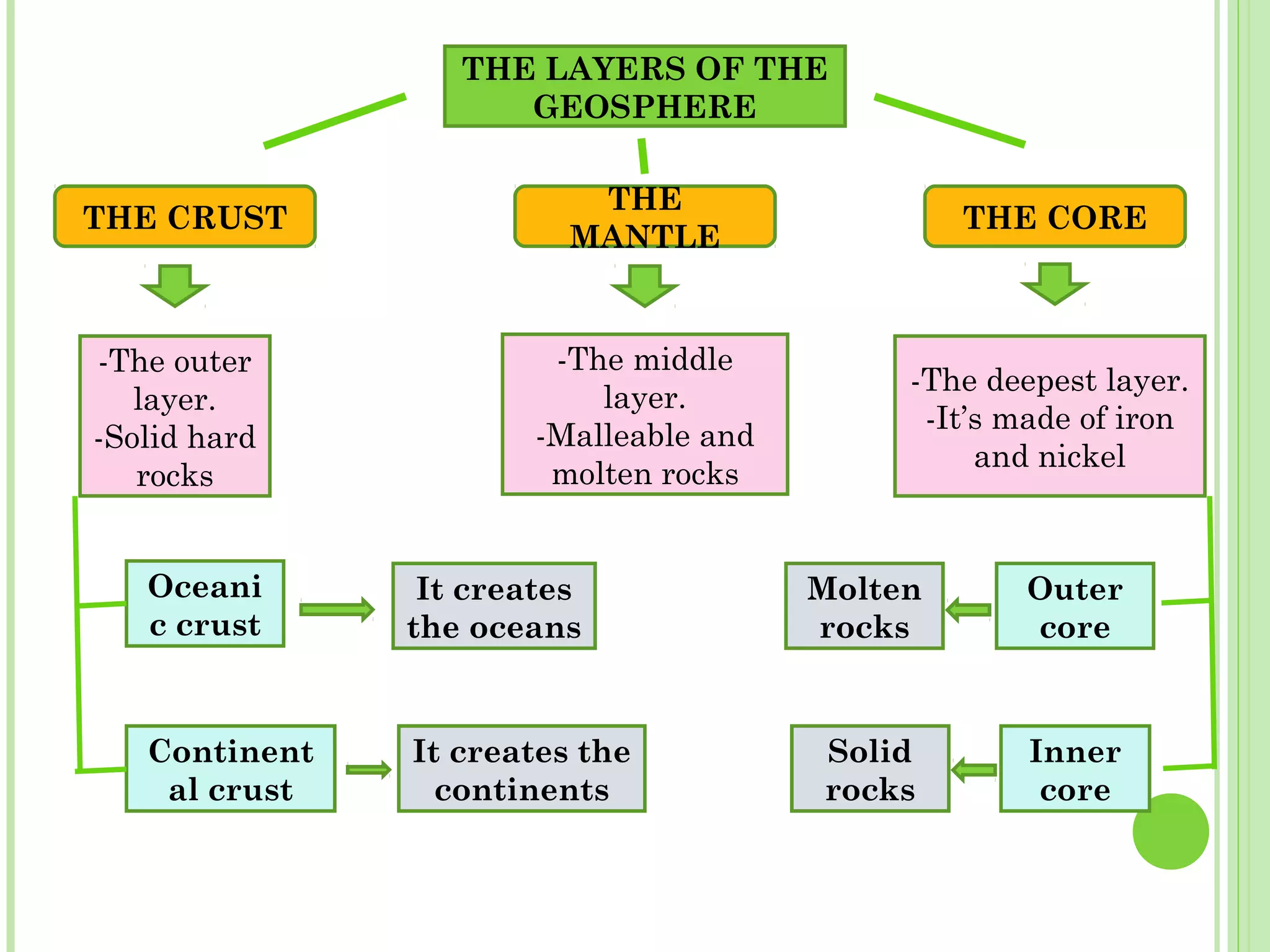
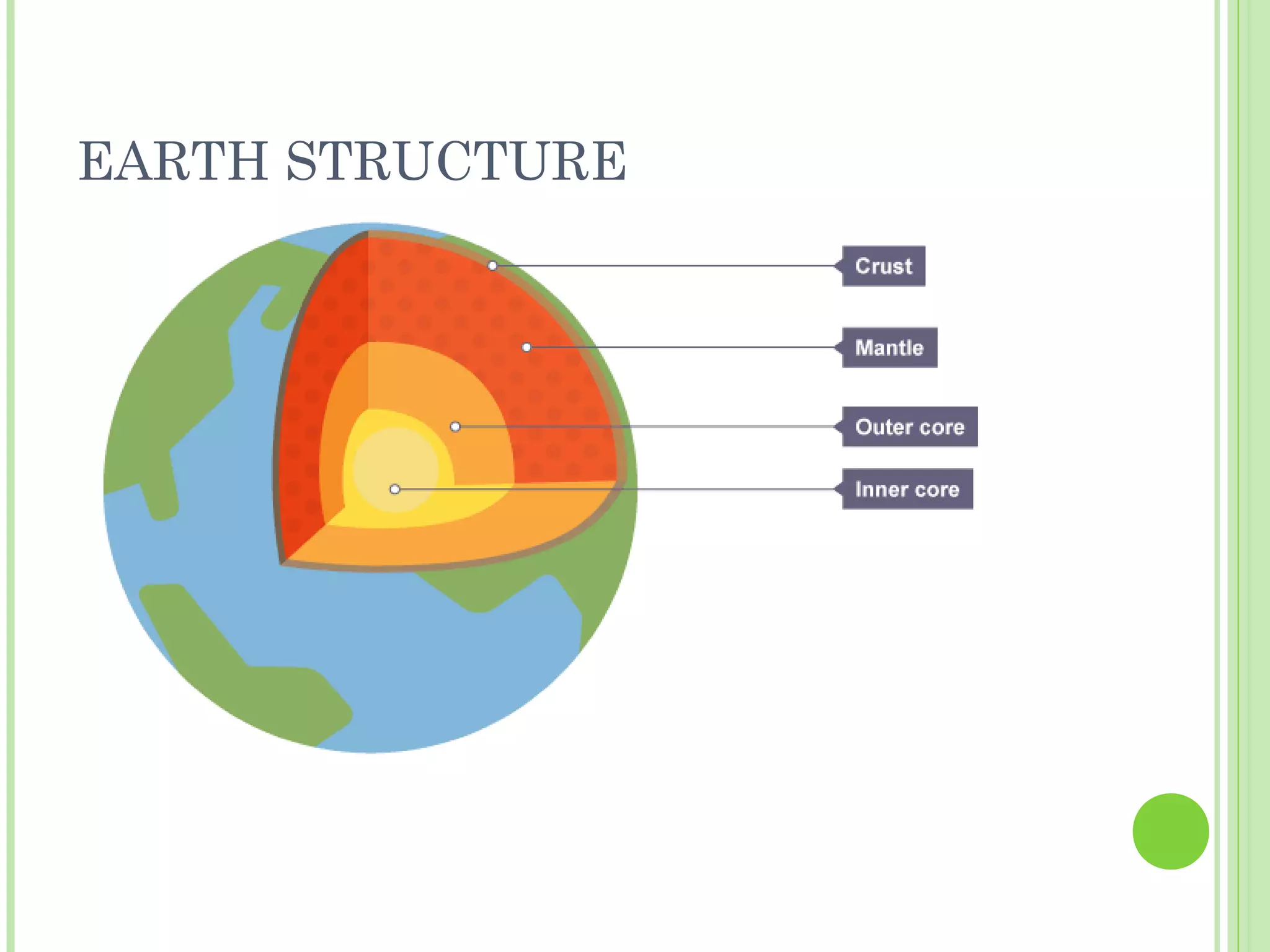
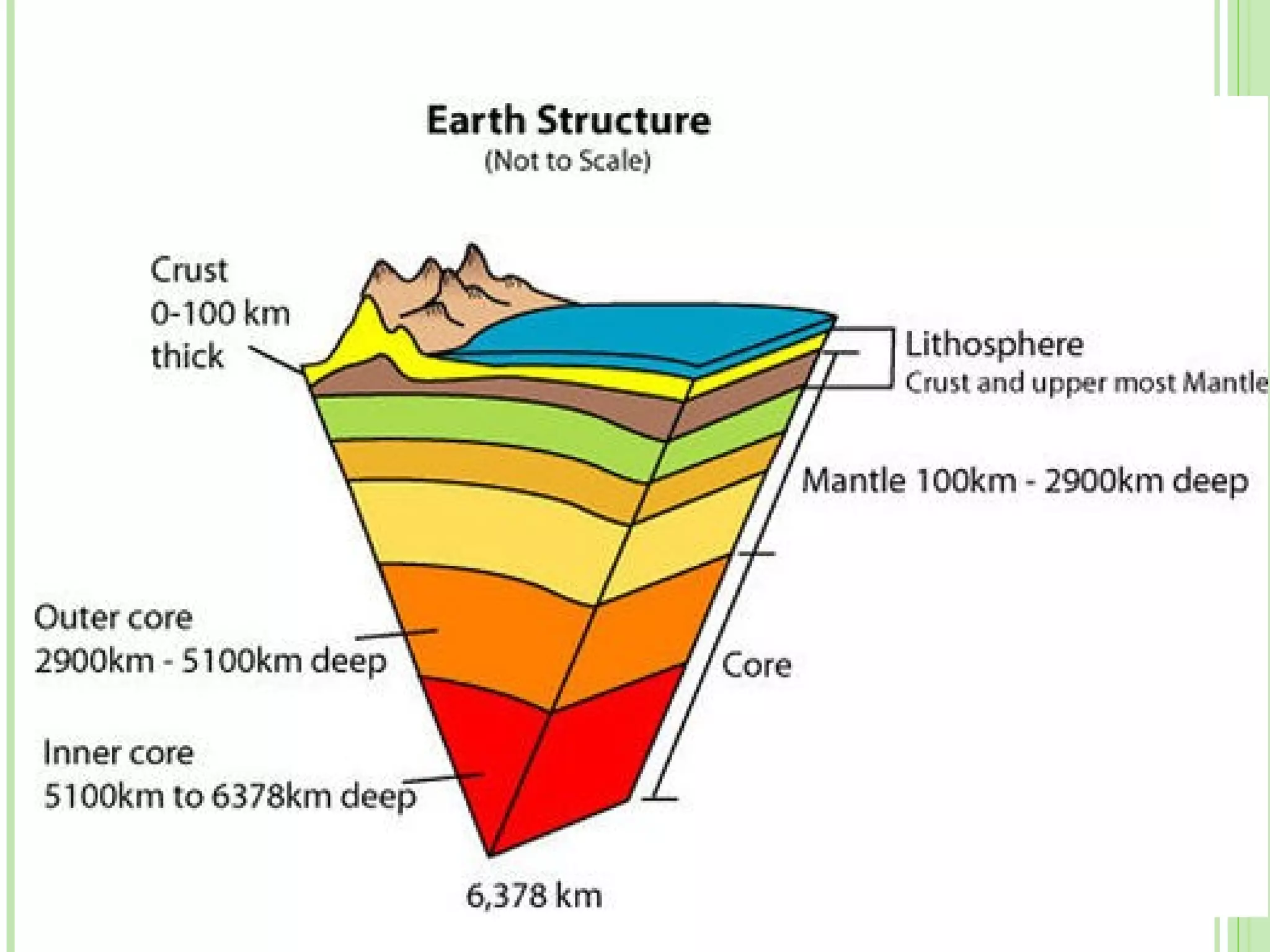
