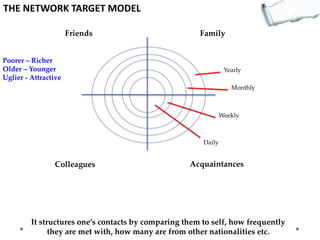
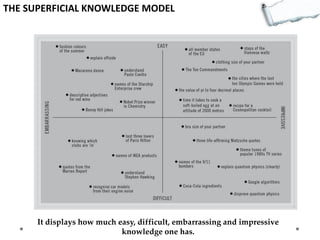
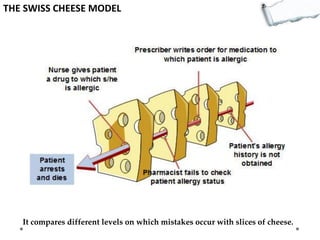
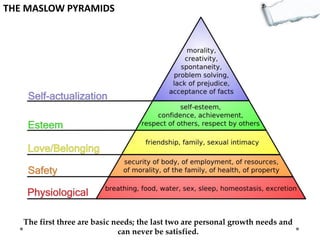
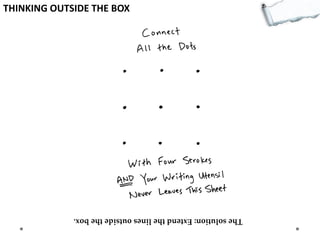
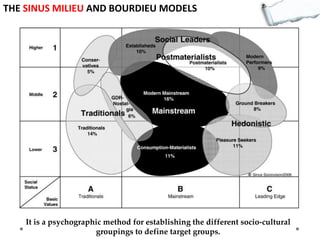
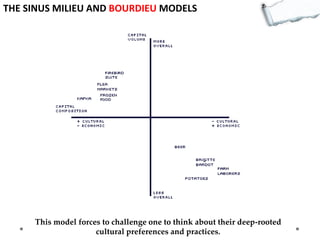
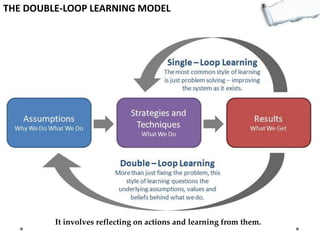
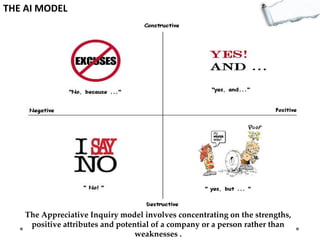
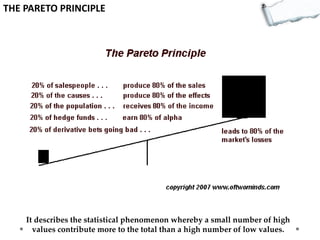
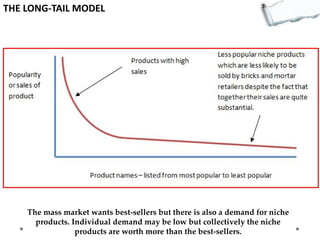
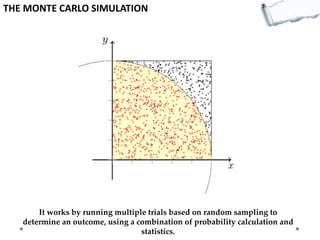
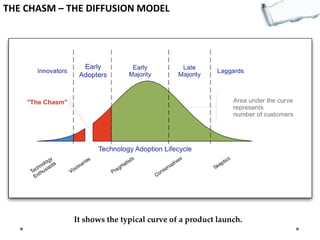
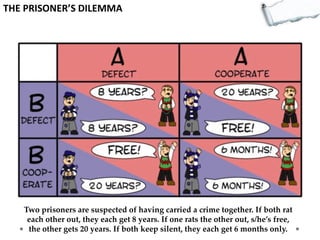
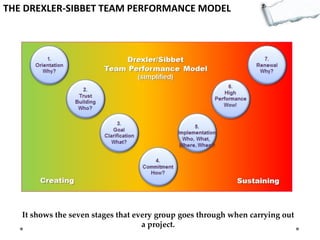
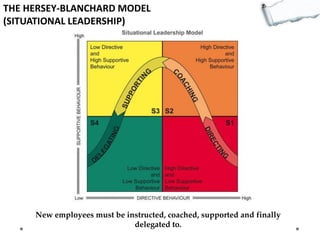
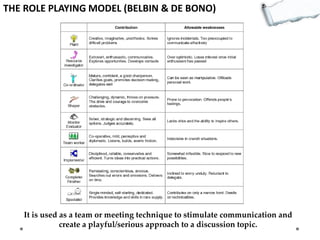
This document outlines several decision making and strategic thinking models:
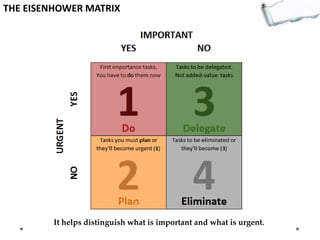
- The Eisenhower Matrix helps distinguish important vs urgent tasks.
