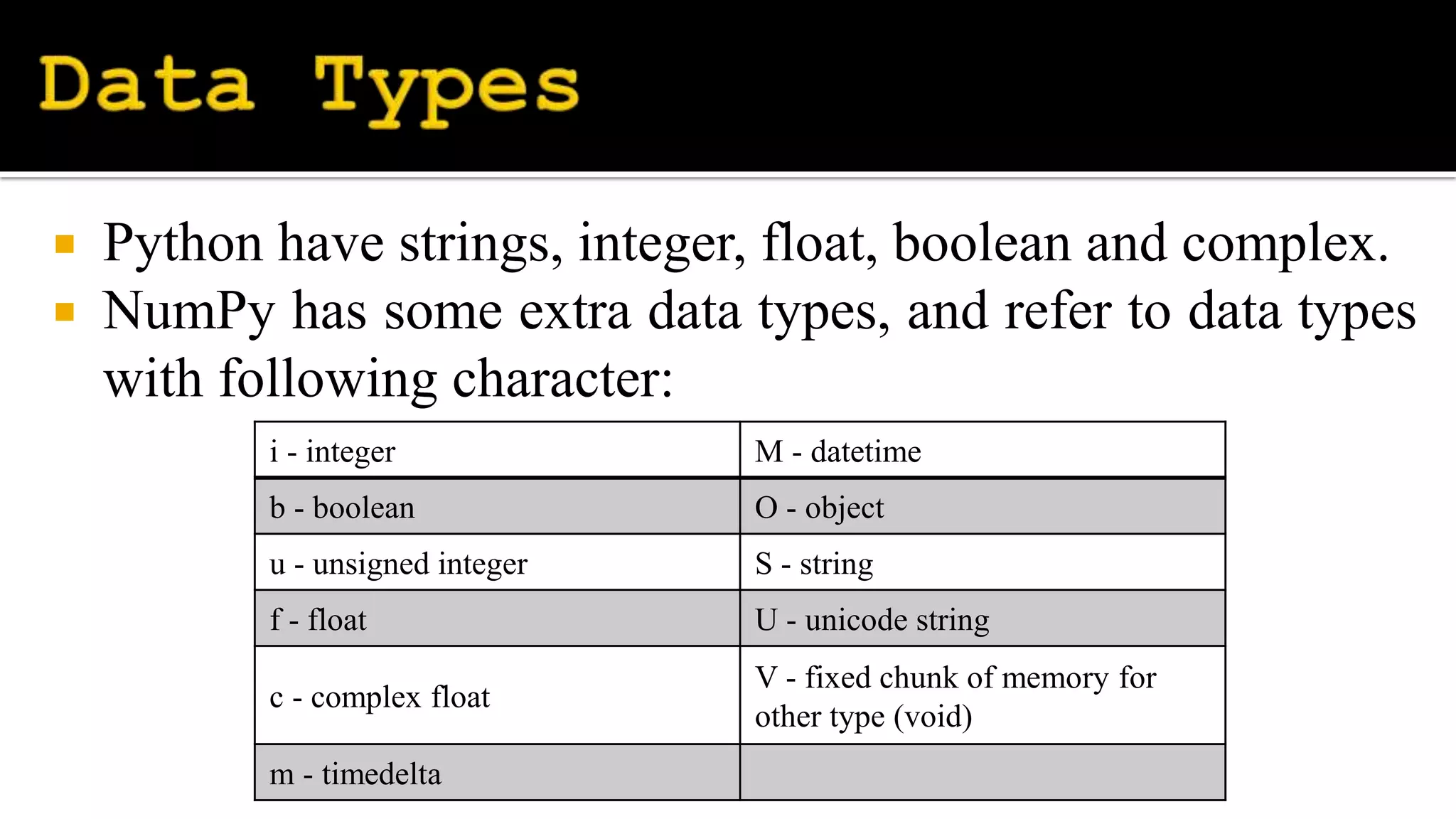
Numpy is a Python library for numerical computations, providing multidimensional arrays and routines for processing them. Key functions include np.arange for spacing values, np.random for random float generation, and various mathematical operations such as arithmetic and trigonometric functions. The library also supports advanced indexing methods, including boolean and fancy indexing, allowing for efficient data manipulation.



![ np.arange() - used to get evenly spaced values
within a given interval.
numpy.arange([start, ]stop, [step, ]dtype=None)
numpy.random.random() - used to generate
random floats number in the half-open interval
(0.0, 1.0).
numpy.random.random([size])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numpy-221217084429-46b42af7/75/NumPy-pptx-5-2048.jpg)





![ The numpy.where() function returns the indices
of elements in an input array where the given
condition is satisfied.
numpy.where(condition[, x, y])
Here,
x – yield True value
y – yield False value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numpy-221217084429-46b42af7/75/NumPy-pptx-12-2048.jpg)