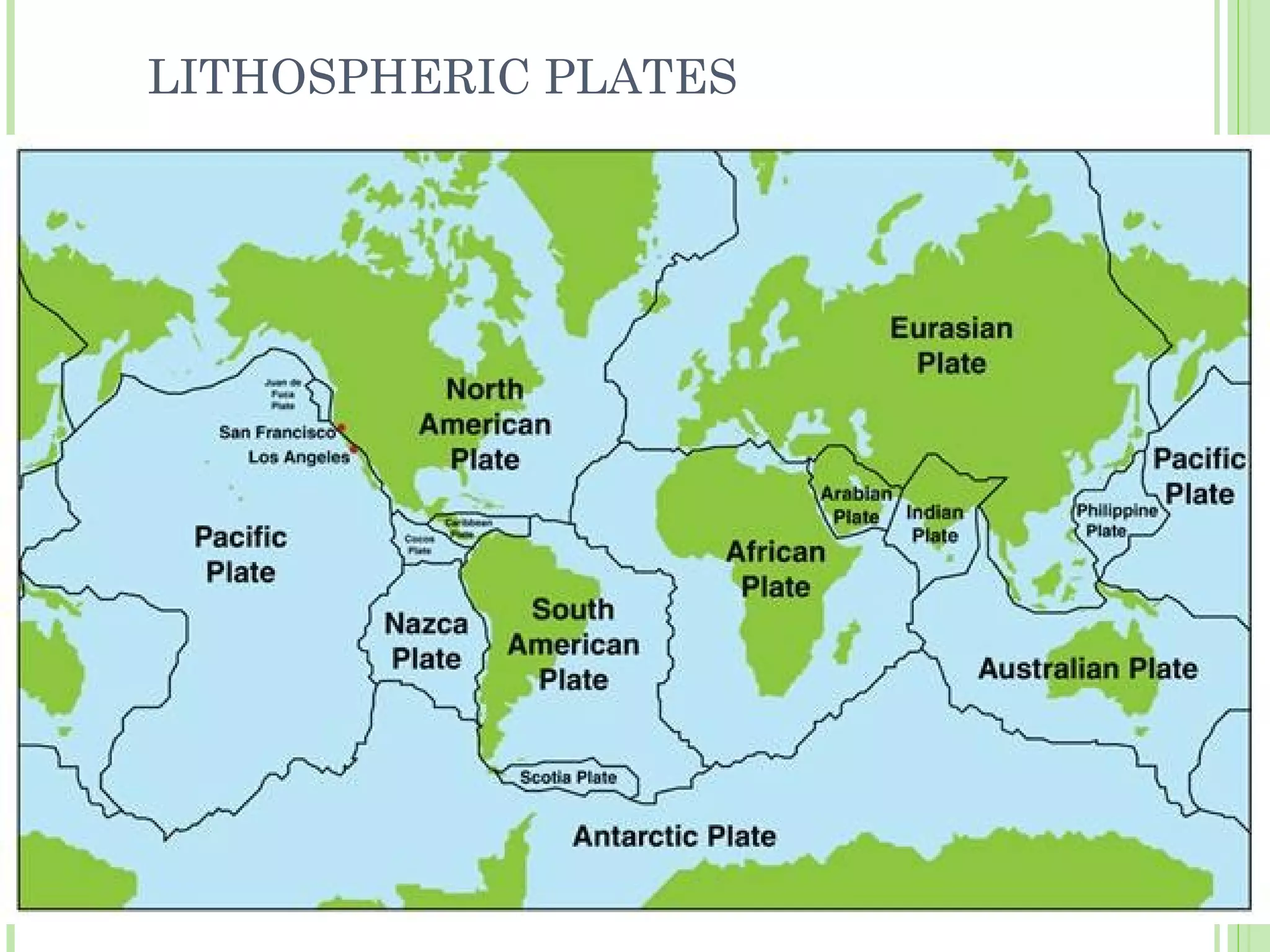
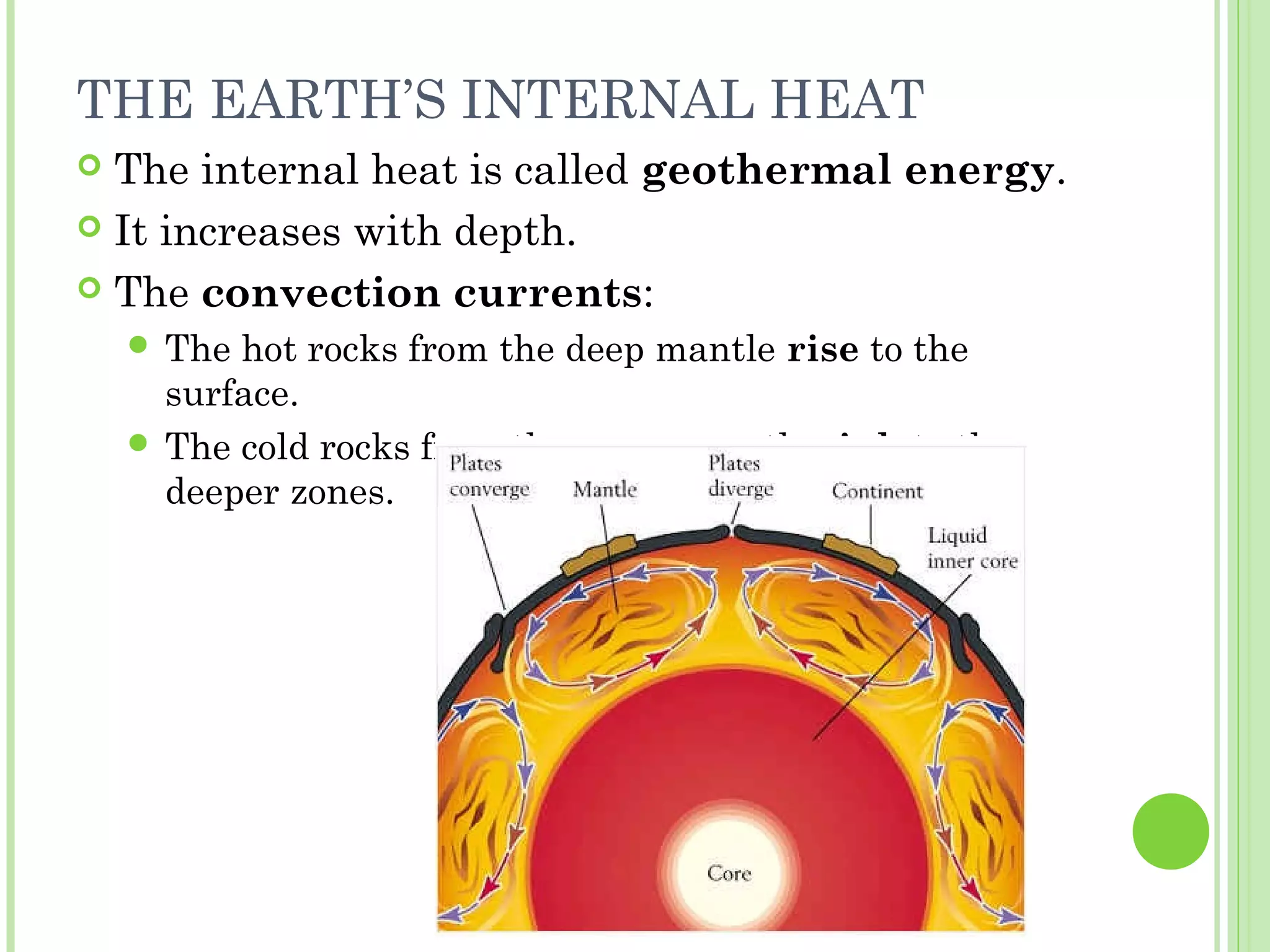
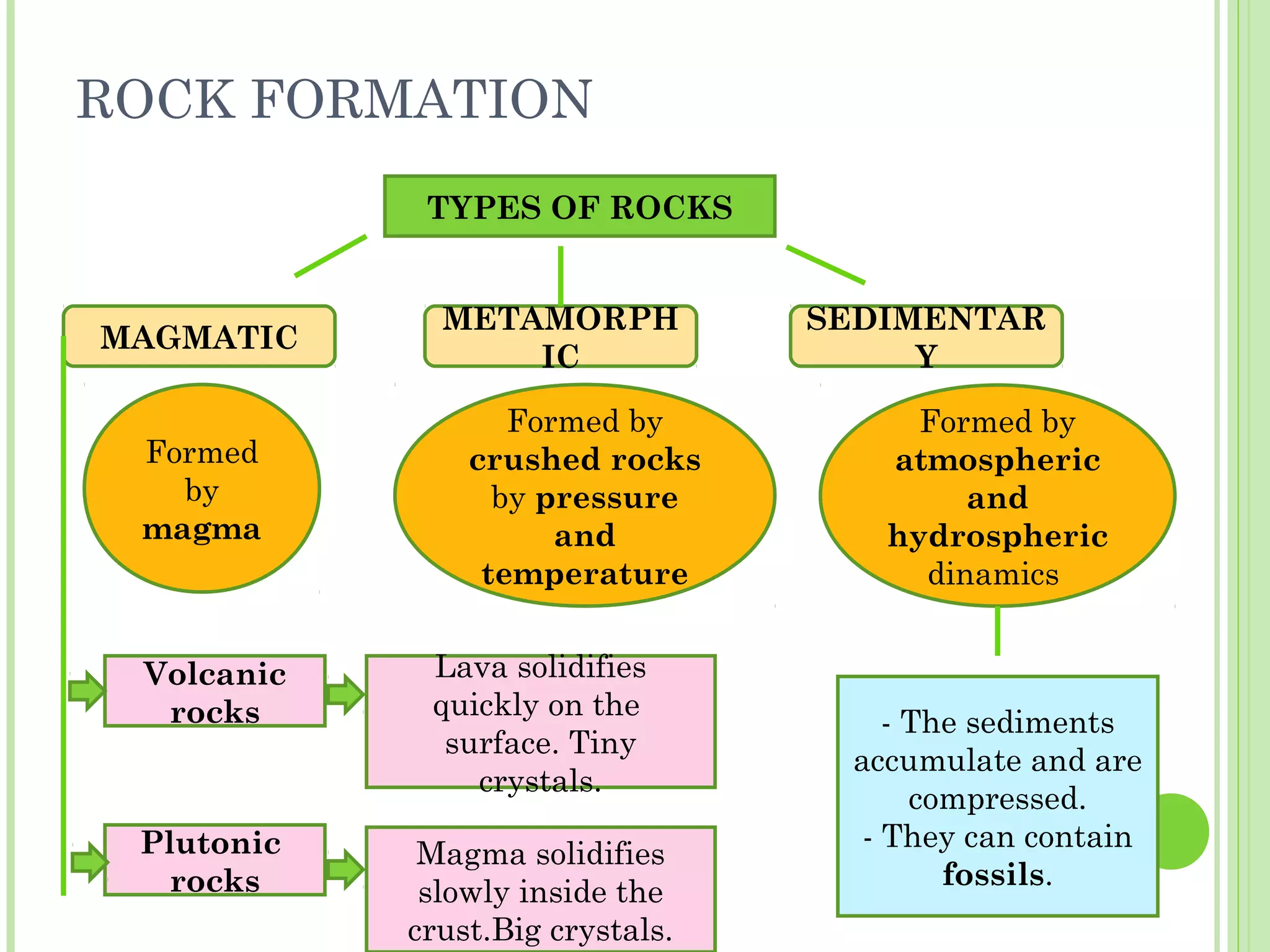
