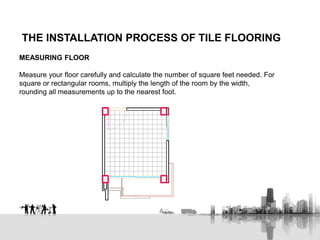
This document provides information on different types of tiles used in construction, including roofing tiles, flooring tiles, wall tiles, drain tiles, and sewer pipes. It describes the characteristics and manufacturing of tiles, the glazing process, and the installation process for tile flooring which involves measuring the floor, purchasing tile, preparing the surface, laying out and installing the tiles, cutting as needed, finishing edges, applying grout, and sealing the grout. The document is from a course on construction materials and finishes.