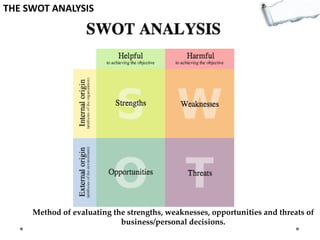
- SWOT analysis evaluates strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of decisions.
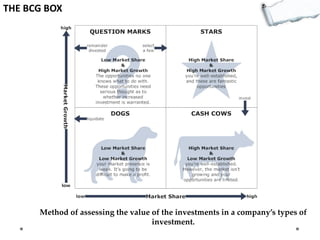
- The BCG Box assesses investment value.
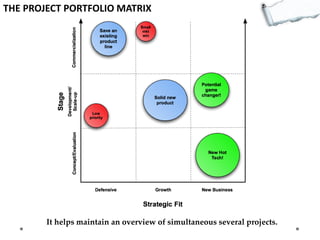
- The Project Portfolio Matrix maintains oversight of multiple projects.
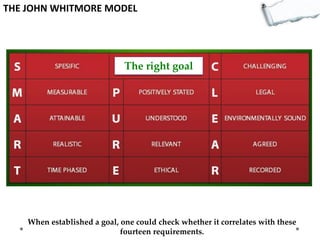
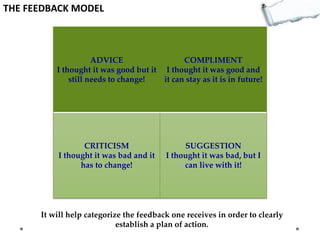
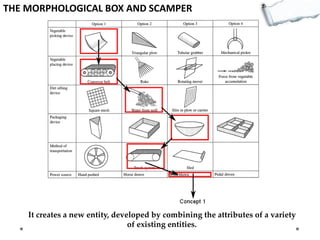
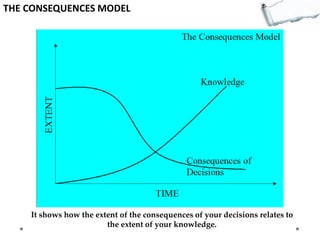
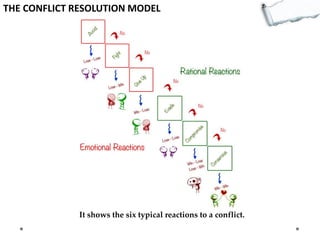
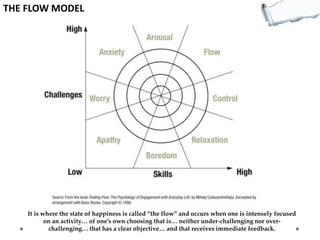
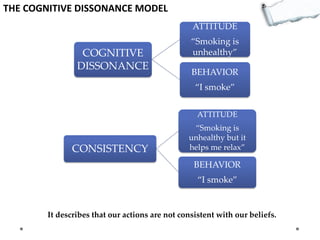
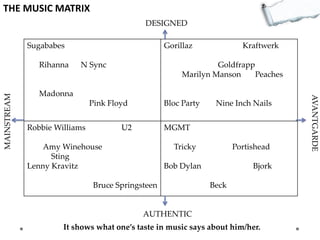
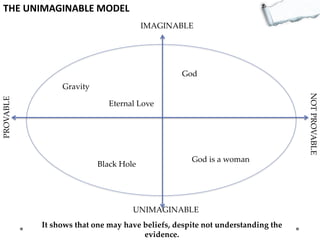