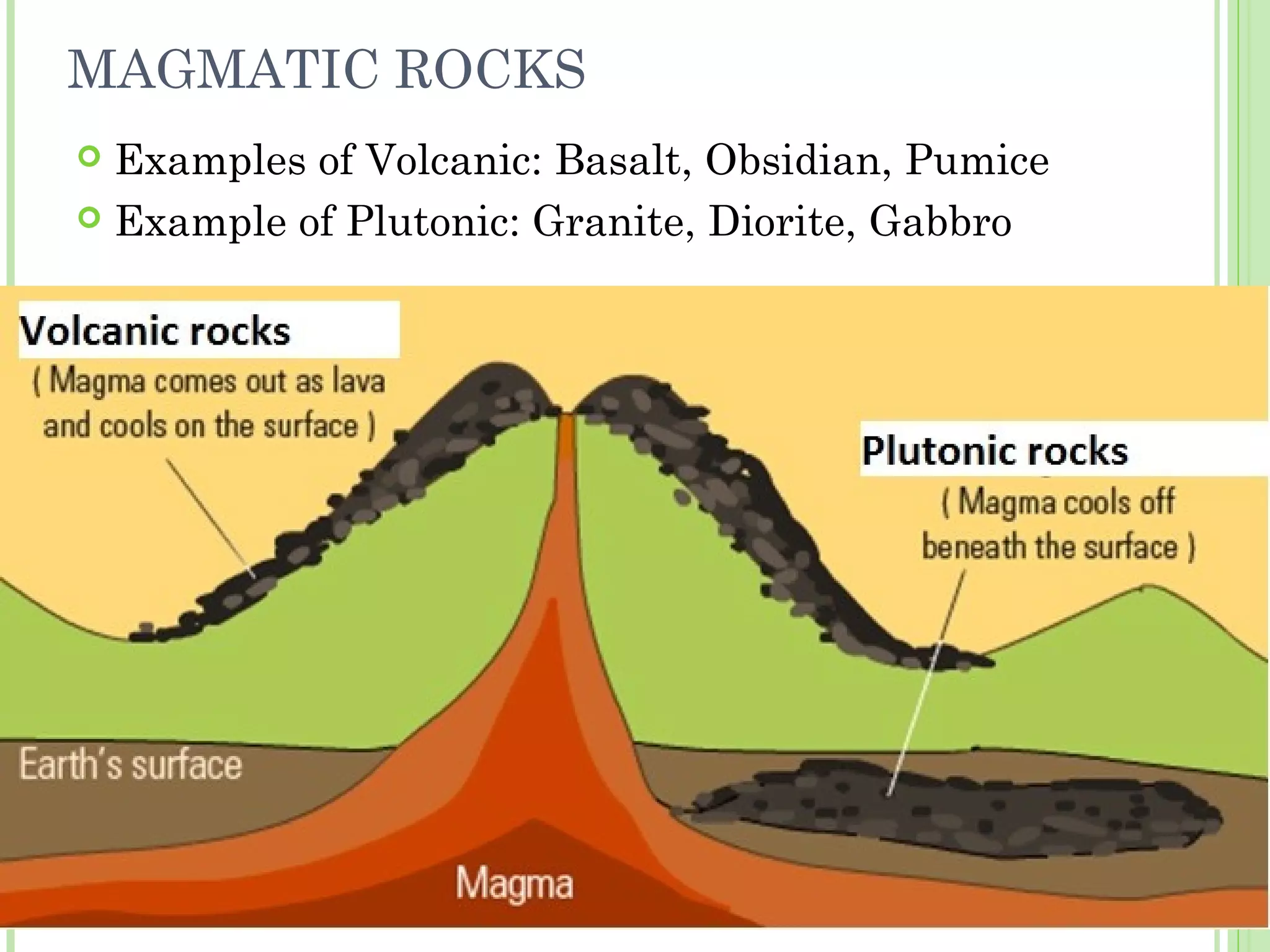
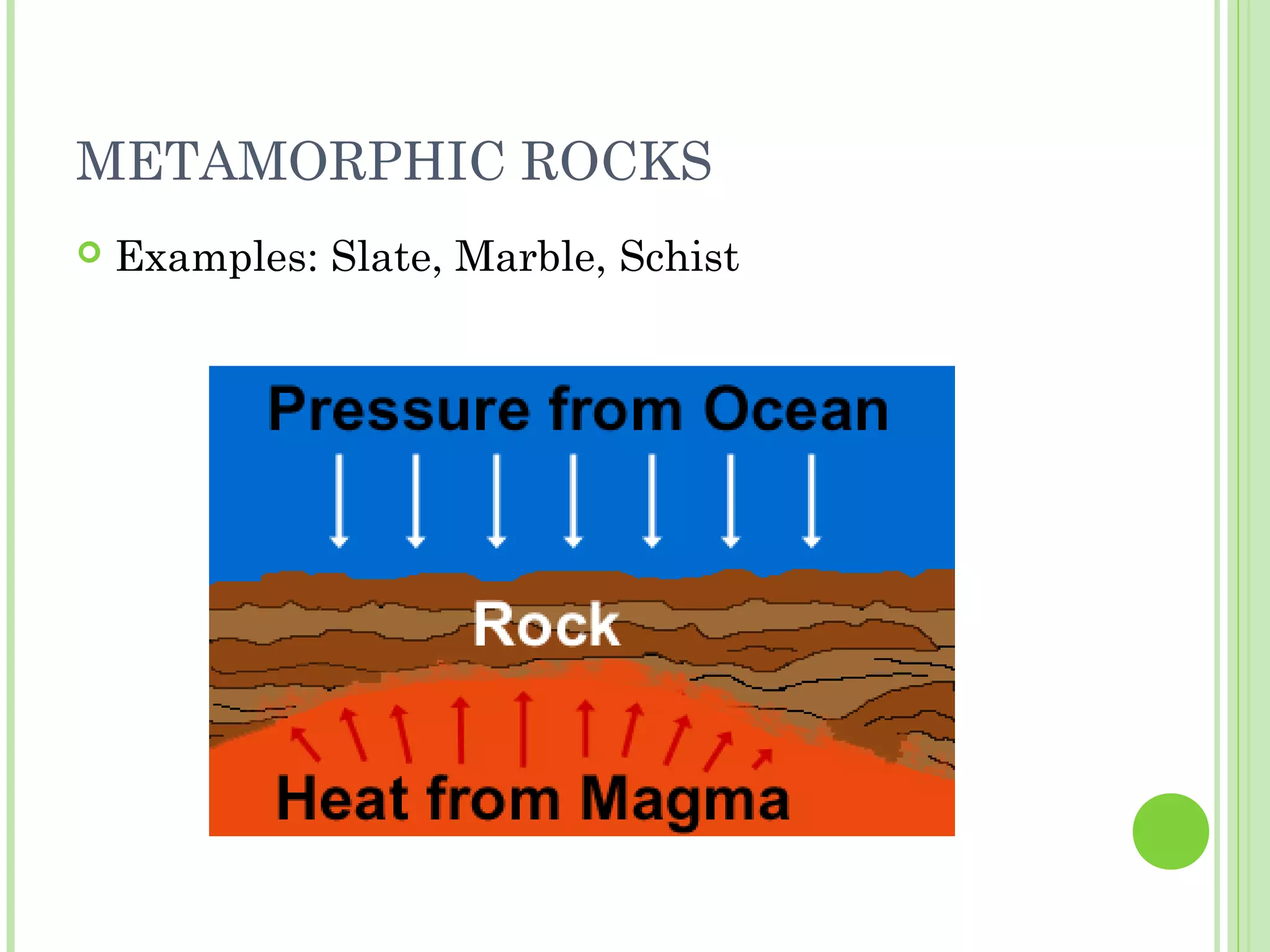
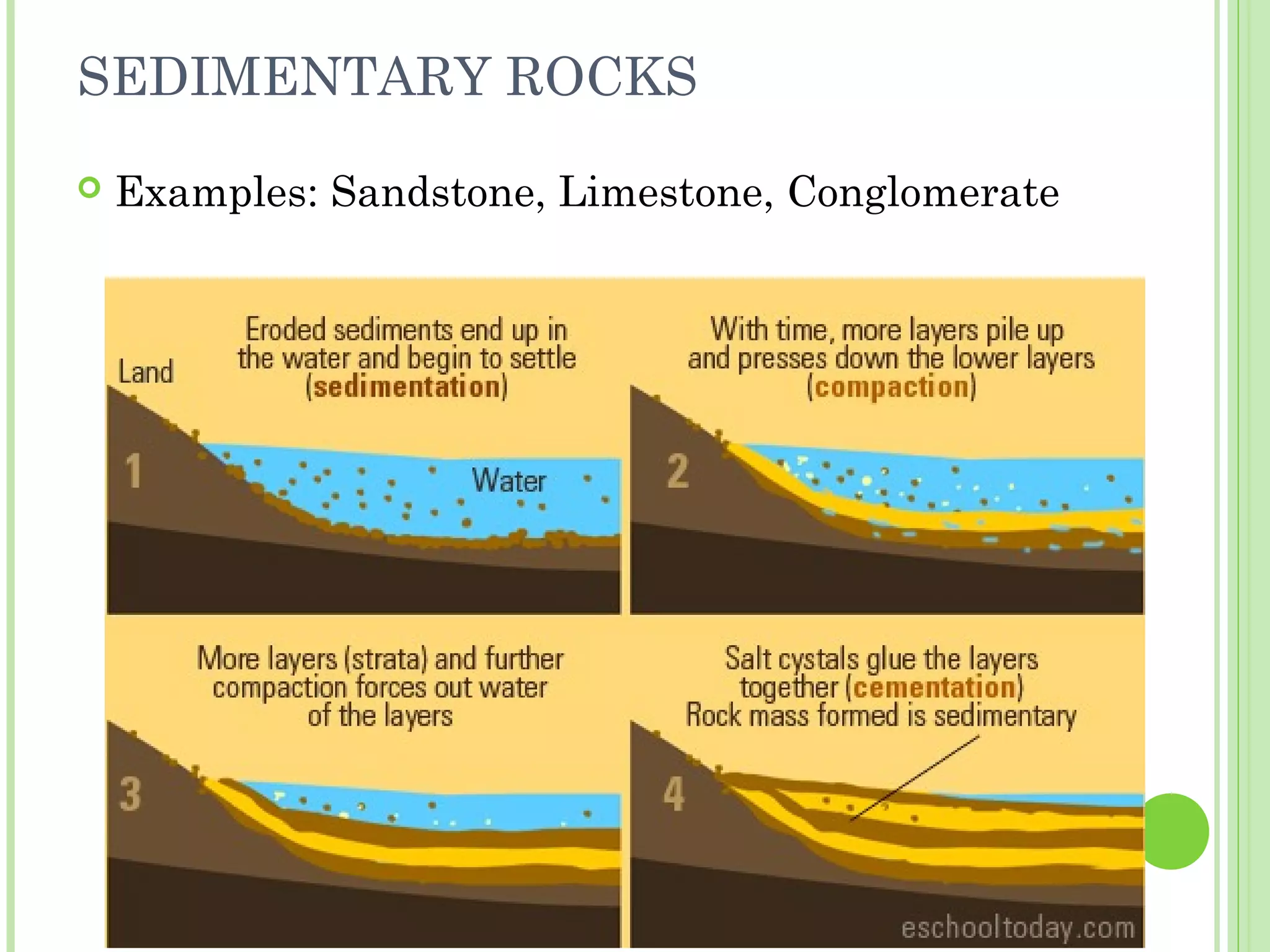
This document provides information about the structure and composition of the Earth. It describes the four main spheres (biosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere). It details the layers of the Earth's interior including the crust, mantle, and core. It explains how the lithosphere is composed of tectonic plates that move and interact at plate boundaries. It also discusses the three main types of rocks: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks and how they are formed by volcanic, pressure-related, and sediment-based processes respectively.