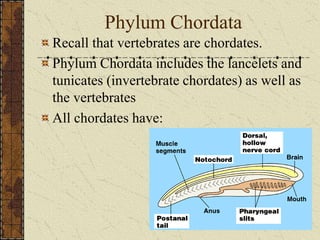
This document provides information about vertebrate animals, beginning with their taxonomic classification and then describing key characteristics of major vertebrate groups including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. It outlines defining anatomical features for each group as well as examples of orders, classes, and important vocabulary terms.