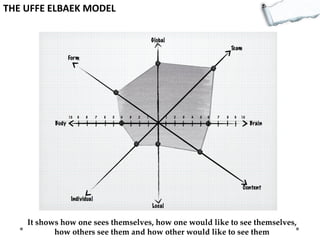
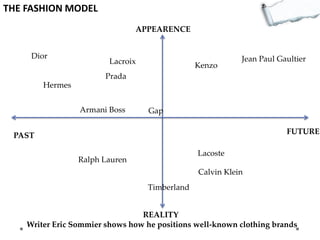
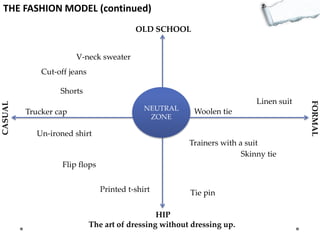
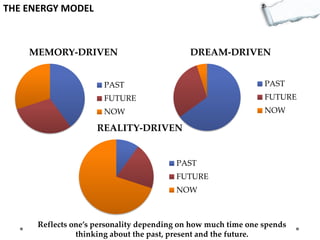
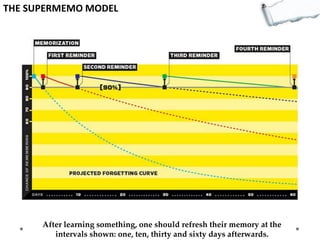
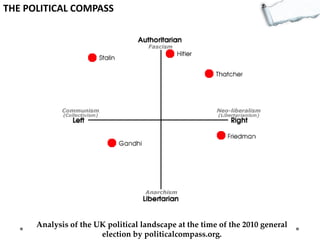
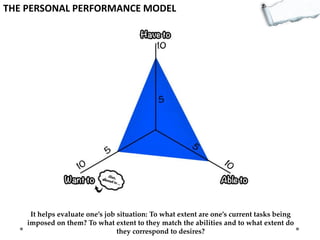
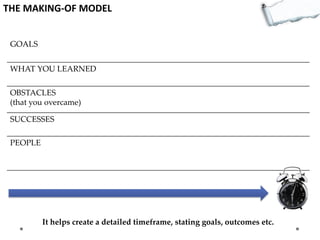
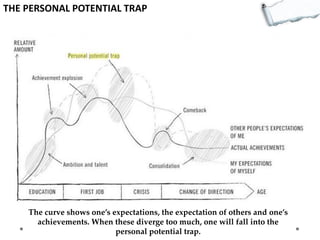
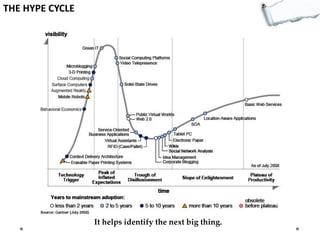
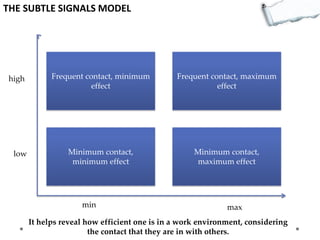
- Additional models provide frameworks for setting goals, providing feedback, creativity, consequences, conflict resolution, and more. The document explores applications of these models to improve decision making and strategic thinking.