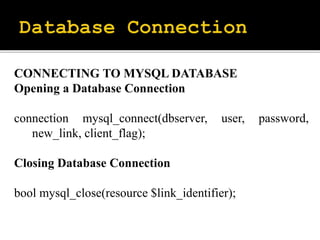
PHP, which stands for Hypertext Preprocessor, is a server-side scripting language that enables dynamic web page creation and integrates with various databases. It was created by Rasmus Lerdorf in 1994 and supports multiple data types, variables, and various control structures such as loops and conditionals. PHP also allows for cookie management and database connectivity, providing essential tools for web development.




















![ Associative array will have their index as string
so that you can establish a strong association
between key and values.
Creating Array:
$array_name=array(“str1”=>value1,
“str2”=>value2, ……
“strn”=>valuen);
Accessing Array Elements:
$array_name[‘str1’];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-191029090418/85/PHP-24-320.jpg)



![ PHP provided setcookie() function to set a cookie.
setcookie(name,value,expire,path,domain,security);
To access cookies, use either $_COOKIE[name] or
$HTTP_COOKIE_VARS[name] variables.
You can use isset() function to check if a cookie is set or
not.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-191029090418/85/PHP-28-320.jpg)