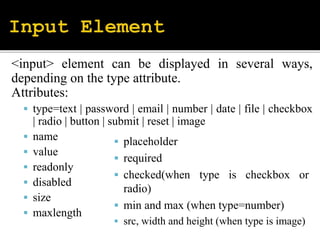
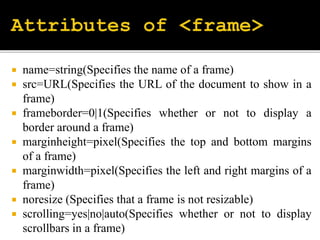
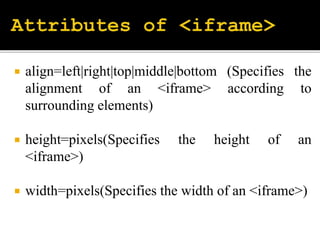
The document describes various HTML form elements including <form>, <input>, <select>, <textarea>, and how to structure forms using these elements. It explains the differences between GET and POST methods for form submission, with GET appending data to the URL and POST not displaying data in the URL. It also covers the <frameset> and <iframe> elements for dividing documents into multiple frames or embedding an inline frame.