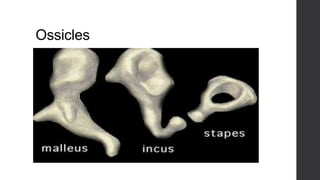
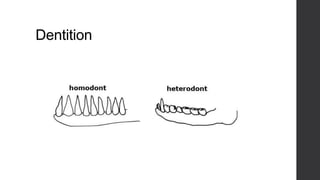
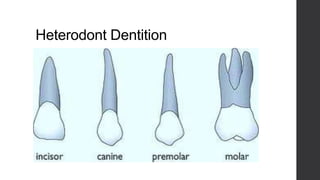
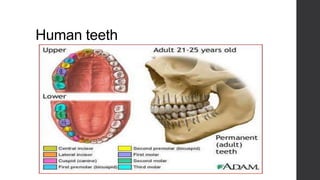
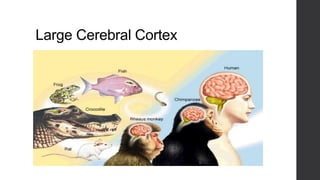
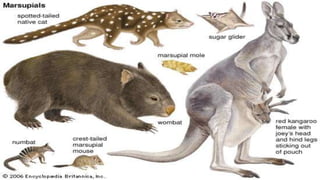
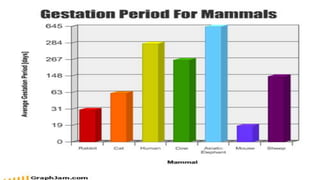
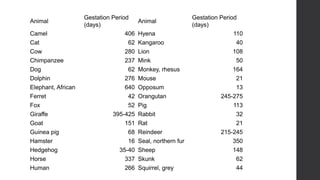
Class Mammalia is characterized by having mammary glands, hair, a diaphragm, and three middle ear ossicles. Mammals also have a heterodont dentition, sweat, sebaceous, and scent glands, a four chambered heart, and a large cerebral cortex. There are three main types of mammals: monotremes like the platypus and echidna, marsupials which have a pouch like kangaroos, and placental mammals which give birth to young that develop fully inside the mother like humans. Gestation periods vary greatly among mammals from 16 days in mice to 640 days in African elephants. Mammals can decrease their metabolic rates through torpor,