This document discusses three types of design thinking: systematic, intuitive, and expansive.
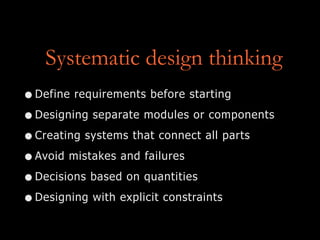
Systematic design thinking involves defining requirements up front, designing separate and interconnected components, and making decisions based on quantitative data. Intuitive design thinking stems from inspiration and involves refining conceptual sketches through alternatives and models. Expansive design thinking emphasizes developing empathy, collaboration across disciplines, and holistic visions that consider social and technical factors.
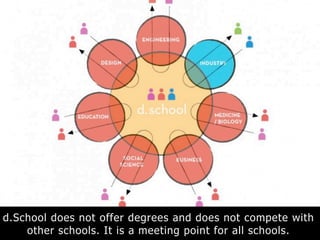
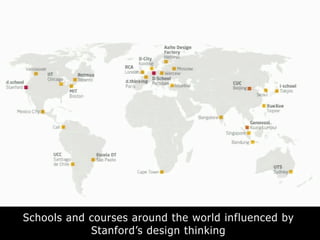
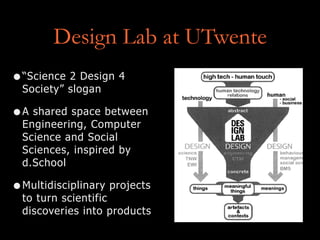
The document provides examples of where each type is commonly used and schools that teach expansive design thinking, such as Stanford's d.School, which aims to spread IDEO's particular approach and uses flexible spaces, prototyping tools, and activities like posting notes to enable collaboration.