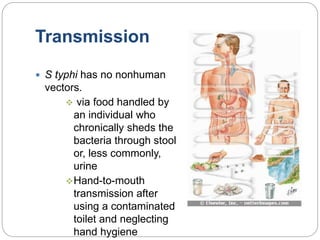
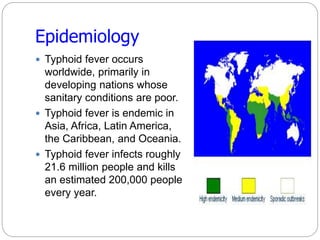
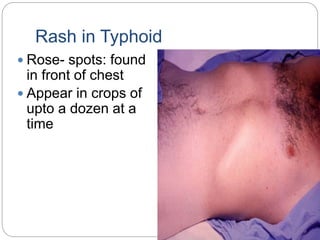
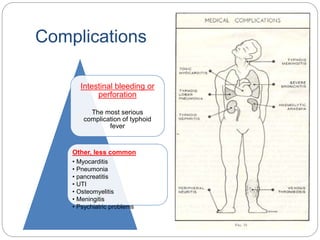
Typhoid fever is caused by the bacterium Salmonella typhi, which spreads through contaminated food or water in areas with poor sanitation. It causes a sustained high fever over weeks and can lead to intestinal bleeding or perforation. Diagnosis involves blood or bone marrow cultures early in infection or serological tests later. Treatment is with antibiotics like fluoroquinolones. Prevention involves handwashing, water treatment, and typhoid vaccination. Some people can become long-term carriers even after recovery.