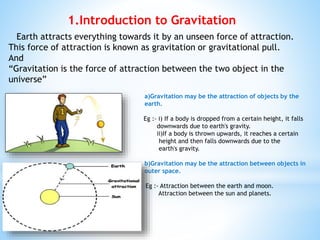
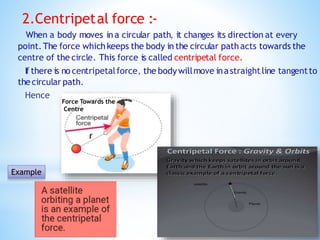
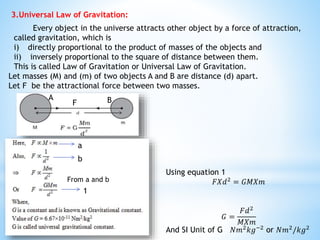
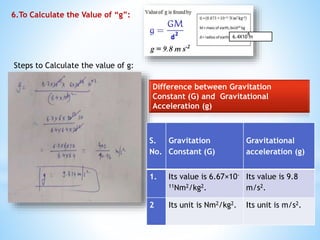
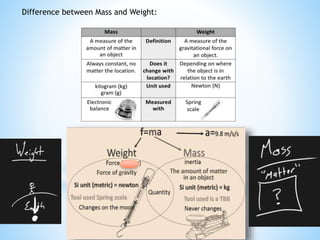
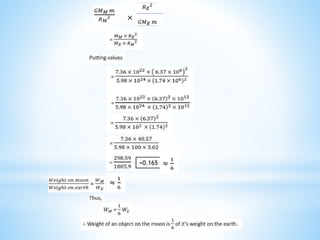
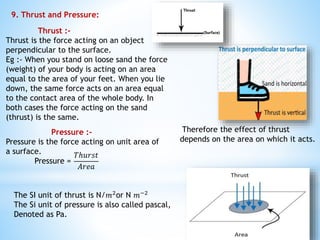
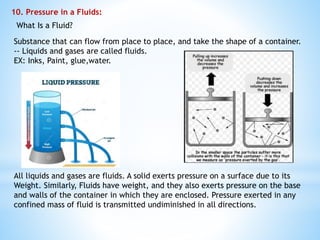
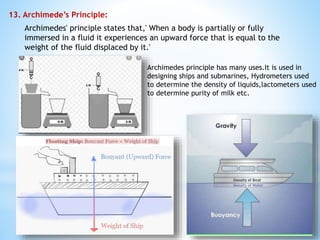
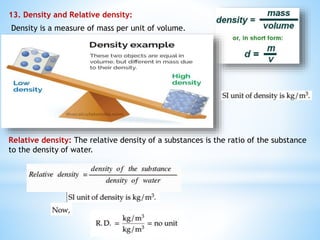
This document provides an overview of key concepts in gravitation and fluid mechanics. It begins with an introduction to gravitation as the force of attraction between objects. It then discusses centripetal force, Newton's universal law of gravitation, and the importance of this law. Further sections cover topics like free fall, calculating gravitational acceleration, mass vs weight, weight on other planets, thrust and pressure, buoyancy, and Archimedes' principle. The document concludes with explanations of why objects float or sink and definitions of density and relative density.