This document defines and explains key concepts in kinematics including speed, velocity, and acceleration. It provides the following definitions:
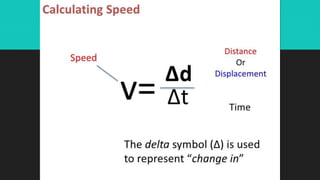
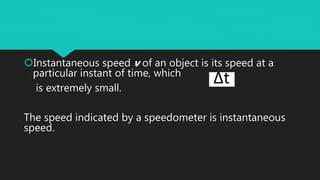
- Speed is a measure of how fast a body moves and is a scalar quantity. There are two types - average and instantaneous speed.
- Velocity is a measure of both speed and direction of motion, making it a vector quantity. Average and instantaneous velocity are also defined.
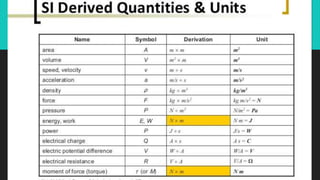
- Acceleration is a change in velocity over time. It is a vector quantity measured in meters/second squared. Positive acceleration means speeding up while negative acceleration means slowing down.











![Calculating acceleration involves dividing velocity
by time — or in terms of units, dividing meters
per second [m/s] by second [s].
Dividing distance by time twice is the same as
dividing distance by the square of time. Thus
the SI unit of acceleration is the meter
per second squared. ( m/s2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4speedvelocityacceleration-180711080520/85/Speed-Velocity-and-Acceleration-16-320.jpg)




