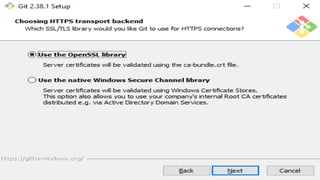
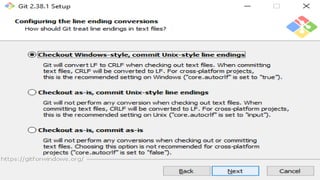
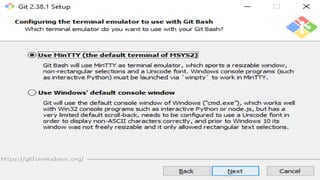
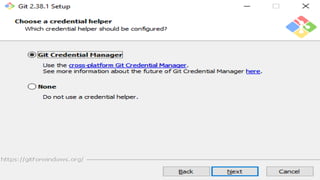
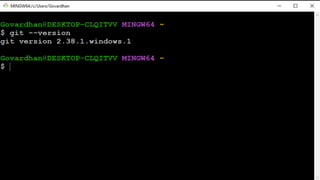
A version control system tracks, manages, and controls changes to software code. There are three main types: local, centralized, and distributed. Git is a free, open source distributed version control system that allows users to track changes in files from small to large projects. With Git, users can add and commit changes to code and revert to previous versions of files. Common Git commands include git config to set user information, git init to initialize a repository, git add to stage files for commits, and git commit to save changes.