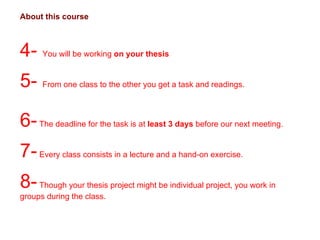
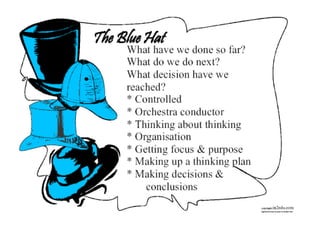
The document is a course description for a concept design course taught by Dr. Mariana Salgado. It provides an overview of the course structure and topics that will be covered during the 5 class meetings. These include defining concept design, developing concepts through scenarios and personas, testing concepts, and final presentations. It also describes some of the methods that will be used during the classes like brainstorming, visualizations, and applying Edward de Bono's 6 Thinking Hats technique to analyze concepts.


![About me It is the first time I run this course I need feedback from you constantly even when I do not ask for it I use a lot of design jargon, so please, stop and ask. My presentations can be found in http://www.slideshare.net/marianasalgado/ My mail is [email_address] Or [email_address] Other places where you find me: http://pinatasdigitales.wordpress.com/ http://www.mendeley.com/profiles/mariana-salgado/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conceptdesign-presentation2-110929104111-phpapp02/85/Concept-design-3-320.jpg)



































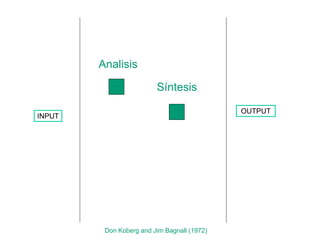
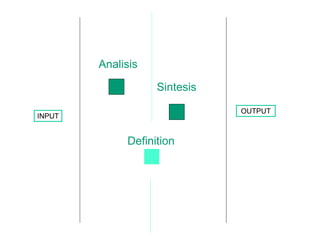








































![Thanks! [email_address] [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conceptdesign-presentation2-110929104111-phpapp02/85/Concept-design-102-320.jpg)