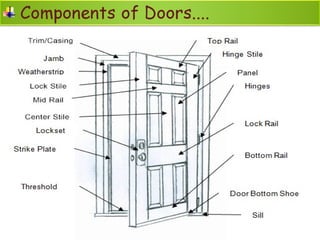
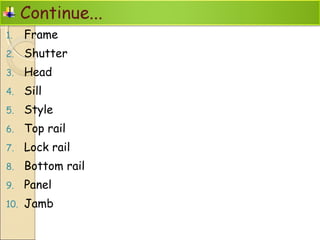
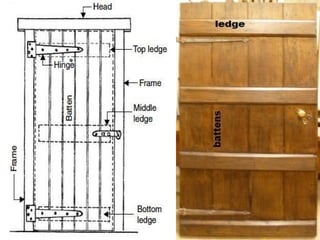
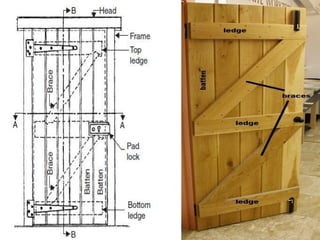
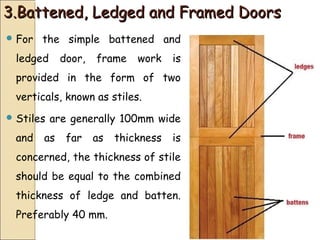
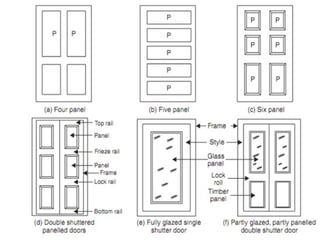
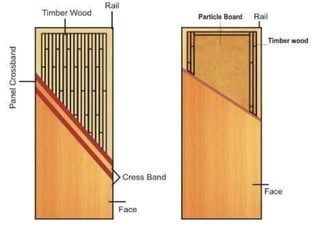
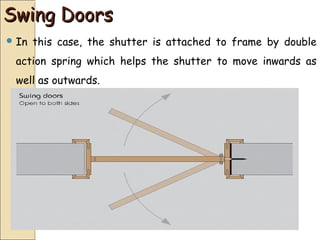
The document discusses the importance of effective communication in the workplace. It highlights key strategies for improving interpersonal interactions and team collaboration. Additionally, it addresses common barriers to communication and how to overcome them.