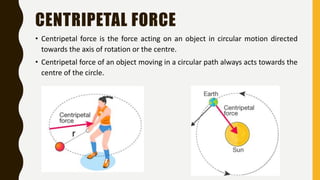
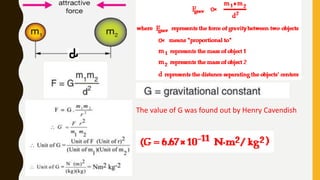
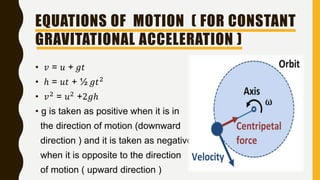
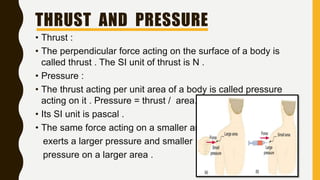
The document provides an introduction to gravitation, explaining concepts such as gravitational force, centripetal force, and Newton's law of gravitation. It covers the differences between mass and weight, the concept of thrust and pressure, and discusses buoyancy and Archimedes' principle. Additionally, it outlines the relationship between buoyant force and the weight of displaced fluid, as well as the idea of relative density.