EXPLORING FORCES: Detailed Notes
8TH CLASS SCIENCE CURIOSITY NOTES
By : K Sandeep Swamy(M.Sc,B.Ed)
For Online Classes (IITJEE & NEET foundation and academics) contact : 9491878325
Subscribe Samyans Eduhub youtube channel
A force is fundamentally described as a push or pull applied on an object. Forces result from the interaction between two or more objects. At least two objects must interact for a force to come into play. The SI unit of force is newton (N).
What is a Force?
Definition
A force is fundamentally described as a push or pull applied on an object.
Interaction
Forces result from the interaction between two or more objects. At least two objects must interact for a force to come into play.
Example
When you push a table, your hand and the table are interacting. When this interaction ceases, the force is no longer experienced.
Measurement
The SI unit of force is newton (N).
What Can a Force Do to Objects?
Forces have several observable effects on objects they are applied to:
Make an object move from rest
Change the speed of a moving object. This includes stopping or decreasing speed
Change the direction of motion of an object
Bring about a change in the shape of an object
A force can cause some or all of these effects simultaneously. None of these changes (speed, direction, shape) can occur without the action of a force. If an object is at rest, it means the forces acting on it are balancing one another.
Types of Forces
Forces can be broadly categorised into two main types: contact forces and non-contact forces.
Contact Forces
These forces act only when there is physical contact between the objects. This contact can be direct (e.g., using hands) or indirect (e.g., using a stick or rope).
Non-Contact Forces
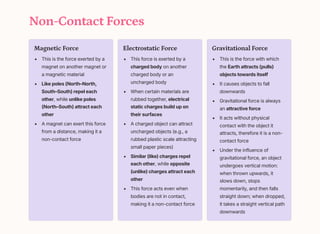
These forces can be experienced even if the objects are not in physical contact. Examples include magnetic force, electrostatic force, and gravitational force.
Contact Forces
Muscular Force
This force is caused by the action of muscles in our body
It is used in everyday physical activities like walking, running, lifting, pushing, jumping, or stretching
Muscular force also plays a crucial role in internal bodily functions, such as chewing food, pushing it through the alimentary canal, and the expansion and contraction of heart muscles for blood circulation
Historically, humans have used the muscular force of animals for various tasks
Friction
Friction is the force that comes into play when an object moves or tries to move over another surface
It always acts in a direction opposite to the direction in which the object is moving or trying to move. For example, a rolling ball stops due to friction
Friction arises due to the irregularities in the two surfaces in contact. Even seemingly smooth surfaces have minute irregularities that lock into each other, opposing motion
The force of friction depends upon the nature of the surfaces in contact. It is greater on rough surfaces
Friction also acts on objects